Maintenance in winter cement-concrete pavement of the road. The device of cement concrete coatings. Materials for the preparation of concrete
Concrete is most commonly used for floor coverings. The material provides high structural strength, resistance to aggressive operating conditions. Floor construction technologies are well studied, do not cause excessive costs and are characterized by a wide range of applications.
Concrete underlying layers are arranged where, during operation, the action of oils, solutions, solvents, and various aggressive liquids is possible. In all other cases, you can get by with the installation of non-rigid sand-gravel, slag, asphalt concrete, clay concrete pads.
The thickness of the preparation depends on the design loads. The characteristics of the soils and the materials used are always taken into account. However, current regulations determine the minimum thickness of the underlying layers. If they are laid in residential and public premises - this is 80 mm, if in production - 100 mm.
On floors with a slope, organized runoff, the seams coincide with the watershed, in other cases - with the expansion joints of the building
The concrete must provide the load-bearing capacity of the preparation. As the main material, a mixture of class B22.5 is used. Less durable concrete (but not lower than B7.5) can be taken at low operational loads, in particular, at low tension in the underlying layer.
If the operating conditions are such that the floor will accept sudden temperature changes, expansion joints are always cut. They are placed with a step of 8-12 m in mutually perpendicular directions.
Soil preparation
Before pouring concrete preparation, it is required to prepare a soil base.
The principle of work is as follows:
- if necessary, excavation of vegetable soil is carried out;
- if a high occurrence of the aquifer is revealed, measures are taken to lower the level of groundwater;
- dusty, clay and loamy soils must be dried. The operation lasts until the bearing capacity is restored;
- if the floor is arranged in unheated rooms + protection against deformation is implemented on heaving bases;
- porous soils are removed and replaced with soil with a small draft, or they are fixed;
- if the base has a broken structure, or it is bulk, it should be cleaned of debris, impurities and compacted. Mechanical or manual rammers are used for work. Manual labor is justified only if the equipment can provoke the displacement of adjacent structures and foundations. According to the technology, soils are poured in layers (10 cm each), ramming each layer.

The surface of the subgrade must comply with all planned design elevations. Based on the lower level of the surface, the soil is leveled, poured, compacted. If mixtures of soils are used for the construction of foundations, they are laid in layers of 50-75 mm with layer-by-layer compaction.
Backfilling of underlying layers
When working on the ground concrete preparation lay the underlying layers.
The works are carried out as follows:
- a layer of building sand is poured onto the base (prepared and leveled). It is spread over the entire area of \u200b\u200bwork in a continuous even layer. The thickness of one layer should be 5-10 mm. Compaction is carried out, for which the sand is pre-moistened;
- then a crushed stone layer is laid out. It is selected by size, composition, stacked and moisturized. As a result, a uniform continuous layer should be formed, 80-200 mm thick. Crushed stone is leveled and rammed mechanically or hand tool. If gravel is used, it is laid in a similar manner;
- on dry grounds, it is permissible to work with adobe mixtures. The material is laid in a layer up to 100 mm, compacted until moisture reaches the surface.
If multi-layer preparation is implemented, each subsequent layer is laid after careful processing of the previous one.
To improve adhesion in the underlying layers, moisturizing is applied between them.
Pouring concrete preparation
The material can be transported to the place of work by concrete pumps, carts, dump trucks. If the structure does not require reinforcement, concrete is laid directly from carts or dump trucks to the center of the pour area. If a reinforcing layer is provided, the concrete is unloaded by tipping to the side.. If required, the placement of the reinforcement mesh is adjustable, but the reinforcement must not be moved when pouring. For large volumes of work, it is advisable to use a concrete pump that ensures uniform distribution of the solution.
The working principle is as follows:
- beacons with strict horizontal control are placed on the base. Boards can be used as the main material, the width of which corresponds to the thickness of the concrete preparation, 4-6 cm thick. On the base, the beacons are fixed with wooden pegs hammered to a depth of 30 cm, in increments of 1.5 m. Instead of boards, it is permissible to take a metal channel;
- if a slope is to be organized on the floor surface, it is provided at the preparation stage by cutting off the upper edge of the beacons at the required level;
- with a large amount of work for the device of concrete preparation, the construction of a collapsible formwork is required, with reliable fixation of all elements;
- concrete is brought to the surface. Concreting is carried out in strips through one;
- first of all, the strips remote from the entrance are poured, successively approaching it;
- when the concrete has set, proceed to the processing of adjacent unfilled strips. The side faces of the finished slabs are pre-treated with hot bitumen. Application layer - 1.5-2 mm. These faces will form expansion joints;
- proceed to the formation of shrinkage seams. To do this, a metal profile is deepened into a freshly poured preparation, 4-5 mm thick, 80-100 mm wide. The profile should be deepened by 1/3 third of the thickness of the preparation. The material is left for 20-40 minutes and removed. When the concrete has matured, shrinkage joints are poured with cement mortar or hot bituminous mastic.

After completion of work, the surface is treated with trowels.
Waterproofing
The waterproofing layer is arranged for concrete preparation with medium and high intensity of exposure to water and other liquids on the floor (+ alkalis, solutions, acids). These can be floors of unheated premises, structures built on subsiding soils, floors on floor slabs, areas with a risk of capillary suction of groundwater. Besides, protection is necessary if the concrete preparation is placed below the level of the blind area.
The choice of material is subject to the following principles:
- if it is required to provide protection against the action of water, chemically aggressive liquids, materials such as polyethylene film, polyvinyl chloride film, hydroisol can be used;
- against the background of medium intensity of action Wastewater waterproofing works successfully. It is permissible to work with bituminous materials, applying them in 2 layers. ;
- against the background of the high intensity of the action of liquids on the floor, it is possible to arrange pasting waterproofing, but with a doubling of the number of layers;
- under concrete preparation, it is permissible to arrange waterproofing based on crushed stone and other bulk materials, followed by impregnation with hot bitumen.
Polymer gluing waterproofing is placed in 1 layer
In the latter case, protection is arranged after filling the crushed stone cushion. The layer is impregnated with an asphalt distributor or manually. Hot bitumen is evenly applied to the base, with a layer 5-6 mm thick. If bituminous impregnation is arranged in several layers, sand (fractions up to 5 mm) or stone chips are allowed through the first one. Compaction is carried out with a roller, after which a second layer up to 0.25 mm thick is implemented, using sand powder.
Regardless of the materials used, the waterproofing layer must be continuous, sealed, protruding above the floor to a height of at least 300 mm from the level of the coating.
Principles of coating waterproofing device:
- the base must be flat, dust-free. The primer is applied on the base bituminous mastics or solutions based on polymers. The composition can be distributed manually with brushes or by means of sprayers;
- as a result, an even thickness, the same primer layer should be formed, in which there are no gaps. Optimal Thickness- 0.5-2 mm;
- the next layers should be applied only after the previous ones have completely dried, which can be determined by the cessation of tack;
- when working with joints, they are covered with mastic and strips of rolled material 10-20 cm wide are glued, after which another mastic layer is applied.
 Principles of work with asphalt waterproofing:
Principles of work with asphalt waterproofing:
- the material can be laid on hot mastics applied in a continuous uniform layer. The applied layer requires leveling, compaction with trowels or rollers;
- the next one is applied after the bottom is ready, that is, the mastic has completely cooled down;
- joints are arranged apart, an overlap of 200 mm is observed;
- upper layer protection must be even, with the observed thickness and slope;
- if they work with cold mastics, the principle of work remains the same.
Principles of work with rolled waterproofing:
- the material can be glued on cold or hot bituminous mastics. Substrate preparation requirements remain typical;
- when using hot mastics, adjustment of the panels is required;
- the roll is rolled out over the base so that an overlap of 100 mm is provided;
- the laid material is left for 24 hours to eliminate irregularities and waves. The temperature in the room should not be below +15 degrees;
- when the panels have rested, they are rolled back, leaving only the first longitudinal row and a guide line for gluing is outlined;
- approximately 0.5 m is bent from the roll to be glued and mastic is applied. The base under the roll is processed with the material;
- the area with mastic is glued, pressing tightly to the base, rolling with a roller from the middle to the edges;
- then turn off the rest and act in a similar way;
- the edges of the glued material are rolled with a roller;
- the next roll is glued with an overlap of 10 cm, observing the lubrication of the edges and processing with a roller. Then they act in a similar way, filling the entire area of \u200b\u200bwork;
- when the first layer is ready, proceed to the device of the second, observing a longitudinal overlap of 20 mm. Control the placement of seams apart.
If the base has no slopes, roll materials rolled over the surface. If there is one, they work from low areas to high ones.
thermal insulation
Effectively apply thermal insulation materials with high density. These can be mats or fiberglass-based plates, mineral wool or more modern polystyrene foam. The optimal layer thickness during work is 100 mm.
