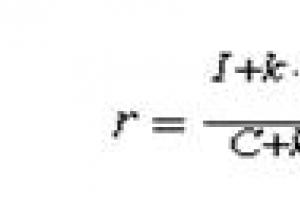Obesity 1 degree in children diet treatment. The development of obesity in a child. Causes of overweight in children
Obesity in children is one of the serious metabolic disorders, which is manifested by the deposition of adipose tissue. This disease brings with it many other problems. , which are very difficult to deal with. In addition, the child's health is constantly poor, since living, just moving around and doing some kind of work with excess weight is not at all easy.
Obesity is a condition in which the weight of the child exceeds the normal parameter by more than 15%. You can also talk about obesity if the body mass index (BMI) of the child exceeds 30. As practice shows, children living in the city suffer most from obesity, and the reason for everything is haste and snacks on the go, in McDonald's, pizzerias and stalls selling buns , shawarma, fast food. It is unlikely that such establishments can be found in the village.
But in rural areas there is another danger - cooking with high-calorie animal fats. Therefore, balance and a rational approach are important in everything.
Today, there is a significant increase in children diagnosed with obesity in the world. And this is a serious endocrinological problem. Almost 80% of obese adults have problems excess weight started in adolescence.
There are many reasons for this state of affairs. But in its nature of development lies polyethology, which means one of the main roles is played by heredity and the environment. So, for example, if both parents suffer from obesity, then the risk of its occurrence in a child is approximately 80%, with obesity only in the mother - 50%, only in the father - 35-40%.
In addition, at risk are children whose birth weight was more than 4 kilograms. However, congenital obesity is diagnosed extremely rarely - only in 1% of cases. Also, those babies who are bottle-fed and gain a lot every month may suffer from obesity. In newborn babies, obesity often develops due to overfeeding with artificial nutrition. As a rule, it is extremely rare to overfeed a child with mother's milk.
Breastfeeding baby - effective prevention obesity in later life.
If you believe the statistics, then obesity most often develops due to a violation of the diet, frequent snacking and refusal to exercise. Foods that can cause fat deposits include:
- bakery products;
- fast food;
- soda;
- sweets;
- juices;
- Dessert;
- sweet teas.
The diet of the child should consist of foods containing proteins and fiber. It is also important to maintain water balance. You should not spend a lot of time in front of the TV or computer and eat food at the same time, since this simply does not control its amount. You need to play outdoor games or at least just take a walk in the yard every evening.
Very often, obesity in children and adolescents appears due to the fault of the parents, as they refuse to work with the diet and follow the diet. And if it does not interest adults, then the child even more so.
Obesity in children is not always a consequence of genetics, sometimes it is one of the acquired serious pathologies. For example, This disease can occur against the background of such diagnoses:
- Down syndrome;
- meningitis;
- Cohen's syndrome;
- hypothyroidism;
- Pradel-Willi syndrome;
- a brain tumor;
- Ischenko-Cushing syndrome;
- encephalitis.
Obesity can be caused by an iodine deficiency in the body, leading to hypothyroidism. Other an important factor are stressful conditions. They are associated with the child's admission to school, a change of residence, a quarrel with loved ones.


Classification
Two forms of obesity can be distinguished: secondary and primary, depending on the time of occurrence.
Primary obesity is of the following types:
- alimentary, caused by malnutrition;
- exogenous-constitutional, caused by hereditary factors.
If genetics is to blame, then it is not the excess weight itself that is inherited, but the peculiarities of the flow of metabolic processes in the body. If we talk about the first type of primary obesity, then it occurs before the age of 3 years, in children 5-7 years old and in adolescents aged 12-17 years. Although its manifestation at a different age is not excluded, but less often.
Secondary obesity occurs due to diseases of a different nature. One of the frequent varieties of this type is endocrine obesity, which can simultaneously occur with diseases of the adrenal glands and ovaries, as well as problems with the thyroid gland.
Degrees of obesity in children (table)
In order to identify this disease in a child, you need to calculate his body mass index (according to the author, it is called the Quetelet index), which is calculated by simple steps: the weight of the child must be divided by the value of his height squared. Let's consider a simple example. For example, a boy is seven years old, his height is 1.5 meters, and his weight is 50 kilograms. To calculate BMI, you need to square 1.5, this will be 2.25. Then 50 must be divided by 2.25, the BMI value will be 22.2. After that, you need to refer to the table of average height and weight (given below) for girls and boys and understand if the BMI is within the normal range. As we can see, these indicators are normal, and the child is not obese.
Norms of weight and height of children under 17 years old


As a rule, the most common degrees of obesity can be called the first and second, which are diagnosed in 80% of children. In the absence of nutritional correction, these degrees quickly progress to more severe ones.
Symptoms
Of course, the main symptom of obesity is visible to the naked eye - it is overweight in children. If the disease occurs in young children, then the appearance of such symptoms is not excluded:
- developmental delay;
- constipation;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- little activity;
- infectious diseases (more often than among peers).
Alimentary obesity occurs with the following symptoms:
- fat deposits in different parts of the body.
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- increased blood pressure;
- loss of interest in physical activity.
Secondary obesity is characterized by more diverse features:
- children late begin to hold their heads, walk, sit;
- teeth appear much later than in children of their age;
- drowsiness;
- decreased performance and school performance;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle in girls;
- dryness of the skin.


Complications
Obesity itself is a dangerous disease. It can develop into complications, thereby worsening the patient's condition. If the diet for overweight children 7 years of age is not followed and treatment is refused, the following diseases may develop:
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- atherosclerosis;
- haemorrhoids;
- pancreatitis;
- hepatosis;
- angina;
- hypertension;
- anorexia;
- cholecystitis.
In addition, obesity can lead to other diseases and consequences, such as flat feet, changes in posture, psychological disorders, arthrosis, and scoliosis. Very often, overweight children suffer from depression due to the ridicule of peers and classmates.
If a child has been diagnosed with obesity since birth, then there is a risk of infertility when the reproductive period is reached.
Diagnosis of the disease
Surely we all remember how we were touched by chubby children at birth - this is really touching. For a newborn baby, this is the norm - after all, he only eats and practically does not move. After about 10 months, when the baby learns to walk, all the swelling disappears, as it increases physical activity and all fats are burned.
However, many parents, seeing how chubby their child was born, are worried - and not whether he is sick with obesity. Only a doctor can diagnose this, but if you do not overfeed the child, then there can be no talk of any obesity. Precisely in order to prevent this disease, every month during the first year of the child, his height, abdomen, and head are measured and measured. In addition, the pediatrician has a special table of averages for a boy and a girl, how many kg they should gain per month.
And therefore, such symptoms that appear externally should not disturb parents:
- rounded tummy protruding forward;
- plump arms and legs;
- tight thighs.
If the child begins to gain more than the prescribed norm, then the pediatrician must adjust the baby's nutrition and his daily routine, if he is more than six months old. Indeed, at the age of 6 months, a child can be interested in toys. It is at this age that babies learn to crawl - which means they are active.