Thermal insulation is laid closely on the base, ensuring a snug fit of the joints. As an alternative, it is permissible to use bulk thermal insulation based on expanded clay. It is applied to the base in layers, followed by leveling and compaction.
In areas where the structure adjoins walls and other vertical surfaces, a gap should be left, which is closed with a tape of soundproofing material.
Concrete pavement technology
Floors with concrete coatings are general-purpose structures that are successfully used both in public construction and in production. A well-made floor is able to withstand high mechanical loads, the action of solutions, oils, salts, and water. On practice the finished system is able to withstand heating up to 100 degrees.

Concrete coating can be arranged on the ground, on the underlying concrete preparation, on cement-sand screeds M150 and higher, on reinforced concrete floor slabs. At the place of work, optimal temperature regime- not lower than +5 degrees, up to a solution of half of the design strength.
Materials for the preparation of concrete:
- Portland cement is not lower than M400 in terms of grade strength;
- gravel or rubble. The fineness should not be more than 15 mm, or 0.6 of the coating thickness. You should count on an average consumption in the region of 0.8 cubic meters per cubic meter of concrete;
- medium or coarse sand;
- water.
If a non-sparking concrete pavement is required, sand and crushed stone based on marble or limestone should be used, which do not spark when struck by metal objects.
The brand of concrete cannot be lower than M200. The mobility of the solution is controlled - 2-4 cm. It is permissible to introduce C-3 plasticizers or other modifying additives into the formulation, which will reduce labor costs during laying.
Concrete laying sequence:
- when starting work, the base is cleaned of dust and dirt;
- if oil stains have formed on the underlying layer, they should be removed with special ready-made solutions or a solution of soda ash (5%). After treatment, the area is washed with water;
- if laying is carried out on prefabricated floor slabs, cracks. . Filling is carried out flush with the surface of the plates.
Recesses, mounting holes are subject to sealing, for which a cement-sand mortar M150 is prepared, not lower than
Proceed to install beacons using either steel pipes, or wooden beam or metal profile. The diameter and height of the material must correspond to the design thickness of the coating.
The first row of lighthouses is laid out with an indent from the wall equal to 0.5-0.6 m. The subsequent ones are parallel to it with a step of up to 3 m. It is permissible to lay out the layout immediately throughout the entire work area or in separate cards, with docking along the axis and offset by the width of the rail.
For fixing take a cement mortar. The guides are aligned according to the level, in accordance with the previously applied markings. To correct the position, light blows of a hammer or hand pressure are used. Horizontalness is checked with a rail or special devices.
The subsequent installation process is as follows:
- before pouring concrete, the base is abundantly moistened. By the time the mortar is laid, the surface should be damp, but without excess water;
- then determine the scope of work, calculating the speed of concrete preparation, laying, the period of initial setting;
- the solution is delivered to the site from the concrete mixing unit by truck mixers. If pouring is carried out along the first floors, the solution is unloaded directly onto the concreting strip. If work is carried out on the second and upper floors, the solution is transferred to transfer bins and portionwise fed to the work site by lifts, cranes;
- the solution is placed between the beacons, through one lane;
- the layer is leveled with shovels or special scrapers so that it exceeds the beacons by 3-5 mm;
- unfilled strips are poured after dismantling the beacons, using ready-made strips as guides and formwork.
 Compaction is implemented with the participation of vibrating screeds, moving them along the lighthouses. If the thickness of the structure is small, the vibration time is minimized, - act until moisture forms on the surface. Excessive vibration exposure can cause settling of coarse aggregate and stratification of concrete.
Compaction is implemented with the participation of vibrating screeds, moving them along the lighthouses. If the thickness of the structure is small, the vibration time is minimized, - act until moisture forms on the surface. Excessive vibration exposure can cause settling of coarse aggregate and stratification of concrete.
The optimal speed of movement of the vibrating screed is set within 0.5-1 meter per minute. When moving the tool, a roller 2-5 cm high should be assembled at its lower edge. In the wall zones, in areas near the columns, compaction is carried out with manual rammers, weighing at least 10 kg.
If breaks were made during pouring, before resuming laying, the vertical edges of the coatings that have had time to harden are dedusted, cleaned and washed with water. Where the working seams are placed, sealing and smoothing is carried out until the seam becomes invisible.
Vacuum technique for concrete floors
When laying concrete pavements on concrete preparation, it makes sense to turn to the vacuum technique. In this case, the coating is carried out simultaneously with the underlying layer. As a result, the strength of the surface layer is increased by a third compared to the original values. A high-quality floor with excellent physical and mechanical characteristics is formed.
According to the technology, a liquid concrete solution is laid on the base, compaction is carried out. With the help of special equipment, excess water is removed from the concrete thickness, which works on the strength and rigidity of the layer.
The concrete formulation is selected based on the quality of Portland cement and available aggregates. But,
To ensure the maximum sealing effect, first, an increased content of the mortar part is added to the concrete composition.
The essence of the vacuum method is as follows:
- the concrete mortar is mixed with an excess amount of water so that the draft of the cone reaches 9-11 cm;
- the mixture is unloaded at the place of laying and evenly leveled over the entire area;
- after pouring, the solution is compacted with a vibrating screed if the layer thickness does not exceed 10 cm. On thicker screeds and in the presence of reinforcement, deep vibrators are additionally attracted;
- suction mats are placed on the leveled and compacted layer and connected through the sleeve to the vacuum equipment;
- the filtered bottom panel of mats is placed directly on fresh concrete;
- the top panel is rolled out, smoothing with brushes or rollers. Work starts from the middle of the web, which will have a good effect on sealing in the system during vacuum processing.
If two or more panels are laid on the surface, they should be placed with an overlap of at least 3 cm. The upper edge should overlap the lower one by 10-15 cm. Then vacuuming begins. The duration of the technology is calculated as follows: 1-1.5 minutes per 1 cm layer of concrete.
 When no water movement is observed, the treatment is stopped. The concrete must gain density at which only a faint trace remains on it. The suction mats are removed.
When no water movement is observed, the treatment is stopped. The concrete must gain density at which only a faint trace remains on it. The suction mats are removed.
After vacuum processing, you can immediately start smoothing. For the first time they work with trowels with discs, the second time - with blades.
Primary treatment of concrete floors
When the filled layer is sufficiently compacted and managed to grab, you can proceed to the primary processing. The readiness of the coating can be determined as follows - when walking on it, light traces should remain.
The main working equipment - trowels, trowels, with installed trowel discs. The operation helps to correct minor defects that could have been made during pouring and compaction; after processing, a finishing horizon is formed.
Secondary grouting is possible after 1-6 hours. Instead of discs, the blades act as the working body. In hard-to-reach areas, they work manually or with a trowel for processing cement screeds. Such areas are subject to priority grouting due to quick setting.
Care
Concrete is a material that must mature in wet conditions. To provide such an environment, the surface is covered with wet burlap, wet sawdust, maintaining the material in this state for 7-10 days.
The frequency of wetting is selected based on temperature and humidity conditions, however, the material should not dry out even partially
Grinding and milling of concrete floors
This type of processing requires the release of the base from debris, mechanisms and devices. In the milling process, ordinary diamond wheels or cutters with a diameter of 250-500 mm should be used.
Milling is carried out in parallel strips, overlapping the edge of the strip in the next approach by 2-3 cm. In one pass, you can work to a depth of 2-7 mm, focusing on the mechanical and physical characteristics of concrete. The purpose of such processing is the complete exposure of the aggregate grains, that is, the surface must reach such a strength that its chipping is impossible.
Work is usually carried out in two stages. At the first stage, the milling machine removes a layer of 3-5 mm in one pass. Next, polishing is carried out in 1-2 passes, using grinding machines. When processing, it is necessary to organize a thorough cleaning of the surface in time.
Finishing
Finishing allows you to improve the performance of concrete floors. When choosing materials, they are guided by the conditions under which the structure will work.
 You can act as follows:
You can act as follows:
- surface impregnation with fluates. The coating is applied no earlier than 10 days after pouring the solution. The temperature regime is observed in the room - not lower than +10 degrees. Before work, the base must be dried and thoroughly cleaned with construction vacuum cleaners. The material is applied until the concrete stops absorbing it. Practice shows that three approaches with an interval of 24 hours are enough for this;
- sealant impregnation. For these purposes, use liquid glass, aqueous solutions of calcium chloride. Processing is performed in three approaches with a daily interval. When the treatment is completed, the concrete must be rinsed with water;
- adding toppings. For hardening, special dry mixtures (corundum, quartz, metal) are used. The type of material is selected based on the design loads. Toppings are applied to fresh concrete after initial setting in two passes using concrete finishing machines;
- as a protective layer, you can use polyurethane, epoxy varnish. The material is applied to concrete during the initial hardening period, immediately after the completion of the grinding operation. Before work, the floor is cleaned with an industrial vacuum cleaner, treated with a moistened rag and primed with the same varnish, but with a diluted solvent. The compositions are spread by brushes, rollers or spraying. Layer-by-layer drying is observed, during which the surface is protected from moisture.