Development of obesity in children
As a rule, obesity begins to develop when the child is gaining a lot of weight, and his parents, grandparents are touched and rejoice at the appetite of their pet. When a doctor talks about obesity, they often do not listen to him and say that he will outgrow it, continuing to feed the baby in the same moderate way. You can’t do this, you need to listen to the recommendations of the pediatrician, especially if the baby is a newborn and is bottle-fed. Failure to comply with the recommendations is fraught with the possibility of developing the first degree of obesity.
If no action is taken, then obesity can develop into a second degree., and the child will regularly eat large amounts of food, since his stomach will be ready to receive food in such quantities. But with the second degree of obesity, other symptoms of the disease, which were mentioned above, may appear. At this degree, only 50% of parents decide to see a nutritionist, because they understand that the child is in danger and sick.


If the parents at this time also decide that the child will “outgrow”, then obesity progresses to the third degree, when all the relatives of the chubby baby begin to sound the alarm. They understand that their child is sick and do not know what to do. At this stage, symptoms of diabetes mellitus, joint pain may appear. It is at this stage of the development of the disease that 90% of parents turn to the doctor, but sometimes it is already very difficult to recover.
Treatment
Treatment for obesity in children should be comprehensive. First of all, you need to follow a diet in order to lose those extra pounds. Often, with obesity, comorbidities also appear, the treatment of which must be carried out without fail. In addition, do not forget to engage in the prevention of excess weight and maintaining the condition that was achieved through treatment.
As mentioned above, diet for obese children should be selected in individually
Thanks to it, you can lose excess weight. The most important thing is to regularly count the calories of food eaten per day, and eat at least 5 times a day, in small portions. You also need to rationally allocate time. With a child of preschool age, you should walk as often as possible, engage in outdoor games. With schoolchildren 7-8 years old, a lot of time should be devoted to sports and circles for development.
If there are concomitant diseases, then you need to contact narrow specialists. Also in case of obesity, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- psychotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- hydrotherapy (especially good swimming).
But sometimes all these measures are not enough to treat obesity, because adolescents may have psychological disorders, and therefore the child will need to be shown to a doctor who can identify the causes of “jamming” of problems. After all, that is why most often overweight is gained in a child of 10 years and older, which occurs against the background of stress.
It is not recommended to use medications for treatment, as they can negatively affect a growing body. These drugs can be very effective, but should only be taken by teenagers over the age of 15. Surgical operations are also not indicated for children.
Diet
Of course, the main measure for treatment is diet. However, you should not resort to a diet found on the Internet. It is necessary to select the menu and nutrition for the child individually, together with the doctor, not forgetting about allergic reactions. It is also very difficult for children to explain why they should not use this or that product. Therefore, at the heart of the diet, favorite foods should be present in some form so that the child does not boycott his parents and does not refuse food at all. With obesity of the 2nd degree in children, it is necessary to reduce the number of calories. This can be achieved with the help of vegetable fats and carbohydrates.
If we talk about teenagers at the 3-4th degree of obesity, then the diet for them should be chosen very strictly. It will be necessary to exclude all sweets, berries and fruits, starchy vegetables, pasta.
- Last meal no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
- The last meal should not be heavy. A glass of low-fat kefir is effective as a dream book.
- Between meals, breaks are at least 3-3.5 hours.
- Most of the food should be eaten in the morning.
Physical activity
In order to burn excess fat, diet alone will not be enough, you still need to exercise. If a teenager is obese, then he can play sports at home. To do this, you need to purchase a simulator, choose a set of exercises. Alternatively, buy a subscription gym. Toddlers need to walk fresh air, play outdoor games, sign up for a sports club.