In addition to polyurethane varnishes for the device of the top layer, you can use polymer coatings(epoxy, acrylic). Paint layers are applied in a thin layer, no more than 0.3 mm thick.. If you want to decorative effect, good choice there will be self-leveling floors forming a seamless matte surface. In conditions of high loads, you can turn to the device of highly filled coatings.
In residential premises, the choice of finishing coating is practically unlimited - it can be tiles, laminate, carpet, cork, linoleum ...
Safety
When constructing concrete floors, safety regulations in construction are always observed. All workers must be familiar with the conditions of work, briefing, training in handling equipment and tools.
The device of floors is carried out using technological equipment. Personal and collective protective equipment, hand construction tools are used. Workplace V hard-to-reach places should be well lit.
When laying waterproofing on hot bituminous mastics, special care is required. Ventilation is provided in enclosed spaces. Prolonged contact of cement mixtures with the skin is unacceptable.
cost of concrete flooring
The concrete flooring technology is available and does not require too high costs. On average, the financial costs of laying 1 sq.m. "turnkey" start from 850-1100 rubles. To this cost, you can safely add the cost of purchasing and shipping materials.
Equipment, tool
Concrete work is carried out with the participation of a standard set of machines and tools.
 The following set should be assembled at the construction site:
The following set should be assembled at the construction site:
- when self cooking solutions require concrete mixers;
- preliminary compaction of soils, underlying layers is carried out by mechanical rammers;
- filling is compacted by vibrating rails, deep vibrators;
- finishing processing is carried out with the participation of trowels, grinders;
- industrial vacuum cleaners are used for cleaning and dedusting;
- level, level - a tool for measuring, controlling the horizontal, evenness of the structure;
- shovel, clean container, spatulas.
conclusions
The installation of concrete floor coverings must be implemented in strict accordance with the technological process. A qualitative result is achieved with professional work, with a phased quality control of the work.
The device of industrial concrete floors is shown in detail in the video:
The very word "concrete" of French origin, it was first used in the XVIII century in France. Prior to this, the water-cement mortar was called differently. Cast masonry with stone filler was called the Greek word "amplekton". The ancient Romans called concrete "rudus". When designating such concepts as mortar for building foundations and walls, the phrase "opus caementum" was used. It was under this name that Roman concrete became known.
The very first concrete discovered by archaeologists dates back to 5600 BC. e. It was found in the village of Lapinski Vir in the former Yugoslavia, in one of the huts of an ancient Stone Age settlement, where it was made into a floor 25 cm thick. The concrete mortar for this floor was prepared using gravel and local reddish lime.
In Egypt, in the tomb of Teve, concrete dating back to 950 BC was found. e. In addition, concrete was used in the construction of the galleries of the Egyptian pyramids and the monolithic vault of the Pyramid of Nîmes.
In ancient Rome, concrete was used as a building material around the 4th century BC. BC e. The material was called "Roman concrete" and was used for about the 7th century. Centuries have passed since then, but structures built of Roman concrete have survived to this day. Some of them, such as the Roman Pantheon, survived several fairly large earthquakes.
Foundation work in ancient Rome was greatly facilitated by the fact that the volcanic soil in its vicinity remained dense for quite a long time, which made it possible to use the most common plank formwork for the construction of foundations.
Studies of ancient settlements have shown that two types of concrete were used for construction - artificial and natural. Natural was made from stones formed from clastic particles of rocks and interconnected by various mineral substances, such as lime, gypsum or calcite. Natural concrete includes breccia, conglomerate and sandstone. When a man came up with artificial concrete, the same stones began to bind together with other substances - gypsum, clay.
The simplest type of concrete is clay concrete, which consists of a hard stone-like material made from a mixture of clay, sand and straw. It acquires sufficient strength after drying in the sun.
Gypsum concrete is called concrete made on gypsum binders obtained on the basis of semi-aqueous or anhydrous calcium sulfate.
Artificial concrete in antiquity was not widely used, because it did not have sufficient strength: clay, lime and gypsum soaked under water, and the structure collapsed. That is why ancient builders preferred to use natural materials. But attempts to create an artificial binder continued.
The ancient Romans noticed that lime, mixed with the so-called pozzolanic (the name comes from the Pozziuoli area near Naples) additives, on the contrary, acquired even greater hardness from exposure to water. This type of lime is called hydraulic lime.
O. Shuatre, famous historian architecture, was able to reconstruct the process of laying stone concrete. To prepare the solution, lime was mixed with pozzolanic additives. Then, a thick layer of mortar was laid between the two facing walls, crushed crushed stone with a grain size of up to 8 cm was laid on top. At the next stage, the mortar was rammed until it filled all the gaps between the crushed stone.
The discovery by the Romans of the properties of pozzolanic additives improved the quality of Roman concrete, which could not but contribute to its further distribution. In the II century. n. e. the Romans developed and began to use new types of binders, such as romancement, which made it possible to improve the physical and mechanical characteristics of concrete structures under construction to a greater extent.
After the fall of Rome, many of the secrets of the ancient architects were lost. Centuries later, the English architect John Smith drew attention to the fact that quicklime mixed with clay hardens under the action of water. He added sand and stone slag to this composition and obtained a fairly durable substance, which he used in the construction of the foundation for the Eddyston Lighthouse. Just as long ago, the properties of binders became known to man - clay and oily earth, which acquired relative strength after mixing with water. However, they did not provide sufficient strength. That is why in China, India and Egypt about 3 thousand years BC. e. through the heat treatment of raw materials, artificial binders were developed - gypsum and lime.
In the 60s of the XIX century. French gardener Joseph Monnier invented the world's most durable concrete tree tubs. He simply rolled up the metal mesh and filled it with concrete mortar. At that time, Monier did not even suspect that in the near future his invention would become the main material for the construction of most buildings, especially high-rise ones.
Centuries passed, concrete began to be used in other industries, seemingly far from construction, such as shipbuilding (in the first half of the 20th century, many river and sea vessels were built using reinforced concrete), aviation (manufacturing of wings and fuselages of aircraft ), railway transport (railway wagons and tank car frames). The Americans went even further: they proposed to build a concrete plant on the Moon with a system of specialized warehouses. To do this, it was supposed to deliver concrete and other necessary building materials from the Earth, and the delivery itself should be carried out using specialized transport ships.
Measures to protect concrete floors
Consider floor protection measures using the example of a basement. First of all, attention should be paid to the evenness of the surface and good compaction of the underlying layer located under the basement floor slabs. The most reliable way to ensure a flat base surface is to install a leveling concrete layer with a thickness of about 8 cm.
If the backfill of the excavation is high, the fill material should be laid and compacted in layers about 30–40 cm thick.
When exposed to groundwater pressure, the basement floor should be designed from rigid reinforced concrete slabs: their dimensions are determined by static calculation. Floor slabs that are not under water pressure must have a thickness of at least 120 cm.
With regard to the use of waterproof screeds and sealing mastic, it can be said that it (use) is advisable only when, thanks to the flat drainage device, it is guaranteed that there will be no long-term impact of groundwater pressure. Waterproof screeds and sealing mastic coating are recommended to be laid only on reinforced, seamless and evenly worn floor slabs.
Before installing a waterproof screed, the surface of the base must be cleaned, moistened and lubricated with cement-sand mastic or primer. In this case, special attention should be paid to the composition of the screed mortar, cement consumption, water-cement ratio and particle size distribution. Additives processed according to the manufacturer's instructions can also improve the density of the solution.
The screed should be installed in one working cycle, its thickness should be approximately 3 cm. The screed should be carefully compacted and smoothed.
As for sealing mastics, they should be applied continuously in several layers. The manufacturer's instructions must be observed. minimum flow mastics.
Before hardening, waterproof screeds and sealing mastics must be protected from uneven and too rapid drying and moistened if necessary.
And immediately after hardening, the sealing mastic must be protected from damage by applying a protective layer.
As a rule, high demands are placed on the floor of basements, mainly regarding the dryness of the floor. Therefore, a waterproofing film should be laid on the floor slab. Two-layer waterproofing with overlapped joints, glued over the entire surface and with a coating screed, preferably a single layer. Particular attention should be paid to a sufficiently wide overlap of the seams (about 10 cm) and careful performance of their gluing. And immediately after installation, the rolled waterproofing should be covered with a protective layer, which should be separated from the waterproofing with a separating film.
Cement-sand, cement-concrete and asphalt concrete floors
These types of floors have a concrete base, which is laid on a concrete preparation - an underlying layer with a grooved surface. Concrete coating is made of concrete grade 200 with a hull draft of 2 cm, on crushed stone with a particle size of up to 15 mm. The concrete mixture is laid in strips 2–2.5 m wide, then the area of the laid concrete is limited by beacon rails and compacted with vibrating rails or areal vibrators, and in cramped conditions with tampers.