Exercise therapy for obesity is necessary measure to alleviate the condition and treat the patient. It is necessary to choose methods for its implementation according to the age and weight of the patient. You can conduct classes in the following forms:
- morning exercises;
- jogging before bed
- outdoor games;
- training sessions.
A set of exercises can be anything, but you should start with simple exercises: walking on toes, heels, full foot. When performing exercises, different organs and muscle groups should be involved.
Prevention
Prevention of obesity is one of the most difficult tasks in modern world. The first thing parents should start with is to teach the child to correct regimen nutrition. You also need to pay a lot of attention to the regime of the day, walk daily with the child in the fresh air.
Any parent should instill a child's interest in physical education and sports, as it is very important for its development. But in this case, parents should be an example for their child.
Obesity prevention is very important because last years This disease is only gaining momentum in popularity. And no matter how sad it may sound, the disease appears more and more often in children of different ages. Many people mistakenly believe that obesity causes nothing but difficulty in moving. However, this serious illness, which is very difficult and can affect many human organs.
Coping with obesity is very difficult for adults, let alone children. That is why you should not allow a set of extra pounds: with a predisposition to the disease, you need to deal with its prevention, and when the first symptoms appear, treat and eliminate extra pounds.
How to deal with obesity in children and adolescents, possible consequences excess weight gain updated: October 20, 2016 by: admin
Every year, the number of children whose body weight is significantly higher than the norm is increasing. Obesity in children and adolescents is common throughout the world, in the United States every second child is overweight, and the diagnosis of "obesity" is established in 20 children out of a hundred. In Russia, children's weight indicators are slightly better, but they make one think: about 15-20% are overweight, and 5-12% are obese. Moreover, in 8-9% this disorder was registered in children living in the city, which is associated with less physical activity and poor nutrition (preservatives, dyes, flavor enhancers). Obesity in childhood is a serious problem that requires action, given that 60% of adults have childhood obesity.
Obesity and overweight - is there a difference?
The term "obesity" refers to a chronic metabolic disorder, which is characterized by excessive accumulation of adipose tissue, as a result, the patient's weight significantly exceeds the age and constitutional features. Thus, obesity is a disease that develops when the body receives "excessive" energy (food) that exceeds its energy expenditure. A child is obese if his body weight exceeds the age norm by 15% or more, and the body mass index (BMI) is equal to/greater than 30. This metabolic disorder predisposes to the development of diseases of almost all organs and systems.
Being overweight is not yet a disease, but in the absence of measures to combat it, it threatens to turn into obesity. They talk about being overweight when the usual clothes suddenly stopped converging in buttons, “bursting at the seams” or simply do not fit. That is, excess weight is an aesthetic defect, which consists of several extra pounds interfering with life.
Body mass index
The body mass index (BMI) was developed by a Belgian scientist and allows you to evaluate the ratio of a person's weight and height, that is, whether body weight corresponds to height. It is used to determine the degree of obesity, underweight or when prescribing drugs for weight loss.
BMI is calculated as follows: human weight (kg) / (height (m) * height (m)).
Causes
The causes of obesity in children are varied and numerous, but the interaction of heredity and external factors plays a role in the occurrence of the disease. The following factors predispose to obesity:
- Irrational nutrition
Lack of a strict (hourly) diet with constant snacking, neglect of homemade food, preference for fast food, convenience foods, crackers and nuts. Excessive consumption of sweets (contain easily digestible carbohydrates): packaged juices, sugary sodas, chocolate and confectionery. Also, obesity is promoted by a high calorie content of the daily diet, overeating, which leads to an oversaturation of the body with energy.
- Attitudes towards food in the family
The child adopts the behavior of elders who have created a cult of food (for example, it is customary in the family to cook high-calorie meals in large quantities). As a result, parents begin to persuade the child to eat supplements, punish for a half-eaten portion, encourage each meal with sweets or, on the contrary, forbid their consumption, which leads to protest and an increase in the forbidden food eaten while adults are not watching.
- Hypodynamia
A sedentary lifestyle, insufficient physical activity, replacing active outdoor games with computer games or watching TV, exemption from physical education classes, refusal to attend sports sections lead to the accumulation of calories and fat deposition.
- Psychological problems
An inferiority complex and chronic stress cause problems in communicating with parents and peers, academic failure, difficult parental relationships, and unhappy love. All these problems children, especially teenagers, prefer to "seize" - an extra chocolate bar, a bag of chips or nuts.
- genetic predisposition
If both parents have obesity, then in 80% of cases the child will have a similar disorder. With obesity only in the mother, the risk of its development is 50%, and with obesity in the father - 38%.
- Acquired and genetic diseases
Obesity is often observed in children with genetic pathology (Down, Cohen, Prader-Willi syndrome), with diseases of the endocrine system (Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome, congenital hypothyroidism, adipose-genital dystrophy), brain damage (meningitis, encephalitis, consequences of TBI, operations on the brain, CNS tumors).
Problems that existed in infancy and at birth can provoke the development of obesity:
- Large birth weight (4 or more kg);
- Excessive monthly weight gain;
- Artificial feeding (high-calorie mixtures);
- Overfeeding a child;
- Violation of the rules and timing of the introduction of complementary foods;
- Maternal smoking during gestation.
The pathogenesis of obesity
There is only one mechanism for the development of obesity, regardless of the cause. The intake of large amounts of food in the body leads to hyperinsulinism. The production of insulin in a significant amount is a compensatory reaction aimed at the absorption of excess carbohydrates by the tissues of the body. Under the action of insulin, hypoglycemia develops, which causes hunger. Excess energy from fatty foods accumulates in the cells of adipose tissue, causing their hyperplasia, and, accordingly, an increase in body weight. An increase in adipose tissue is accompanied by a change in the work of the hypothalamus. The synthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone increases, which forms hypercortisolism and impairs the sensitivity of the hypothalamic nuclei to signals of satiety, hunger, and others. Hyperinsulinism leads to the frequent development of hypoglycemic conditions (hunger), which creates a vicious circle of obesity: hypoglycemia - hunger - satiety (overeating) - hyperinsulinism - hypoglycemia - hunger.
Classification
Given the causes of the development of the disease, there are 2 forms of obesity in childhood:
- Primary:
- exogenous-constitutional, due to genetic predisposition (it is not overweight that is inherited, but the peculiarities of the course of metabolic processes in the body);
- alimentary, due to irrational nutrition.
- Secondary (consequence of congenital and acquired pathologies):
- endocrine (ovarian sclerocystosis, hypothyroidism, adrenal diseases - Itsenko-Cushing's disease);
- obesity due to genetic diseases;
- cerebral (diseases, injuries and tumors of the brain);
- medication (taking hormones, anabolic drugs).
Obesity, which has developed due to nutritional errors, often appears in children in critical phases development:
- early childhood (from one to three years) - the period of primary rounding;
- preschool age (from 5 to 7 years) - the period of secondary rounding;
- puberty (from 12 to 17 years) is a serious hormonal change that can provoke metabolic disorders.
Degrees of obesity in children:
- 1 degree - the weight of the child is more than normal by 15 - 29%;
- Grade 2 - the weight of the child is more than normal by 25 - 49%;
- 3 degree - the body weight of the child is more than normal by 50 - 99%;
- Grade 4 - the weight of the child is 2 times more than the norm (by 100%).
In 80% of cases of obesity among children, grades 1 and 2 of the disease predominate.
Clinical picture of obesity
Clinical signs of the disease depend on the age of the child. In different age periods, the clinical picture of obesity is different. It should be borne in mind that all the symptoms of the disorder appear on the rise, at a new stage in life, the signs of the disease become brighter. The main symptom of this pathology is an increase in the subcutaneous fat layer. Obesity in a child up to a year is accompanied by the following symptoms: a delay in the development of motor skills (late in holding his head, sitting down, getting up), a predisposition to allergic reactions and constipation, reduced motor activity, frequent colds.