Simultaneously with the laying of the concrete mixture on the floor surface, it is smoothed out with long-handled trowels, wooden trowels and metal trowels. Excess cement is removed with a scraper with a rubber band.
At the end of the concrete laying, the floor surface is finished with an ironing board or rubber band. Smoothing must be done before the final hardening of the concrete mass.
The cement coating is made on the basis of a cement-sand mortar of a grade of at least 150 with a cone draft of 3–4 cm.
(Last Updated On: 03/07/2018)
Cement-concrete and reinforced concrete pavements designed to pass heavy traffic of heavy vehicles, long time retain their high transport and operational properties and are very durable. However, even with high quality construction works and proper maintenance during operation, over time, cracks, shells, destruction of the edges of the seams, vertical displacements of the edges of the slabs at the seams, spalling of the corners of the slabs, peeling and other damage appear on the concrete pavements.
One of the main causes of wear and destruction of coatings is the effect of transport on them, which contributes to the emergence of vertical and horizontal stresses in the coating. The magnitude of the vertical stress depends on the type of passing traffic and on the degree of evenness of the road surface. Horizontal (tangential) forces are caused by the friction of the tire on the pavement during braking and other changes in the speed of vehicles and by wheel impacts when hitting bumps. If, under the action of moving loads, subsidence of the base soil occurs during the period of waterlogging, this leads to deformations of the coating slabs.
Another reason for the wear of coatings is the tendency of cement concrete to significant deformations during shrinkage and temperature changes, which, combined with the brittleness of this material in conditions of limited dimensional change pavement in the plan can lead to the appearance of cracks in it, which reduce the durability of the structure, increase the water permeability of the coating, reduce its flexibility and strength.
In cement-concrete and reinforced concrete pavements, the following types of cracks are usually distinguished: shrinkage cracks associated with the settlement of the base of the reinforced concrete element, caused by overloading of reinforced concrete at an early age; cracks due to chemical decomposition, as well as the limited ability to change volume during deformations caused by shrinkage from drying or temperature changes. Finally, often the cause of the formation of cracks are the stresses that occur during bending.
During operation, in addition to the mechanical load transmitted through the wheel of the car, the coatings are also exposed to atmospheric and other influences, so they must be chemically resistant, well resist the adverse effects of weather conditions, primarily frost. Damage to cement-concrete road slabs under the influence of frost is usually expressed in peeling of their surface or swelling of the soil base.
Very often, deformations in cement-concrete pavements, including those made of prestressed concrete and reinforced concrete slabs, occur as a result of the use of substandard materials, violations in the technology of preparing and laying the concrete mixture, and non-compliance with the rules for the care of freshly laid concrete. In the case of the use of prefabricated coatings, the low frost resistance of concrete can be explained by non-compliance with the design mode of heat and moisture treatment of products. Of particular importance is the water-thermal regime of the road base and subgrade, since the results of the mechanical impact of transport on the road change depending on it.
It should be noted that even small deformations violate the evenness of the coating and lead to a decrease in the speed of movement. The movement of heavy vehicles on a pavement with minor damage leads to its even more intensive destruction, therefore, with heavy traffic, the timely repair of cement-concrete pavements becomes very important.
The main types of deformations and destruction of cement-concrete and reinforced concrete coatings and the causes of their occurrence are given in Table. 89.
The technology of repairing cement-concrete pavements, carried out in the specific conditions of the city, should be based on the use of repair methods that reduce the time of work, as a result of the use of materials that contribute to the speedy commissioning of repaired areas, full mechanization of the main labor-intensive operations using maneuverable, high-performance machines and mechanisms.
All joints in cement-concrete pavements must be filled with mastic. Joints in which the filling material has crumbled or there are gaps between the vertical walls of the concrete slabs and the material filling the joint are cleaned and refilled with mastic. The compositions of the mastics used in the maintenance and repair of cement-concrete coatings are given in table. 90.
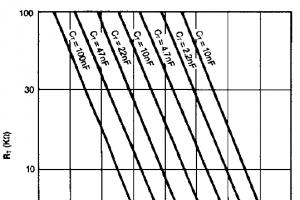
For the preparation of bituminous mastics, only dehydrated bitumen is used. Mastic is prepared at factories and delivered to the consumer in a container with a passport attached, which indicates its physical and chemical properties. If there is no centralized supply, mastics are prepared at local bases as follows: dehydrated bitumen is heated to 150-170 ° C, after which rubber crumb is introduced into it. Bitumen with crumb rubber is boiled for 2.5-3 hours with constant stirring. After combining the rubber crumb with bitumen, the remaining components are gradually added, and the mastic is boiled again for 30 minutes at 150-170 ° C with constant stirring.
When repairing, the seams are thoroughly cleaned of old mastic with steel hooks or special tools and hard brushes, and then blown with compressed air and dried. 2-3 hours before pouring, the vertical walls of the joints are coated with bitumen BND-90/130, BND-60/90 or BND-40/60, diluted gasoline in a ratio of 1: 1, or liquid bitumen brand SG-15/25 with a flow rate of 0 .3-0.5 l/m2. The seams prepared in this way are filled with hot mastic, heated to 160-170 ° C, 3-5 mm below the surface of the coating. The mastic is poured with a seam filler in two steps: first, the seam is poured to 2/3 of its depth, and then the upper part of the seam. If, after pouring, it is necessary to immediately open the movement, the seams are sprinkled with mineral powder or a strip of roll paper 10-15 cm wide is glued onto them.
To clear and fill joints in cement-concrete pavements, a machine is also used, mounted on a self-propelled cart, in front of which a cutter knife is mounted, designed to remove old mastic from the joints, and a device for filling joints with new mastic. The machine has a complete installation for blowing out the cleared seams.
To prevent the development of surface hairline cracks in the plates, the places of their occurrence are covered with a thin protective layer. To do this, bitumen of grades SG-70/130 and MG-70/130 (0.7-0.8 l / m2) is poured over a dry and dust- and dirt-free coating. Then fine crushed stone 5-10 mm in size is scattered in the amount of 0.8-1 m3 per 100 m2 of coating or coarse sand in the amount of 0.3-0.5 m3 per 100 m2 of coating and rolled with light rollers.
Cracks with a width of 1 to 5 mm are filled with liquefied bitumen grades SG-130/200 and MG-130/200, heated to a temperature of 80-100 ° C. Before sealing, they are thoroughly cleaned and dried. Cracks with a width of 5 mm or more are cleaned of dirt, weak spots are cut down, concrete fragments are removed and thoroughly blown with compressed air before filling. The cracks prepared in this way are smeared with liquefied bitumen and filled with mastic: with a crack width of 10-25 mm - with compositions 1, 2 and 3, with a width of 5-10 mm - with compositions 4, 5 and 6.
All surface and through cracks in concrete pavements must be repaired as soon as possible. short term after their appearance. Seams and cracks are recommended to be closed in spring and autumn in cool weather, and in summer - in the morning.
To repair minor damage to cement-concrete pavements, hot or cold asphalt mix, poured asphalt, black gravel or black stone chips can be used. Cement-concrete pavements using asphalt concrete mixtures are repaired in a dry and relatively warm season at an air temperature of at least 5 ° C. concrete mix or black gravel. The area to be repaired is thoroughly cleaned of dust and dirt, dried and lubricated with a thin layer of liquefied bitumen grade SG-15/25, heated to a temperature of 60 ° C (binder consumption 0.3-5 l / m2), and sealed with asphalt concrete mix or black gravel.
Minor damage in the form of shells, potholes and destruction is thoroughly cleaned of concrete fragments, dust and dirt and lubricated with a thin layer of liquefied bitumen (consumption 0.3-0.5 l / m2). Then cold or hot asphalt mix or black gravel is laid and compacted. When potholes are filled up to a depth of 5 cm, the asphalt concrete mixture is laid in one layer, with a depth of more than 5 cm - in two layers. With small sinks and potholes, the hot mixture is compacted with manual or metal vibratory rollers and heated rammers weighing 12-16 kg. With a large surface of potholes to be filled, the hot asphalt concrete mixture is compacted with rollers weighing 5-6 tons.
The asphalt concrete mixture is laid taking into account the compaction coefficient equal to 1.3-1.4 for hot mixtures, and 1.5-1.6 for cold mixtures. The repaired areas should have a smooth interface with the adjacent surface of the concrete pavement. It should be noted that the repair of cement-concrete pavements using asphalt concrete and black crushed stone mixtures is short-lived due to their poor adhesion to cement concrete. In addition, light-colored cement-concrete pavements repaired with black mixtures have an unsightly appearance. For these reasons, the repair of concrete pavements using asphalt concrete and black gravel mixtures can only be considered as a temporary measure.