Alimentary obesity is accompanied by the deposition of fat accumulations in the abdomen and thighs, in the pelvis, back and chest, which manifests itself in the form of hanging fat folds, obesity of the face (double / triple chin, swollen eyes, overhanging cheeks) and upper limbs (numerous constrictions). In schoolchildren, increased body weight is accompanied by: shortness of breath, poor exercise tolerance, increased blood pressure. A quarter of children during puberty are diagnosed with a metabolic syndrome, which includes, in addition to obesity, insulin resistance, arterial hypertension and dyslipidemia (imbalance of blood triglycerides). Obesity can also be accompanied by impaired uric acid metabolism and dysmetabolic nephropathy.
Secondary obesity is combined with manifestations of the underlying disease. With obesity caused by congenital hypothyroidism, the acquisition of motor skills is delayed (hold the head, sit down, stand up), the timing of teething also shifts. With acquired hypothyroidism (diagnosed in adolescents as a result of iodine deficiency), obesity is combined with weakness and fatigue, drowsiness, dryness and flaking of the skin, menstrual irregularities, and reduced academic performance.
Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome (cushingoid obesity): fat accumulations are deposited on the neck, face, abdomen, while the limbs remain thin. Girls at puberty develop hirsutism and amenorrhea.
In the case of obesity against the background of prolactinoma (pituitary tumor), there is an increase in the mammary glands (gynecomastia), galactorrhea, headache, and menstrual disorders in girls. With ovarian sclerocystosis, in addition to obesity, girls have acne, increased oiliness of the skin, disruptions in the menstrual cycle (oligomenorrhea and amenorrhea), excessive hair growth. Adipose-genital dystrophy in boys is accompanied by cryptorchidism, obesity, underdeveloped penis, and in girls by amenorrhea.
Consequences of obesity
Obesity not only affects the appearance of the child, which leads to the formation of an inferiority complex in him, the appearance of difficulties in adapting to the outside world, difficulties in communicating with people, social isolation, but also provokes the development of a large number of somatic diseases and impaired reproductive function (infertility).
The higher the degree of obesity, the greater the risk of disability of the child and premature death. The likelihood of developing pathology increases of cardio-vascular system(hypertension, angina pectoris, heart failure and atherosclerosis). Obesity affects the state of the digestive tract with the subsequent formation of pancreatitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, gastritis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, fatty liver hepatosis, hemorrhoids, chronic constipation.
Also, overweight children are in the group high risk on the development of non-insulin dependent diabetes, diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. Significant weight gain in childhood affects the musculoskeletal system and contributes to skeletal deformity, postural disorders, flat feet, hallux valgus (X-shaped) deformity of the legs, pathological fractures and the development of osteoporosis (the process of bone tissue formation is disturbed).
Sleep disorders occur: sleep apnea (stop breathing), snoring. The mental state of children suffers, they have a tendency to depression and deviant behavior, bulimia and anorexia, drug addiction and alcoholism. In the future, these children are significantly more likely to develop malignant tumors.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of obesity and determination of its degree includes the study of anamnesis, determination of the type (mixed, artificial or natural) of infant feeding, nutritional habits today, level physical activity. Examination of the child includes measurement of height and weight, waist and hip circumference, calculation of BMI. All indicators are compared with special tables (the weight norm ranges from 25 - 50 - 75 centiles) and overweight or obesity is established. When conducting a mass examination, a technique for measuring the thickness of the skin fold is used.
Allied specialists are involved in the diagnosis of obesity in order to find out its cause: a pediatric endocrinologist, a neurologist, a gastroenterologist, and a geneticist. Additionally, laboratory tests are prescribed: blood biochemistry (sugar, glucose tolerance test, cholesterol, triglycerides and lipoproteins, total protein and liver tests, uric acid), hormones ( thyroid-stimulating hormones, insulin, prolactin, cortisol, estradiol). If necessary, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, electroencephalography, MRI of the pituitary gland are performed.
Treatment
Treatment of obesity in children has the following goals:
- weight loss of the child;
- therapy of concomitant pathology;
- maintaining a reduced weight;
- prevention of weight gain.
First of all, the doctor must determine the cause of obesity, after which an individual treatment is selected for the child, which includes the normalization of nutrition and the appointment of a therapeutic diet, exercise therapy, if necessary, drug therapy and (if indicated) surgical treatment.
Therapeutic diet
A diet for a child is developed by a pediatric nutritionist. The purpose of therapeutic nutrition is to inhibit the formation of body fat and stimulate the destruction of accumulated deposits. It is important to bear in mind that adherence to a therapeutic diet for children three years old and younger is contraindicated. Medical nutrition for obesity should be varied and balanced and include the following principles:
- Fractional nutrition
The child should eat often, up to 6-7 times a day, but in small portions, with breaks between each meal of no more than 3 hours.
- food processing
For younger children, the food is boiled, steamed, stewed or baked (no crust). Older children are allowed to occasionally eat fried foods.
- salt restriction
Exclude from the diet all pickles, marinades, smoked meats, fast food and a variety of snacks (chips, nuts, crackers). Also limit the amount of salt to 5 grams per day. The consumption of salty foods causes thirst, and the intake of a large amount of liquid provokes its delay in the body (edema).
- Fluid intake
Categorically refuse to use sweet carbonated drinks, packaged juices and nectars, replacing them with unsweetened teas, herbal decoctions and freshly squeezed juices without sugar.
- Food calorie distribution
The main nutritious meals (meat, fish, poultry) should be consumed in the first half of the day, when the child's physical activity is high. The last meal should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime (maximum at 19.00).
- Increase in plant fiber
A child should eat vegetables, berries, fruits and a variety of greens without restrictions and in any form (raw, stewed, boiled). From fruits, sweet fruits are not recommended: bananas, pears, persimmons, figs, dates, grapes.
List of allowed products:
- lean meats, fish and poultry;
- fermented milk products of low fat content, cottage cheese;
- boiled eggs;
- cereals: millet, buckwheat, barley, barley, oats.
- coarse bread.
List of prohibited products:
- pastries, culinary products, cookies;
- pasta;
- White bread;
- semi-finished products and sausages;
- jam, raisins, honey, sweets;
- semolina;
- chocolate and cocoa;
- spices and spices (increase appetite).
Physical activity
The doctor will prescribe exercise therapy for the child, which should be carried out daily for at least 60 minutes. Also, obese children need to take walks regardless of the weather, participate in active outdoor games, go swimming, ride a bike. It is optimal to enroll a child in a sports section. Parents should introduce the concept of “violation of the regime”, when the child could not resist and ate the forbidden. As a punishment, physical exercises are required (10 sit-ups, 5 push-ups, and so on). effective method to combat excess weight is a massage that stimulates metabolism, improves blood flow and lymph flow, and normalizes muscle tone.
Medical and surgical treatment
Taking medications and dietary supplements for weight loss is not recommended for children under 15 years of age. At the 3rd degree of the disease, it is possible to prescribe orlistat and metformin under the supervision of a doctor. Physiotherapy is an alternative to medical treatment: heliotherapy, hydrotherapy, mud therapy and more. Surgical correction is used in extreme cases (the child's weight exceeds the norm by more than 100%).
Question answer
Question:
How should childhood obesity be prevented?
Prevention of the development of the disease should begin during the gestation period (rational nutrition, refusal to bad habits). In infancy, observe the rules and terms for the introduction of complementary foods, adhere to breastfeeding as long as possible. Do not force the child to eat up his portion, follow a diet, do not increase his calorie content. You should also limit the amount of animal fats and quickly digestible carbohydrates (pastries, sweets) consumed, stimulate the child to lead an active lifestyle (games, sports sections, walks, hikes).
Question:
Is it possible for a child to arrange fasting days?
If the child has not reached the age of 10, it is better to refrain from such experiments. Older children can stick to meat and vegetable unloading day. For 300 - 350 grams of lean beef or chicken, 600 - 1000 grams of fresh vegetables, such as cabbage, should be taken. Divide all food into 6 parts and eat during the day, drinking large number liquids (herbal teas and decoctions).
Question:
What can replace sweets (chocolate, cake) for a child?
Of course, fresh, but unsweetened fruits. Infrequently, you can pamper your child with marshmallows (contains pectins), jelly and jelly.
Chubby babies cause real tenderness in many adults. However, being overweight is not only a matter of aesthetic beauty. To maintain good health, you should maintain weight within the normal range for your age. The problems of childhood obesity will be discussed in our article.

When do people talk about obesity?
A pathological condition in which weight changes upwards and exceeds normal age indicators by more than 15% is called obesity. Many specialists use a parameter such as body mass index to establish a diagnosis. This is the ratio of height in meters to twice the weight in kg. The body mass index is expressed in absolute numbers. Exceeding it above 30 indicates that the child has obesity.
Obesity can develop at any age: both in newborns and in adolescents. According to statistics, obesity is slightly more common in girls under 8 years of age than in boys. However, after puberty, this ratio changes. Often parents of newborn babies confuse obesity and large sizes body.
If at birth the weight of the child exceeds the norm, then this does not give grounds for making a diagnosis of obesity.


Obese babies live in different countries. There are more of them in economically developed countries than in developing ones. This feature is largely due to overnutrition, low physical activity, as well as the abuse of fast food. In Asia, the number of overweight babies is several times lower than in Europe and America. This is due to the historical food culture and the lack of an abundance of foods containing saturated fats on the Asian menu.

The incidence rates are increasing every year. This trend is rather unfavorable. Two out of ten babies in Russia are obese. In the post-Soviet countries, the incidence is also increasing every year. Approximately 15% of babies living in Belarus and Ukraine suffer from obesity of varying degrees.
In rural areas, there are somewhat fewer children who have problems with being overweight. In many respects, this feature is due to greater physical activity than in the city, as well as high-quality food, which does not contain numerous chemical additives and preservatives. According to statistics, urban kids are obese in 10% of cases. For rural small residents, this figure is lower - about 6-7%.


The onset of the disease in childhood is extremely unfavorable. Many parents believe that being overweight only adorns the child and makes him pretty, however, they are mistaken. It is from an early age that eating habits begin to form in babies. After all, you probably noticed that from the first months of life, the child has his own taste preferences. Some children love porridge and chicken, while others cannot do without eating sweet fruit.
Little sweeties can be identified from a very young age. If parents at this time encourage each achievement of the child with a candy or a sweet high-calorie cookie, then subsequently the baby develops improper eating behavior. During the rest of his life, he will be pathologically drawn to sweets and chocolate. Moreover, an adult person will not be able to find any logical explanation for this.

Pediatric endocrinologists deal with the treatment and diagnosis of various weight problems. The danger of obesity is that it can lead to persistent disorders in the work of many vital organs. Subsequently, babies develop cardiovascular, neurological disorders, chronic diseases. gastrointestinal tract, and severe disorders metabolism. Late diagnosis of the disease and non-compliance with the diet contribute to the progression of the disease.
Causes
Obesity in children can be caused by a variety of reasons. Most of the factors arise as a result of external influences. Such an action should be long and regular. This ultimately leads to the development of obesity.
Causes of overweight problems include:
- Overnutrition. The daily excess of the calorie content of the daily diet contributes to the oversaturation of the body with various nutrients. He begins to store all the surpluses in reserve. Ultimately, this leads to the fact that the child develops morbid obesity.

- Excessive consumption of sweets. Such fast carbohydrates are very dangerous. Once in the body, they begin to be absorbed already in oral cavity. The glucose (ordinary sugar) contained in such sweets quickly leads to hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar levels). In order to normalize blood sugar levels, the body secretes a huge amount of insulin and hyperinsulinemia occurs. This condition is fraught with the fact that all excess sweets are deposited in special fat depots - adipocytes, which contributes to the development of obesity.
- Insufficient physical activity. Active movement is required to burn excess calories from food. Toddlers who eat a lot of high-calorie or sweet foods, but do not attend sports sections and spend most of their time at home with a tablet or phone, are at risk for their possible development of obesity. The balance between incoming calories and their utilization and ensures the maintenance of normal weight at any age.


- Heredity. Scientists have found that 85% of parents who have problems with being overweight have babies who also have problems with being overweight. For a long time, experts believed that there was an “obesity gene”. However, there is no scientific evidence for this to date. Most likely, in families where family members have developed obesity, improper eating habits have formed. High-calorie nutrition in this case leads to weight problems in both adults and babies.
- Chronic diseases. Various pathologies of the pituitary, adrenal glands, thyroid gland lead to pronounced metabolic disorders. Typically, such diseases are accompanied by multiple adverse symptoms. Being overweight is just one of their clinical manifestations. To eliminate obesity in this case, treatment of the underlying disease is indispensable.


- Large birth weight. If a newborn baby has a body weight of more than 4 kg, then this is a significant risk factor in his later life for the formation of overweight. In this case, obesity is not big weight at birth, and further overfeeding of the child. Low physical activity only exacerbates the development of the disease.
- Strong emotional stress. More and more scientists say that various "jamming" leads to the development of weight disorders. This condition is more common in teenagers. Excessive workload at school, the first unrequited love, the absence of friends causes a strong desire in the child to “relieve” stress with a chocolate bar or candy. In children aged 5-7 years, the development of this type of obesity is often caused by a painful divorce of parents or moving to a new place of residence.


In some cases, the combined effect of several factors leads to the disease. Eating disorders with reduced physical activity always have the most important impact on the fact that the baby has extra pounds.
The intervention of parents in this case should be as delicate as possible. You need to show the child that you are on his side and are trying to help, because you love and care for him very much.
Classification
There are several clinical forms of the disease. This influenced the creation of several classifications, which highlight the main options for obesity, taking into account some features. These nosological groups are needed by doctors to establish a diagnosis and choose the right treatment tactics.
All normal weight indicators by age are usually collected in a special centile table. With the help of this document, you can determine the approximate norm of body weight for a child of different sex and age. All children's doctors resort to these tables to determine whether a particular baby has signs of obesity. The norm is the correspondence to the 25th, 50th and 75th centiles. If the child has a weight correspondence of 90.97 centiles and above, then this indicates that the baby has obesity.

Doctors distinguish several clinical forms of the disease:
- Primary. It can be exogenous-constitutional and alimentary. In violation of eating behavior and nutritional problems, they speak of food (alimentary) obesity. If the baby has some features of the constitution and hereditary characteristics, then this is an exogenous-constitutional option. Obesity is treated in this case by prescribing therapeutic nutrition and with the obligatory selection of optimal loads.
- Secondary. Also called symptomatic. This type of obesity is characteristic of many chronic diseases that cause severe metabolic disorders. In girls, this condition occurs with various diseases of the ovaries, and in boys, mainly with pathology of the thyroid gland. Treatment of excess weight in these situations is impossible without eliminating the causes of the underlying disease. The correct tactics of therapy necessarily include a complex treatment of all chronic diseases that are the main cause of obesity.