More promising is the repair of cement-concrete coatings using concrete mixtures. The pavement repaired with concrete mixtures is more durable, and the color is not much different from the existing cement-concrete pavement. It is recommended to prepare the concrete mixture for the repair of coatings of the same composition and from the same materials (or close to them) that were used to prepare the concrete mixture of the previously laid coating. For the concrete mixture, high-strength Portland cements are used with the addition of up to 2% calcium chloride to the mixing water. To increase the workability of the concrete mixture and the frost resistance of concrete, it is recommended to add air-entraining additives to the water: soap naphtha, sulfite-yeast brew, abietic resin, etc. more than 40 mm at deeper cuttings.
When peeling concrete, damage that captures only the top layer of the coating is repaired to the depth of destruction, but not less than 7 cm. When repairing, damaged areas of the coating are outlined with chalk or paint in straight lines. According to the applied contour, the old concrete is cut down with a concrete cutting saw and pneumatic tools. After cleaning, the prepared places are kept in a moistened state for about 24 hours, i.e. until the old concrete is completely saturated with water. The cutting surface is smeared with a thin layer of cement-sand mortar.
Immediately after applying the cement paste to the walls and bottom of the cutting, the concrete mix is laid above the level of the surface of the coating, taking into account the settlement during compaction. In small, shallow and narrow clearings, the concrete mixture is compacted manually with wooden or metal rammers weighing 12–16 kg; in deep and wide clearings, the mixture is compacted with surface vibrators. Finally, the surface of the repaired area is finished with hard brushes and wooden trowels with a rubber band. After compaction and surface finishing, freshly laid concrete is treated: film-forming materials are applied to the surface of the coating according to the technology used in the care of freshly laid concrete during capital construction.
In foreign practice, in particular in the USA, for the repair of cement-concrete pavements, fiber concrete was used on an experimental basis, which is a high-strength cement-concrete mixture with fibrous filler, which is usually steel, glass or plastic.
Compared to ordinary fibrous cement concrete, it has a number of advantages: if only 1% of fibrous substances are present in the volume, its tensile and bending strength increases by 100%; resistance against cracking is increased by 60%; resistance to dynamic loads - 9 times higher; wear resistance - higher by 30%; it can withstand compressive loads even after reaching the tensile strength; its resistance to fatigue, shear and torsion is greater, and cracking, peeling and chipping are less; compression resistance is also slightly higher. Due to the indicated physical and mechanical properties, fiber concrete can be laid in small layers and save materials.
During the operation of cement-concrete and reinforced concrete coatings, concrete failures along expansion joints are often encountered. The method of repairing the edges of the seams depends on the nature and size of the damage. Small damages up to 5 cm wide are sealed with mastic after removing loose concrete particles and cleaning the repaired area. Deep damage with the edges of the seams, destroyed to a width of more than 5 cm, is sealed with concrete. old concrete removed along the entire length of the site to a depth of at least 7 cm with a slope towards the lower part of the clearing. Reinforcement, pins and anchors are kept whenever possible.
To form a seam, a wooden gasket with a removable rail is installed, reaching the surface of the coating. The gasket is installed in such a way that it coincides with the direction of the existing seam. If the old gasket is preserved in the lower part of the seam, then it is increased so that there are no gaps between the boards and no concrete bridges can form. Old pins, anchors and reinforcing bars are straightened or new ones are laid. The planes of contact of the new concrete with the old one are coated with a cement-sand mortar, after which the concrete mixture is laid and compacted. The upper part of the gasket after the concrete has hardened is removed and the seam is filled with mastic.
Driving on pavement repaired with cement mixture allowed to open after 15 days. When replacing parts and whole slabs in the pavement, traffic on the newly laid concrete is allowed after 20 days,
Using ordinary concrete, the pavements are repaired in layers of at least 7 cm thick. At the same time, due to the slow curing of the newly laid concrete, traffic on the repaired section of the road has to be closed for at least 15-20 days. In addition, the laying of thick layers of new concrete over the old concrete pavement, as a rule, is associated with a laborious process of cutting old concrete to a considerable depth and a large consumption of materials. Therefore, in recent years, serious attention has been paid to the development of methods for repairing concrete coatings using concrete mixtures that ensure reliable adhesion of the built-up thin layer of concrete to the existing coating and accelerated hardening of concrete while ensuring its strength and frost resistance.
In Soyuzdornia, a study was conducted to develop a method for repairing cement-concrete pavements using fast-hardening cements (BTC) or Portland cement grades of at least 600 with the introduction of additives that accelerate the hardening of concrete. Studies have shown that the developed method provides reliable adhesion of the layer to be built up with old concrete, accelerated hardening of concrete and, in connection with this, a reduction in the term for closing traffic for the period of repair from 15-20 to 1-3 days. To repair coatings using this method, materials are used, the approximate consumption of which is given below.
Repair of concrete pavements with damage in the form of shells, potholes, chipped edges of the seams and corners of the slabs, edges of the slabs at the seams, peeling of the slabs is associated with building up a new layer over the old concrete. Thorough cleaning of the repaired surface is one of the most important operations, on which the adhesion strength of the old concrete to the new one largely depends, and, consequently, the quality of the repair as a whole.
The contaminated repaired surface of the slab is cleaned of dust, dirt and oil stains with mechanical steel brushes, then a 28% hydrochloric acid solution is poured at the rate of 0.5-0.6 kg/m2. After the reaction has ceased, the coating is thoroughly washed with a jet of water under pressure from a watering and washing machine until the acid remains are completely removed. Free water is removed by compressed air from the compressor in such a way that the surface of the plate being repaired is moist, but not wet.
If the surface of the slab being repaired is especially heavily contaminated, when it is impossible to clean the coating chemically, it is cleaned mechanically with a sandblaster or in some other way. In the presence of fragile concrete, it is removed with a pneumatic or power tool to a depth of undamaged concrete, but not less than 2 cm. The repaired area is thoroughly cleaned of concrete fragments and dust, and then washed with a jet of water under pressure. Then a cement adhesive prepared on site in a paddle mortar mixer is applied to the surface to be repaired. compulsory action. When preparing the adhesive, cement is loaded in a mortar mixer, water is added, the amount of which is determined by calculation (depending on the accepted water-cement factor), and thoroughly mixed. The prepared cement adhesive is distributed in an even layer over the surface to be repaired in two steps with hard hair brushes or paint brushes. The thickness of the cement adhesive should be within 1-2 mm. Cement adhesive at a temperature of more than 20 ° C should be used within 15-20 minutes after its preparation so that it is applied to the repaired surface before setting.
After the disappearance of the water film from the surface of the cement adhesive, approximately 10-15 minutes after applying it to the cleaned surface of the repaired coating, the cement concrete mixture is laid in such a way that after its compaction the surface of the repaired coating would be on the same level with the existing coating. For small volumes of work, the concrete mixture is compacted with a surface vibrator, vibrating platform or vibrating screed. Finally, the concrete is finished with a wooden trowel with a rubber band. To create a roughness, the surface of the repaired coating is finished with a stiff hair or metal brush perpendicular to the direction of movement. Care for freshly laid concrete in repaired areas is carried out by generally accepted methods.
When using fast-hardening cement and providing care for the repaired area using film-forming materials, traffic on the repaired area is opened after 1-2 days. When using Portland cement of a grade of at least 600 with an additive that accelerates the hardening of cement, as well as when using fast-hardening cements without film-forming materials, traffic on the repaired area is opened after 3 days.
To build up worn cement-concrete coatings in layers of 2-5 cm, a non-shrinking concrete mixture is used. This mixture adheres strongly to the surface of the coating, provides high abrasion resistance and increased frost resistance. The non-shrinking concrete mixture is made up of two types of cements - Portland cement grade 700 and expanding Portland cement grade 400-600. For 100 parts by weight of Portland cement grade 700, 25-100 parts of expanding Portland cement are taken.
Considering that fast-hardening cement is used as the main binder, it is advisable to prepare and deliver the cement mixture by mobile concrete mixers.
Portland cement M700 is subjected to additional grinding in the presence of triethylolamine and sulphite-yeast mash, which increases the resistance of concrete to abrasion and frost resistance. If Portland cement grade 700 was crushed without additives, then they are introduced into the concrete mixer during the preparation of the concrete mixture. The approximate consumption of materials per 1 m3 of concrete mixture is as follows:
On fig. 120 shows a graph of the increase in the strength of a non-shrinking cement-concrete mixture used in the repair of pavements on Leninsky Prospekt in Moscow.
Laying a new layer of concrete should be carried out on a carefully prepared surface of the coating. On the surface of the coating, the concrete mixture is laid out in such a way that, after compaction, the repaired surface is 1-2 cm higher than the existing coating. .
IN last years a method has been developed for repairing cement-concrete coatings using colloidal cement glue, which is prepared at the work site in a vibro-adhesive mixer-activator. The glue consists of Portland cement grade 600 - 70% and sand - 30%; water is added to obtain a water-cement ratio of 0.3. Mixing glue lasts 5-7 minutes.