Pediatric endocrinologists identify several dangerous periods during the development of the child, when the chance of obesity in the baby is as high as possible. These include the age of up to 3 years, 5-7 years, as well as puberty (12-16 years). At this time, parents should carefully monitor the appearance of their child. If the baby has signs of being overweight, then you should definitely consult a pediatrician about this problem.

There is also a classification according to the severity of overweight. It was proposed by A. A. Gaivoronskaya. With the help of this classification, obesity can be divided into several categories, depending on the quantitative excess of weight over normal indicators.
According to this division, there are several degrees of the disease:
- Obesity 1 degree. In this case, the weight exceeds 15-24% of the age norm.
- Obesity 2 degrees. The excess of body weight over normal values is 25-49%.
- Obesity 3 degrees. The excess of body weight over normal values is 50-99%.
- Obesity 4 degrees. The excess of body weight over the norm is over 100%.

Appearance
Excess weight significantly changes the appearance of the child. Excess fat accumulates in the subcutaneous fat. Normally, its layer is expressed moderately. With obesity fat cells(adipocytes) increase in size and volume, which leads to an increase in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer. Its greatest accumulation is localized in the abdomen, on the outer surface of the arms and legs, in the buttocks and thighs.
During puberty, there are specific differences in the distribution of subcutaneous fat. So, in girls, the largest accumulation of excess kilograms is deposited mainly on the hips and buttocks, that is, in the lower half of the body. This type of obesity is also called pear-shaped”, as the volumes of the lower half of the body increase predominantly.


The male type of obesity is also called obesity by type " apples". In this case, the accumulation of extra pounds occurs mainly in the abdomen. This type of disease contributes to the fact that the waist disappears, and the configuration of the child's body becomes excessively rounded. Toddlers look uniformly plump, and in some cases even overly full.
Obesity of 2-3 degrees is accompanied by an increase in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer in the face and neck. This leads to a change in the appearance of the baby. He has not only cute plump cheeks, but also a short-looking neck. At 4 degrees of obesity, the palpebral fissures narrow somewhat. Appearance the child becomes sick and causes no longer tenderness, but compassion.
Main symptoms
Obesity causes not only a change in the appearance of the child, but also leads to the appearance of various adverse symptoms in him. So, in sick babies, jumps in blood pressure are observed, the pulse accelerates, resistance to physical exertion decreases, a headache appears, and shortness of breath develops. With prolonged obesity adolescence the child may develop metabolic syndrome. This is a dangerous condition caused by persistent hyperinsulinemia. It is dangerous because it can lead to various cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
With the development of obesity at school age, multiple adverse symptoms appear. So, it becomes more difficult for children to focus on learning new things. educational material, they quickly get tired, they have daytime sleepiness, slowness. For a teenager, public opinion is very important.

Often, obese children experience significant communication problems and make new friends poorly. This leads to the fact that a teenager feels useless and closed to communication, including with parents and people close to him.
If obesity is secondary, then, in addition to being overweight, the child also has other, more dangerous symptoms. So, in adolescent girls with pathologies in the ovaries, the following clinical signs appear: hair grows excessively all over the body, acne occurs, severe hair loss appears, menstrual cycle, the skin becomes excessively oily and prone to any pustular inflammation. In adolescent boys with secondary obesity, which developed against the background of pathologies of the pituitary gland or reproductive system, disorders such as gynecomastia (enlargement of the mammary glands), cryptorchidism, underdevelopment of the external genital organs and others appear.
Severe obesity leads to respiratory problems. Excessive subcutaneous fat in the abdomen and chest leads to the fact that the diaphragm is significantly compressed. This condition causes the child to develop sleep apnea. This pathological condition occurs during sleep. It is characterized by pauses in breathing, which contributes to the development oxygen starvation vital organs.

Excess pounds put a lot of pressure on the musculoskeletal system. It becomes much harder for the baby to walk and move. In the later stages of the disease, the child cannot even perform normal active movements. While walking, the baby feels pain in the joints and muscle weakness. This leads to the fact that the child walks less on the street and is more at home.
Complications and consequences
The long course of the disease has negative long-term consequences. Obese children are much more likely to develop cardiovascular, neurological and orthopedic diseases. Persistent violations in the reproductive sphere lead to the fact that in adulthood they cannot conceive a child and experience significant difficulties with bearing.
Pathological fractures are also most common in people who are obese. In this case, bone fragility is due to significant pressure on the organs of the musculoskeletal system of excess weight. According to statistics, boys who are obese in childhood often develop various anatomical disorders in the feet. This can lead to the development of flat feet and valgus deformities in them.


Disturbed eating behavior leads to the fact that the child has numerous chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The most common are: chronic gastritis and pancreatitis, cholelithiasis with the development of calculous cholecystitis, enterocolitis and irritable bowel syndrome.
Often these pathologies in babies move from acute to chronic course. This leads to the fact that the child is assigned medications on a permanent basis throughout life.
Diagnostics
Often, parents do not pay attention to the presence of obesity in the baby. Especially if the child is preschool. They think it's cute. Many fathers and mothers believe that all symptoms will go away on their own by adolescence. In some cases this actually happens. However, they do the child a disservice.
Childhood is a very important period of life. It is at this time that the baby forms all the basic habits and behaviors that he will then transfer to adulthood. Eating behavior is also formed in childhood. All taste preferences then remain throughout life.

If the baby gets used to eating fast food or too fatty and fried foods, then later this behavior is fixed in him as a persistent eating habit. In adulthood, it will be extremely difficult for him to refuse such products. In order to avoid this, you should carefully monitor the diet from an early age.
When signs of obesity appear, be sure to take the baby for a consultation with the doctor. The specialist will be able to identify the cause of the disease, prescribe a set of examinations to detect secondary obesity, and also recommend to parents what course of therapy is required.
Obesity is a disease that needs to be carefully monitored and treated.
Treatment
According to clinical guidelines, obesity therapy is carried out taking into account the severity of overweight. An integral part of the treatment is the appointment of a diet. If a child has risk factors that provoke the development of obesity, then the diet should be followed throughout life.
Medical nutrition should be low-calorie. Fatty foods, especially those with saturated fats, are completely excluded from the children's diet. In the diet of an obese baby, a sufficient amount of coarse fiber must be present. It is mainly present in fresh vegetables and fruits. Industrial sweets (cakes, pastries, sweets, chocolate, etc.) are completely excluded.