The repair technology consists in applying glue with a layer of 2-3 cm with hard nylon brushes on a thoroughly cleaned surface of the coating. Then a layer of high-strength concrete is laid and evenly distributed over the adhesive. To prepare 1 m3 of concrete mix, 420 kg of Portland cement, 180 kg of ground quartz sand, 1600 kg of ordinary quartz sand; 180 liters of water and 1.8 liters of sulphite-yeast mash.
The concrete mixture is compacted with a vibrating platform in 2-3 passes along one track. The thickness of the concrete layer being built up can be in the range of 1.5-5 cm. The freshly laid mixture is covered with a layer of wet sand and kept for a day, after which the movement is opened.
Methods have also been developed for repairing cement-concrete pavements using polymer materials and in particular, epoxy resins. Repair of concrete pavements using epoxy resins, in comparison with the conventional method of repair, reduces the consumption of stone materials by 10-15 times; acceleration of the opening of traffic from 15 days to 6-8 hours; reliable adhesion of the layer to be built up with old concrete; high strength properties of the layer being built up and its chemical resistance.
For the repair of cement-concrete coatings, an epoxy adhesive of the following composition can be recommended:
In some cases, Portland cement can be added to the epoxy adhesive in an amount of 15-25%. Epoxy mixture, depending on the nature of the damage, is prepared from epoxy glue and mineral mixture in a ratio of 1:3 to 1:7. The granulometric composition of the mineral material used to prepare the epoxy mixture is selected according to the principle of the highest density. The approximate composition of the mineral mixture: 65-70% stone fines 1.25-5 mm in size and 30-35% pure quartz sand or stone fines 0.5-1.25 mm in size. For sealing shells, a mixture is used in a ratio of 1:5 or 1:6. To repair the edges of the seams and places where sealing is difficult, use the most greasy mixture in a ratio of 1:3 or 1:4.
During repair work, epoxy glue is prepared in small portions of 10-20 kg. To prepare the adhesive, dibutyl phthalate is poured into the epoxy resin and thoroughly mixed, after which polyethylene polyamine is introduced and thoroughly mixed again until a homogeneous mixture is obtained. The prepared epoxy adhesive can be used to prepare an epoxy mixture or for pouring over a repaired surface, followed by scattering of stone fines and compaction. The epoxy mixture, in order to avoid the loss of the viability of the adhesive, must be placed in the case no later than 1 hour after its preparation.
Cleaning of repaired areas is carried out chemically or mechanically with special care. Sinks and small potholes are primed with epoxy glue at the rate of 0.5 kg / m2 using hard hair brushes, filled with an epoxy mixture of 1: 5 composition, compacted with a rammer and smoothed with a trowel to the level with the surface of the coating. Traffic is opened 5-8 hours after the repair is completed.
Cement-concrete coatings subject to peeling are protected from further destruction by a protective and leveling layer 3-5 mm thick. For the device of a protective and leveling layer, epoxy glue is poured onto the cleaned and dry surface of the coating in a thin, even layer. The consumption rate of epoxy glue, depending on the condition of the repaired surface, is 1-1.5 kg/m2. Clean and dry stone fines of hard rocks with a particle size of 2.5-3.5 mm are scattered over the layer of epoxy glue at the rate of 5-5.5 kg per 1 kg of epoxy glue. Fine stone is rolled with rollers weighing 1-1.5 tons in 2-3 passes along one track 20-30 minutes after scattering. The movement is opened 5-7 hours after the end of the compaction.
The relatively high cost of epoxy resins is an obstacle to the widespread adoption of this repair method. However, in some cases, when individual slabs need to be repaired on roads with heavy traffic that cannot be closed for a long period, this repair method may be the most appropriate.
During the operation of hard pavements, as a result of deformation of the subgrade, subsidence of individual slabs can be observed. The coating can be repaired provided that it is not too cracked. It is possible to eliminate subsidence and level the slabs with jacks with simultaneous blowing of sand, as well as injection of plastic materials under the slabs. When using jacks, the slab is lifted simultaneously at several points, and sand is injected through pre-drilled holes. Since subsequently there is practically no soil precipitation under the slab, the slab is raised flush with the roadway and the holes are filled with concrete.
When repairing sagging concrete slabs with a mortar, it is injected under the sagging slab, due to which the slab rises to its original position. The mixture used here may consist of soil and water and one or more additives. As additives, cement is usually used. The solution introduced under the slab hardens and the bearing capacity of the base is restored.
It is advisable to fill the voids under the slabs with sand treated with organic binders. Under the influence of loads acting on the slab, the treated sand sticks together, forms a dense mass, and is not squeezed out from under the slabs. However, bitumen-treated sand tends to caking prematurely and form clods that make it difficult to pump.
In foreign practice, to fill voids under concrete slabs, a mixture of sand with a binder is used, consisting of bituminous powder and a solvent, which must be adsorbed on the surface of any solid material. A mixture of sand, organic material and a solid adsorbent with a solvent does not cake. Subsequently, the solvent in the pores of the adsorbent begins to interact with the bituminous powder and forms a binder that sticks together the sandy mass. Approximate composition of the mixture: 100 parts by weight of dry sand with fractions of 0-4 mm, 10 parts of tripoli, tar oil with a boiling point of 250 to 400 ° C in the amount of one third of the mass of tripoli and 2 parts of powdered coal sand with a softening point 90°. The mixture is mixed in a forced-action mixer and injected into the voids under the plates with compressed air.
In the practice of operation of cement-concrete pavements, there are cases when the pavement does not meet the strength requirements arising from the movement of vehicles with increased carrying capacity. In this case, the existing coating is reinforced by building up a layer of concrete. Laying a new layer of concrete is possible both directly on the existing coating, and on a separating layer of stabilized materials.
The thickness of the reinforcement layer can be determined by the formula
![]()
where h is the thickness of the reinforcement layer, cm; and k - coefficients taken when splicing layers; k1=1.05; k=1; when laying the top layer on the separating layer k1=1.2; k=1; hm - thickness of a monolithic concrete coating from the material of the upper layer, designed for a new load, cm; E1 and E - moduli of elasticity of concrete of the existing coating and reinforcement layer, kgf / cm2 (Pa); h1 is the thickness of the existing coating, see
When reinforcing cement-concrete coatings in the layer to be built up, it is necessary to provide pin connections in places of through expansion joints. All work on strengthening the coatings is carried out with a set of concrete-laying and finishing machines according to the technology used in the construction of coatings.
Repair of pavement pavements made of cement-concrete and reinforced concrete slabs consists in sealing damaged joints, eliminating subsidence of individual slabs and replacing worn or damaged slabs. Restoration of the joints between the slabs consists in cleaning them from dust and dirt, as well as the old aggregate and filling them with new materials (sand or cement mortar). The sagging slabs are lifted and shifted to the side, and the places of subsidence are covered with sand and carefully compacted. Slabs are laid on the compacted surface, upsetting them with wooden rammers (small slabs) or vibrators, and then the seams between the slabs are sealed.
Works on overhaul pavements of roads and sidewalks from prefabricated slabs, when it is necessary to replace slabs in large areas, they are carried out after dismantling the old pavement using the same technology that is carried out during new construction.
The roadbed in Russia and abroad is different: in our country, highways for various purposes they are made of asphalt, and in Europe and the USA they are mainly made of concrete. This is the obvious difference in their quality. In Russia, concrete roads have not become widespread due to their significant cost - after all, the country's vast expanses and updating the canvas will cost the population another increase in taxes. However, no one forbids homeowners to equip car parks and porches from durable concrete.
What are concrete roads for?
The construction of concrete roads is expedient in places where there is no possibility of frequent repairs and there is a need for a durable roadbed. In Russia it is:
- Autodromes;
- Runways and landings at airports;
- Parking of cars and other equipment;
- Pedestrian paths and sidewalks in cities;
- Coastal roads and embankments where high humidity and water exposure prevail.
The service life of a concrete slab exceeds the service life of asphalt up to 2-3 times. For this reason, it is advisable to replace asphalt concrete pavements that do not withstand climatic conditions with cement concrete everywhere, which is gradually happening in the United States.
The difference between asphalt and concrete
Why isn't asphalt pavement as durable as concrete pavement? It's all about the basic materials:
- Asphalt is a composite of sand, crushed stone, mineral fillers, and their binder is bituminous polymers.
- Concrete is a sand and gravel mixture mixed with cement and additives.
The main difference between concrete and asphalt is the binder in their formulations. Bitumen, unlike cement, does not form a durable stone, sags under weak soils under load, softens in the sun and winters poorly. Concrete, subject to the technology of preparation and installation, is devoid of these shortcomings.
The roadbed consists of several layers:

- The underlying is crushed stone that drains water from the soil, and sand that compensates for the loads coming from above and below the soil.