In addition to therapeutic low-calorie nutrition, optimally selected physical activity is required. With a slight degree of overweight, a visit to sports sections is suitable. With a significant excess of extra pounds, playing sports without medical supervision is very dangerous. In this case, physiotherapy exercises are well suited.
The intensity and complex of physical exercises are agreed with a sports medicine doctor or a professional instructor with a specialized education. Excessively active training in obese babies is not acceptable, as they can cause various complications in the child's musculoskeletal system. Physical exercises should be performed at a calm pace and with a certain frequency of repetitions.


Various physiotherapy methods can also help in the fight against excess weight. Cavitation, ultrasound therapy, therapeutic massage eliminate extra centimeters. It is important to remember that physiotherapy alone can never completely eliminate obesity. The treatment of obesity requires a systematic approach that includes mandatory proper nutrition or therapeutic diet, as well as the selection of optimal physical activity.
To eliminate the symptoms of secondary obesity, treatment of the underlying disease is required. In this case, advanced diagnostics may be required. Usually, the treatment of secondary obesity is carried out by pediatric endocrinologists with the active participation of gynecologists, nephrologists and other specialists as needed. Obesity prevention plays a very important role in preventing overweight in babies.
Rational nutrition, active physical activity and a good psycho-emotional mood contribute to excellent health and maintaining a normal weight throughout life.

Should the weight and height of the child comply with the norms? Dr. Komarovsky answers these and other questions regarding the problems of excess weight in children.
The birth of a child is a great joy in the family. Pleasant chores in preparation for a new family member, changes in life, the first trip to the children's clinic. Every mother knows how much her baby weighed at birth.
All children are weighed from the first minutes of their lives, a visit to the pediatrician does not pass without this. This procedure is considered one of the most important during the examination. But not every mother can assess whether the child's body weight is normal.
It is very important to monitor the body mass index of children in order to prevent the moment when the weight gets out of hand.
Read also

What is body mass index?
Body mass index- This is a value that represents the ratio of weight to height. In short, BMI indicates the physical condition, determines whether a person’s weight is normal, excess or deficiency.
This term is considered indispensable in the diagnosis of obesity and other diseases, directly related to excess or deficiency of mass. The weight of both adults and children should always correspond to height.
Body mass index (BMI) calculator
How to correctly calculate the body mass index on your own?
If there is no Internet at hand, and it is simply necessary to find out the body mass index, then this is very easy. In children, the body mass index is usually calculated using the Ketele formula. Accurate weight the baby is divided by twice the height. As a result, you will get a two-digit number.
Basic indicators of BMI
After finding out the body mass index of the child, it is necessary to compare the obtained numbers and determine which parameters it falls into. The normal value of BMI in children older than a year ranges from 18.5 to 25.
- If the readings are below normal more than 2.5 points, this may indicate a significant lack of body weight in children. A body mass index below 16 suggests the possible presence of serious health problems, the development of anorexia.
- The value is above the norm is also not a good result - it indicates the beginning of the development of obesity. A body mass index under 30 is slightly overweight, which can be managed with diet and increased physical activity. A body mass index of more than 30 confirms the presence of obesity. Such figures should force parents to act as soon as possible. In this case, the help of a specialist is mandatory.
All this does not apply to babies from birth to the age of one. They have a slightly different norm value and range from 13 to 21.
The easiest way to calculate
The easiest way to find out your child's body mass index is through the Internet. It will take a few minutes and will give the most reliable results.
The online calculator takes into account the gender, height, weight and age of children. The result should be a two-digit number, which is the body mass index.
A special program will not only calculate the BMI itself and show the acceptable limits, but also reveal the presence of a problem situation or its absence.
It must be remembered that all children are different, and in certain children, the body mass index exceeding the boundaries indicated by the norm does not always signal some kind of disease. About 10% of children will never meet the set limits, which is considered their individual norm. Remember that only a doctor can determine this.
What is the weight:
In accordance with age norms and the calculated body mass index, children are divided into categories:

Table of BMI in children

Read also

What to do if overweight or underweight is determined?
In no case can not ignore the occurrence of problems with weight. Osteoporosis, anemia, weakened immunity, disorders in the endocrine system - this is a small part of what threatens a child with a large deviation in weight.
When exhausted, children may experience dysfunction of vital organs, hair loss, general apathy and fatigue. Obesity primarily affects the spine, increasing the risk of heart disease. If timely action is not taken, the consequences can be irreversible.
Measures to be taken:

Parents should not forget that their own way of life directly affects their children. Such social factors as lack of mobility, overeating, excess fatty and high-calorie foods in the diet of adults are copied in the first place.
About Centile BMI Tables
 Children and teenagers are growing every day. Of course, they all develop in different ways, but the increase also has its established measures. For a more accurate assessment of the full development in pediatrics, centile tables are used.
Children and teenagers are growing every day. Of course, they all develop in different ways, but the increase also has its established measures. For a more accurate assessment of the full development in pediatrics, centile tables are used.
Parents can use them on their own, so as not to miss the moment of development of the pathology in the baby from birth. In these tables, the ratio of height and body weight is estimated, and the norms for the physical development of children are indicated.
All you need to have is a scale and a measuring ruler. For children under two years old, you should find a special scale for the accuracy of the data. If there are none, then you can first weigh the adult, then pick up the child and repeat the procedure.
What are centiles?
centile- this is a value that indicates some parameter, which corresponds to a certain number of subjects who have good health and development. In this case, it is height, weight, head and chest circumference. All this must be measured before using the table.
There are a large number of centile tables and graphs. There are tables for girls and boys, since gender determines the presence of different developmental norms. Boys outstrip girls in growth, and girls mature faster sexually. In such graphs, you can track the average performance of children from birth to 17 years.
The purpose of all of them is that the center is the average number that most children have. At the edges of the table indicate the lowest and highest values. So you can determine how close the child is to the average, corresponding to the norm.
These are some WHO growth corridors showing us children of the same age from the lowest to the highest. The closer the readings are to the edges of the table, the greater the deviation from the average value, a certain signal about the presence or possibility of developing the disease.
 When working with the table, you need to determine in which of the columns your child's indicators are located. Find out which centile corridor your measurements fall into. Depending on the measurements, the indicators of children's development are evaluated in points.
When working with the table, you need to determine in which of the columns your child's indicators are located. Find out which centile corridor your measurements fall into. Depending on the measurements, the indicators of children's development are evaluated in points.
The range of scores is from one to eight. The norm is considered to be indicators ranging from three to six. It is important that these scores do not differ by more than 2 points with age. Otherwise, certain health problems can be assumed.
These tables are necessarily used for routine examinations of children up to a year. Based on them, the pediatrician judges the proportionality of the physical development of children.
You should not make any diagnoses after comparing the indicators of centile tables with those of your children. After all, these tables are just conditionally normative values. You should know the hereditary and characteristic indicators of each child. Only the doctor will determine whether the development is harmonious.
The health of children is directly dependent on their body weight, which is why it is so important to monitor this. This is especially true for babies from birth to three years. After all, such children cannot tell themselves what worries them.
Only some external signs can give a signal that problems have begun in the body. Excess body weight inhibits physical development, it is difficult for a child to roll over, get up and take the first steps.
Being underweight can cause malnutrition useful substances developmental arrest in children. may directly depend on the condition of the child. It is the care of the baby's body mass index that will help to identify the pathology in development and eliminate it in a timely manner.
- primary obesity. It occurs due to malnutrition or is inherited. Moreover, not obesity itself is inherited, but concomitant disorders of the body's metabolic processes. If the mother is diagnosed with obesity, then in 50% of cases these disorders will pass to the baby. If the father has 38%, both have 80%.
- secondary obesity. It is caused by acquired diseases, for example, of the endocrine system.
Allocate 4 in children:
- I degree (weight above the norm by 15-24%);
- II degree (weight above the norm by 25-49%);
- III degree (weight above the norm by 50-99%);
- IV degree (weight above the norm by more than 100%).