- Reinforcing - this layer of low-grade concrete that binds the bedding.
- The main roadbed is a layer of concrete.
When laying highways with heavy traffic of heavy vehicles, the road must be made of unstressed and stressed reinforced concrete, the reinforcing cage in which does not allow the stone to crack under the weight of heavy trucks.
In private construction, as well as in the organization of the roadbed on water-saturated soils or from their high level waterproofing for the roadway is laid on the sand and gravel embankment (roofing materials can be used). The layer prevents constant wetting of concrete and, as a result, corrosion of stone and reinforcing cage.
Canvas types
A concrete road is good for high-speed highways with heavy traffic, and for village driveways. For these cases, choose different types fabrics that differ in quality and cost:
- High quality, single-layer pavement for all types of roads, suitable for laying top and bottom layers;
- Concrete for the bottom layer of the canvas is cheap - it has low strength, its components are minimum requirements. A coating of such material can be used in the arrangement of adjacent territories with a small flow of cars;
- Medium performance concrete for heavy and advanced pavements. Can be laid on roads of settlement significance;
- In a separate group, you can make the organization of the road with ready-made concrete slabs.
Filling materials
M400 concrete is a universal material for laying roads. Its strength is sufficient to withstand the pressure of the wheels of cars and trucks on urban and rural roads.
The basis of concrete is Portland cement, resistant to water (1 part). Plasticizers are also introduced into the solution, which increase the hydrophobicity of the coating and its strength. The composition of the working solution also includes:
- Crushed stone - 5 parts;
- Sand - 2 parts.
For concreting the road, it is rational to order ready-made concrete from the factory - even for a small site, you will need a lot of mortar, which must be poured quickly, preventing individual batches from seizing.
Pavement pavement materials may vary in properties depending on the intended load and paving conditions.
Requirements for the quality of concrete roads
When choosing components for the preparation of road concrete, they are guided by SNiP 3.06.03-85 "Roads". The document regulates the requirements for the quality of the finished canvas:
- Resistance to mechanical stress is the main requirement for the road surface. For roads of different purposes, the indicator is determined individually.
- No cracks in the coating after laying and during operation. Compliance with the construction technology of concrete roads and the right composition of the working solution helps to solve the problem.
- Water resistance and chemical resistance. Highways are located in different conditions of relief and soil quality, and in the absence of an organized drainage system (in case of violation of construction technology), water accumulates on the canvas, worsening its quality.
concrete requirements
The quality of the canvas is determined by the constituent components, which must also undergo a thorough selection in accordance with the profile GOSTs. For example, the strength of crushed stone, which can ensure reliable and long-term operation of the road, is at least 1200 kg/cm 2 . For a pillow, less durable crushed stone of 800-1000 kg / cm 2 will do.
Mobility of concrete solution - 2 cm when testing with a cone. A large number of mineral inclusions of different fractions helps to avoid deviations from this parameter.
Another requirement for concrete is high bending strength; for this, plasticizers are introduced into the solution and the canvas is additionally reinforced with reinforcement.
Pros and cons of concrete roads
Compared with asphalt roads concrete has a number of advantages:
- High strength and rigidity of the coating;
- Resistance to heat, temperature changes;
- Long service life without the need for repair;
- Good grip of the road surface and automobile wheels increases traffic safety.
The disadvantages of the roads are fewer, but they are significant:
- High construction cost;
- The need for strict adherence to technology in the preparation of solutions and the selection of components;
- The need for a full set of concrete strength before the start of the road.
Concrete road construction
Let us consider in detail the stages of the construction of concrete roads, since the duration of the service life of the coating depends on the observance of the laying technology.
 Earthworks are among the most expensive and complex. Before they begin, a detailed project is drawn up based on a geological study of the relief. If possible, the laying plane of the road is made horizontal - the mounds are removed, a board with rock compaction is made into the recesses.
Earthworks are among the most expensive and complex. Before they begin, a detailed project is drawn up based on a geological study of the relief. If possible, the laying plane of the road is made horizontal - the mounds are removed, a board with rock compaction is made into the recesses.
The fertile layer of soil is removed: during the major construction of the highway completely, for private laying adjoining areas are enough 15-20 cm. The lower ones are compacted with rollers and vibration plates with a lot of weight. This is one of the most important stages - the rigidity and integrity of the coating under intense dynamic loads depends on the strength level of the base.
At the stage preparatory work with soil, a drainage system is thought out to divert ground and rain water. To do this, the base is not made in an ideal plane, but at a slight angle of 2-4%. Along the road, concrete gutters or natural slopes can be equipped, along which water flows into the receiver or into the ground.
Bedding laying
Crushed stone and sand are poured onto the compacted soil. They perform the function of load compensator and water drainage.
The thickness of the bedding layers depends on the type of relief and the properties of the bases and fluctuates around 20-40 cm. When laying long-distance roads between sand and gravel, geotestile is often laid - it does not allow fractions to mix and embankments perform their functions better.
On bases with a high level of groundwater, it is rational to thicken the rubble embankment - it does not wash out and drains water well. Sand must be laid under layers of concrete - it forms a dense cushion.
Both sandy and crushed stone layers must be compacted with a roller or vibrating pits to achieve high cushion strength.
For convenience, the litter layer is sometimes covered with a thin concrete screed up to 5 cm thick, and a waterproofing sheet is laid on top.
 Concrete is weak to bending loads, so the use of reinforcement is never superfluous - the choice of its type again depends on the characteristics of the base. In some cases, reinforcement may not be applied at all.
Concrete is weak to bending loads, so the use of reinforcement is never superfluous - the choice of its type again depends on the characteristics of the base. In some cases, reinforcement may not be applied at all.
The diameter of the reinforcement for the concrete canvas is taken only constructively according to the calculations. Usually these are bars from 10 mm welded into a mesh with a cell from 150 mm. Reinforcing products are laid in a concrete layer at a height of at least 4 cm from the bottom plane. It is important that the mesh is in the lower part of the slab, since it is in it that the breaking load is concentrated and cracks form.
The easiest way to make formwork is to use thick boards with a section of 50 × 150 mm (the choice of height depends on the design layer of the concrete base and coating). Also suitable for thick plywood. Boards and plywood are fixed with reinforcing pegs stuck into the ground from the outside of the canvas. When laying paths for pedestrians and parking lots for cars, the formwork can be replaced by a curb stone installed in preparation for pouring.
Concrete pavement
 The pouring of the road with concrete must be carried out continuously, so the materials for the canvas are prepared immediately in the right amount. It is advisable to order concrete from the factory; during the construction of large roads, temporary mobile workshops for the production of mortar are installed near the facilities, which reduces delivery costs.
The pouring of the road with concrete must be carried out continuously, so the materials for the canvas are prepared immediately in the right amount. It is advisable to order concrete from the factory; during the construction of large roads, temporary mobile workshops for the production of mortar are installed near the facilities, which reduces delivery costs.
If necessary, low-grade concrete (for example, M200) is laid on the base with backfill, then with M400 finishing mortar with additives.
The laying of the top coating takes place in 2 stages: first, a substrate of 30-40 mm is poured, a reinforcing mesh is laid on it and the rest of the thickness is poured.
The total thickness of the layer is about 12 cm, sometimes more or less.
Concrete is poured into preparation without interruption and the surface is immediately leveled. The material is constantly brought up, work is going on around the clock.
After laying, the concrete must be compacted by vibrocompression. The procedure expels air bubbles and compacts the structure of the finished coating.
Cutting and sealing expansion joints
The device of a concrete road includes cutting the canvas into segments. This is possible, then the concrete will gain sufficient strength of 50-60% and will withstand the weight of a person and cutting equipment.
The seams are needed to compensate for the thermal expansion to which the concrete stone is subjected to varying degrees. With seasonal changes in the volume of slabs, cracks do not form in the pavement.
Sawing is carried out with a special tool - jointing.
Temperature joints are made at a distance determined by calculations. One of the definition formulas is the coating thickness × 30.
To prevent water from penetrating the slab through the seams, they are filled with bitumen-polymer sealants.
Care and prevention of concrete pavement
So that the work is not wasted, according to the technology, the concrete road can be opened for traffic only after the concrete has fully gained strength, that is, after 28 days.
To prevent the destruction of the canvas, it is protected by polymer impregnations, which form a waterproof film on the surface. True, these reduce the roughness of the road and its adhesion to the wheels. This is a negative quality for high-speed highways, so in most cases the canvas is left as is. If soil preparation and laying technology have been observed, the seams are cut correctly, nothing threatens the integrity of the slabs for a long time.
Another way to prevent and repair concrete roads is to lay a wear layer. Asphalt is applied to the concrete, which ensures the adhesion of the wheels to the coating, and extends the life of the highway itself by several times. In addition, repair asphalt concrete pavement much cheaper.
When cracks appear, measures must be taken to eliminate them. To seal small violations, special putties are used, to repair deeper damage, a concrete mortar is used. In all cases, the crack is cleared and moistened before the introduction of aggregate.
If a fault occurs, you will have to remove the entire section of the canvas. The reason for such deformations is insufficient compaction of the soil base or embankment.
Asphalt is the main material used for road construction. After a few years, such a coating needs to be repaired, then its operational properties are restored annually. Concrete pavement is much better than asphalt pavement, but it is used to a limited extent. There are reasons for this, related to insufficient funding, low productivity, climatic conditions, insufficient amount of cement of the required grades, and relief areas. This technology is not particularly popular in Russia yet, since asphalt roads are much cheaper. However, we note that gradually the cost of these types of linen is slowly equalized. The construction of concrete roads, bridges, runways at airfields begins.
Advantages of concrete roads
Such coatings have certain advantages:
- the road made of concrete is of good strength, it does not need repair work. The coating can be used for at least four decades, and for asphalt this period is limited to a decade with annual repairs;
- automotive technology consumes less fuel. This is due to the fact that during the movement of a heavy vehicle, road concrete is not subjected to deformation, from which vehicle it is necessary to move a fifth of the fuel less;
- The coating is resistant to sudden changes in climatic conditions. It is not affected by heavy rains or sudden changes in temperature;
- there is a preservation of air purity, because cars need less fuel, the exhaust gases of which pollute the environment;
- natural resources are used sparingly. Limestone is used to make concrete, and oil is used to make asphalt.

Construction technology
The device of concrete roads includes certain stages:
- The ground base is being prepared. It is rolled to achieve the desired density, if necessary, moistened or dried.
- Water drainage is organized to extend the operational period of the canvas and give the ride safety.
- The underlayment is being installed. It is a sandy layer, the thickness of which is up to two to four tens of centimeters.
- The formwork structure is being assembled. Its elements are made of lumber, while taking into account the height of the fill.

If water seeps into the ground, the pavement is gradually destroyed.
The construction technology is complex, and each stage will be considered in detail.
Concrete road structure
The canvas includes certain layers:
- underlying - for its device, gravel is used, which drains groundwater, and sand, with which the resulting loads are compensated;
- reinforcing - represented by low-grade concrete that binds the bulk layer;
- the roadbed is a concrete surface.
The construction of a concrete road for heavy vehicles is made of stressed and non-stressed reinforced concrete, the reinforcing frame base in which does not allow the stone to crack from the weight of trucks.
In private types of construction work or when arranging a concrete pavement of roads on soils oversaturated with moisture, it is laid out on a sand cushion waterproofing material, which prevents severe wetting of the roadway, followed by corrosion of stones and reinforcement. As a waterproofing material, ordinary roofing material is used.
Execution of works
Let's take a closer look at what this or that is. construction stage road concreting.
Preparation
Earthworks are difficult, and they are quite expensive. Their beginning is preceded by the preparation of a detailed design solution, the conclusions of which are based on geological studies of the area. If there is such an opportunity, then the concreting of roads is carried out horizontally, removing small hills or laying compacted rock in the recesses.

If a major highway is being built, then the layer of fertile land is removed in full, and for the installation of a concrete road in the yard, it will be enough to remove from fifteen to twenty centimeters of soil.
The prepared base is compacted by rollers and vibration mechanisms, which are characterized by a large weight.
This stage is considered a crucial moment, since the stiffness index and the integrity of the road surface depend on the strength of the base, even when dynamic loads are quite intense.
At runtime earthworks the device is being thought out drainage system to be able to remove ground and rain moisture. For this purpose, the base is brought out in a plane, the inclined angle of which is from two to four degrees. Concrete gutters are installed on the sides of the road or slopes of a natural type are arranged, along the slopes of which water will enter the receiving wells or go into the ground.

Litter layer
A sand cushion is arranged, the thickness of which is twenty to forty centimeters. This element can be omitted, but it perfectly protects against moisture coming from the ground, improves the drainage process. The bedding layer is necessary to prevent erosion and heaving during frosts, which leads to the formation of depressions and cracks in the cast-in-place concrete.
Most problems appear on clay, peat and other areas of the terrain that can hold water. In most cases, such layers are partially removed, the bottom is covered with large stones and gravel. The rolled layer reaches a height of thirty centimeters. The costs and time required for construction will depend on such preparation.
The minimum thickness of the base depends on the type of soil and climatic conditions. Determine it according to a special table. If the layer is laid out from various materials, then a geotextile is spread between them.

Align the layers in accordance with the designed slopes. Stone backfills are strengthened with binders - cement, granulated slag from metallurgical production, to which quicklime is added, ash from thermal power plants, ground slag.
formwork
For the manufacture of this structure, boards are used, the height of which corresponds to the level of pouring concrete for the road. As a rule, it is equal to ten to fifteen centimeters. When determining its dimensions, it must be taken into account that ribs are arranged along the edges of the concrete to improve strength. The thickness of the boards should not be less than 5 cm. Each structural element should be covered with a special compound that will facilitate detachment from the hardened concrete.
Requirements are imposed on wooden formwork panels in terms of strength from expansion by their fresh concrete mass and the forces that arise as a result of tamping.
If heavy equipment is used for the construction of roads made of concrete, with which the concrete is compacted, then a formwork made of steel material should be installed. It will last much longer. At the heart of each element is a sole that improves stability.

Formwork sections are set in one line, firmly fixed. This is especially important if the vibrating of the concrete mass is carried out by heavy machinery. In places where the level of the base is reduced, lean concrete is poured under the formwork to improve stability.
Reinforcement
If technological process Since the construction of a concrete road involves this type of work, the reinforcement should be a metal mesh, the cell area in which reaches 150 mm. sq. This choice of material will make it possible to avoid expansion and the appearance of cracks in the concrete thickness.
Laying of the reinforcing mesh is carried out in the process of pouring the concrete mixture at a height of three to four centimeters from the lower level. Before this, the poured concrete is leveled, the frame mesh is covered, and, if necessary, fixed. Now you can continue to work.
fill
The litter layer is covered with a material that is resistant to getting wet, waterproofing, or simply moistened. Road concrete, corresponding to GOST, is laid out in thickness in one go. When reinforcement is applied, the process is carried out in stages.
Concrete for the road, the brand of which meets all the requirements, is applied quickly, since it does not have a long pot life. It is not recommended to add water to the mass, because the mechanical properties of the coating will deteriorate. Since construction volumes are large, factory-prepared road cement is delivered to the place of work. The mixture is unloaded in one cubic meter and leveled to give the entire layer the same density.
The best option for laying a concrete canvas is two or three layers.
The concrete mixture is compacted by special mechanisms, represented by wooden or metal beams, which are acted upon by pneumatic hammers mounted on them. Such a device descends into the mixture, begins to move in it. Having processed one section, the timber is moved further.
If reinforcement is used, then the vibration device should be located five to seven centimeters above the upper edge of the frame.

In a special machine, in addition to the vibration device, there is also a leveling device located in front.
The concrete composition must be flexible and sufficiently mobile, but not too liquid, so that it cannot float, flowing through the formwork panels. All this will negatively affect the strength of the coating.
Seam cutting
A prerequisite is the device of expansion joints. This type of work is possible when concrete reaches a certain level of strength, which is 50 - 60 percent. In this form, the canvas is able to withstand the weight of not only the worker, but also a special tool for cutting seams.
In this way, the thermal expansion to which concrete is subjected to varying degrees is compensated. Road segments at seasonal changes do not form cracks.
Sawing is performed by jointing - a special tool. The distances between the seams are determined by design calculations. As a rule, for this, the thickness of the monolithic coating is multiplied by thirty.

To prevent moisture from getting into such seams, they are filled with mastic.
Materials for constructing a concrete web
M400 - universal concrete composition. Its strength allows it to withstand loads from various wheeled vehicles. The basis is Portland cement, which is resistant to moisture. Plasticizers are also added to the solution to improve hydrophobicity and strength.
The concrete mixture consists of:
- cement - 1 part;
- gravel - 5 parts;
- sand - 2 parts.
The composition of concrete and its characteristics are specified in the construction project.

Slab covering device
Concrete slabs for the road are made as follows:
- Forms are being prepared right size, or shuttering boards are exposed.
- If necessary, a reinforcing cage is prepared to improve the strength of the plates.
- Pouring is carried out with ready-mixed concrete, it is advisable to immediately tamp to remove air bubbles.
- After some time, when the concrete hardens, you can remove the formwork and give the slabs time to gain the desired strength.
With the help of such material, you can make a concrete road with your own hands. Under all conditions, it will serve you well for a long time.
Conclusion
The concrete pavement of the road is durable, but needs some care. The resulting cracks must be immediately repaired so that they do not increase in size. To do this, use special putty compositions or concrete mortar. If a fracture has formed, the entire section of the concrete sheet should be removed.