In 80% of cases of primary obesity, I and II degrees are diagnosed. The presence of a slight excess weight in a child, as a rule, does not cause any anxiety in parents. Most often, they rejoice at the good appetite of the child, and they treat the diagnoses of pediatricians with a grin, arguing their position as “well, he feels good.”
If the diet is not followed at the first stage of obesity, then the disease continues to progress and goes into stage II. There is shortness of breath, increased sweating, the child begins to move less and more often demonstrate a bad mood. However, even here parents are in no hurry to treat their child. The disease continues to develop. If in the first two stages the situation can be corrected by a diet, then in the subsequent stages everything is much more difficult.
If the weight of the child is higher than normal by more than 50%, then obesity of the III degree is diagnosed. At this time, the teenager begins to hurt the joints of the legs, the pressure rises, and the level of sugar in the blood fluctuates. The child himself becomes irritable, complexes appear, which leads to depression. Exacerbate the situation of ridicule from peers. It is at this stage that parents begin to do something. However, the standard diet is not able to solve a problem of this magnitude.
Complications and consequences
Health problems can begin, including with a little overweight. Therefore, you should not hope that everything will go away by itself, it is necessary to treat the child at the first signs of the disease.
Obesity increases the risk of diseases:
- Decreased immunity;
- Cardiovascular system: hypertension (increased pressure), angina pectoris (pain in the center of the chest), atherosclerosis (arterial disease);
- Musculoskeletal system: chronic diseases of the joints, violation of posture, deformity of the foot;
- Diabetes;
- Disorders of the digestive system: pancreatitis, fatty hepatosis (which can lead to cirrhosis of the liver);
- Chronic cholecystitis, cholelithiasis;
- Dysfunction of the gonads in adolescents: underdevelopment of the genital organs in boys, disruptions in menstruation in girls;
- Hemorrhoids, constipation, fistulas.
Being overweight makes a child unhappy nervous system, which will result in:
- Malnutrition: from bulimia to;
- Sleep disturbance, snoring, etc.;
- Frequent headaches, depression.
Due to the risk of complications, the treatment of obesity in children should not be delayed.
In children under three years of age
Obesity in children of the first year of life is diagnosed quite often, but it is more of a recommendation than a serious diagnosis. The development of the disease in children under one year is associated with:
- heredity;
- Maternal smoking during pregnancy;
- Feeding with a high-calorie mixture;
- Incorrect introduction of the first complementary foods;
- Overfeeding;
- Wrong diet;
- Late onset of crawling and walking;
- Little mobility.

Breastfeeding in the first year of life is a good prevention of obesity in infants.
The most common solution to a problem identified in a child under three years of age is diet. With timely treatment, the disease disappears in 2-3 years.
When diagnosing obesity in babies, a centile table is used, which shows the relationship between their age, weight and height. Information is being collected about the child's diet and diet, the corresponding diseases of his close relatives. The value for children from one to three years is not indicative.
In school-age children and adolescents
With the beginning of school life, children begin to move less, and use their pocket money to buy buns, chocolates and other high-calorie foods. Add to this the stress that schoolchildren experience in an unfamiliar environment for them, and the reasons for weight gain become obvious.
Obesity in children and adolescents is most often caused by:
- sleep deprivation;
- Predominantly sedentary lifestyle;
- Lack of diet;
- Hormonal changes in the body (puberty);
- Stress.
It is worth noting that teenage obesity most often passes into adulthood.
Diagnosis of obesity in schoolchildren and adolescents, as in children under three years old, begins with an anamnesis. Height, weight, chest, waist and hips are measured, BMI is calculated. With the help of special centile tables, the relationship of these parameters can be traced and a correct diagnosis can be made.
To determine the cause of obesity in children, prescribe:
- blood for biochemistry, which determines the level of sugar, cholesterol and other substances that increase the risk of complications in obesity. At elevated level additional glucose tests are ordered.
- Blood and urine tests for hormones to determine endocrine disease.
- Computed or magnetic resonance imaging when pituitary disorders are suspected.
In addition to a pediatrician and a nutritionist, you may have to go through an endocrinologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist and other doctors. It all depends on what additional diseases will have to be treated.
Features of treatment
If you notice that your child is overweight, you should definitely contact a nutritionist. Most likely he will need only a special diet. Obesity in the early stages is much easier to treat. If obesity has already passed into the III or IV degree, then you need to act as soon as possible.
First of all, the treatment of obesity in children requires nutritional correction.
The diet includes:
- Reducing the size of 1 serving;
- Compliance with the regime of fractional five meals a day (preferably with the whole family). In this case, dinner should not be later than three hours before bedtime;
- Replacing sweet store-bought drinks with water;
- Inclusion in the daily diet of fresh fruits, berries and vegetables (with diabetes sweet fruits should be excluded);
- Exclusion from the diet of fatty meat, fish;
- Sufficient water intake;
- Limiting the consumption of "fast" carbohydrates: flour products, pasta,;
- Limiting the consumption of sweets (from sweets, give the child honey, dried fruits, marmalade, marshmallows and dark chocolate), and in case of diabetes, sugar-containing foods should be excluded to the maximum;
- Limit salt intake, exclude pickled and pickled vegetables from the diet;
- Exclude fast food, chips, snacks and more.
During this period, any diet that implies, as well as is contraindicated for the child. Since they will only aggravate the course of the disease. In the daily routine, it is necessary to include walking, lasting at least 30 minutes, and playing sports 3-5 times a week. In the morning it is advisable to do exercises.
Drug treatment, like specialized treatment, is prescribed only by a doctor.