Types and types of circuit breakers. Marking of circuit breakers What are electric machines
Installation of protective equipment is an important stage in the construction of electrical networks. In the event of the occurrence of large currents, heating occurs, causing the melting of the insulating layer of the conductor. This situation leads to a fire. A sharp increase in the magnitude of the current is associated with a short circuit that occurs during the operation of faulty equipment.
In order to avoid the risk of fire and damage to the wires, various types of electric machines are used depending on the parameters used in conjunction with them. electrical appliances.
Principle of operation and varieties
Principle of operation electrical switches consists in breaking the electrical circuit when a short circuit occurs. Or exceeding the permissible power for which the electrical network is designed. Electric circuit breakers are always located at the beginning of the protected section of the circuit. In this case, the type of connected load does not matter.
According to their form and parametric values, automata are divided into:
- by the number of poles;
- according to the time-current characteristic;
- by rated current.
 It is also necessary to note the current limiting class. This value is characterized by the speed of the device's response to an emergency situation. The division is into three classes. For domestic use third class is used.
It is also necessary to note the current limiting class. This value is characterized by the speed of the device's response to an emergency situation. The division is into three classes. For domestic use third class is used.
Regardless of their characteristics, the principle of operation for all switches is identical. To connect the machine to the electrical network, it is necessary to set the control switch to the "on" position. The current flowing to the switch is fed through the input terminal to the solenoid coil, and from it to the bimetallic plate. The plate is a strip of two pressed metals with different coefficients of thermal linear expansion. The current from the plate comes to the output terminal and then enters the electrical circuit. The plate and solenoid are called releases.
Current release - important element designs, it can be:
- electromagnetic (solenoid);
- thermal (bimetallic plate);
- combined (combination of thermal and electromagnetic);
- independent (remotely acting on the switch, it turns off).
 There are two conditions under which the electrical switch will trip to open the line: overload mode and short circuit mode.
There are two conditions under which the electrical switch will trip to open the line: overload mode and short circuit mode.
The principle of operation in overload mode is based on the ability of a bimetallic strip to bend under the influence of heat. With an increase in power to the line, the current flowing through the electric machine increases, exceeding the working value switch. As a result, the release heats up, its plate bends, and the contact breaks. Accordingly, the electrical circuit is broken. The current supply is stopped. The amount of current at which the plate breaks the contact is set at the factory with an adjustment screw. After the plate has cooled, it returns to its previous shape, and the contact appears again.
In the short circuit mode, the current increases very quickly, the magnetic field formed by it in the solenoid sets the core in motion. The core acts on the release, and the electrical circuit breaks, and an arc appears. The appearance of an arc negatively affects internal parts automatic machine, therefore, a device for extinguishing it is used. The arc chute is made of plates parallel to each other, passing through which the arc dissipates.
Thus, the main structural parts can be noted:
- current terminals;
- release:
- control lever;
- release adjusting screw;
- arc chamber.
Number of poles
 The number of poles indicates how many wires can be passed through the switch at the same time. There are devices with the number of outputs from one to four. The device of a single-pole switch is no different from a multi-pole one, only in the second case, when the passage of electric current several chains are broken at the same time.
The number of poles indicates how many wires can be passed through the switch at the same time. There are devices with the number of outputs from one to four. The device of a single-pole switch is no different from a multi-pole one, only in the second case, when the passage of electric current several chains are broken at the same time.
Single-pole devices are more often used in living conditions and are placed in the break of the phase wire, the zero is connected directly through the block, as an introductory machine, its use is not recommended. For installation at the entrance, two-pole circuit breakers are used, the phase and neutral wires are connected to them at the same time. For use in a three-phase network, a three-pole machine is already used as an input. To protect a four-phase electrical network, for example, a star-connected motor, a four-phase automatic machine is used. In this case, three phase and one neutral wire are connected.
The usual scheme for building protection on electrical switches comes down to installing an input automaton of the required number of poles. After it, single-pole ones are installed - one for each group. In this case, the value of the rated current of a single-pole machine is already calculated based on the parameters of the group to which it is connected. Its value is chosen less than the input value.
Time-current characteristic
 This parameter indicates the ratio of the actual current flowing through the machine to the nominal value. Depending on the value of the ratio, the sensitivity of the automaton is determined, which is characterized by the number of false positives. There are machines various kinds. They are marked with letters of the Latin alphabet. The most common switches are labeled B, C and D.
This parameter indicates the ratio of the actual current flowing through the machine to the nominal value. Depending on the value of the ratio, the sensitivity of the automaton is determined, which is characterized by the number of false positives. There are machines various kinds. They are marked with letters of the Latin alphabet. The most common switches are labeled B, C and D.
Electric machines with characteristic B are switched off within 5-20 seconds. In this case, the current value can exceed the nominal value by five times. These models are widely used in domestic premises. Marking C means switching off interval 1-10 seconds, while the load is ten times the value. Class D circuit breakers are used to protect engines. The operating current exceeds the nominal by 14−20 times.
Rated current
Indicates the amount of current that can pass through an electric machine without it tripping. Strictly defined values \u200b\u200bare produced from 1 to 63 amperes. There are 12 values in total: 1A, 2A, 3A, 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A.
The choice of rated current depends on the power value that the wiring can withstand without damage. This value is determined by the cross section of the wire and the material of its manufacture. In homes, the most popular machines for use are 6A, 10A and 16A. Automatic machines with a nominal value of 20A, 25A, 32A are used in apartments as introductory, i.e., two-pole.
Location and accommodation
 The method of placement (whether it is a single-phase electric machine or another type) is strictly vertical. The fixed part of the control lever must be on top, i.e. the device is switched on by switching from bottom to top. Devices are placed in accessible places, and the possibility of their mechanical damage is excluded.
The method of placement (whether it is a single-phase electric machine or another type) is strictly vertical. The fixed part of the control lever must be on top, i.e. the device is switched on by switching from bottom to top. Devices are placed in accessible places, and the possibility of their mechanical damage is excluded.
DIN rail mounting is the most popular. Usually such a rail is installed in the shield. Electrical switches structurally have special grooves into which the rail is inserted.
What are the machines, how are they marked - you need to know this information in order to choose the right device. Regardless of the manufacturer and type of electric machines, they are always marked on the front side. Marking is carried out according to a single scheme. It includes an indication of all the main parameters:

On the control lever, inscriptions are made indicating the set position - “on.” and "off" or "1" and "0".
Leading brands and manufacturers
Leaders in production circuit breakers are the following brands:

These are well-known brands that produce any kind of electric machines. They differ high quality housing, long service life and high mechanical strength. Often, protective covers are additionally installed on them. These manufacturers produce their devices from solid materials. Their quality is confirmed by certificates and a warranty period given by manufacturers for their products.
Topic: what types of electric machines are divided into, their types and classification.
The circuit breaker is an electrical device, the main purpose of which is to switch its operating state when a certain situation occurs. Electric automata combine two devices, this is a conventional switch and a magnetic (or thermal) release, the task of which is to timely break the electrical circuit in case the threshold value of the current strength is exceeded. Circuit breakers like everything else electrical devices, also have different varieties, which divides them into certain types. Let's get acquainted with the main classifications of circuit breakers.
1 "Classification of machines by the number of poles:
A) single-pole machines
b) single-pole machines with neutral
c) bipolar machines
d) three-pole machines
e) three-pole circuit breakers with neutral
e) four-pole machines
2» Classification of automata according to the type of releases.
The design of various types of circuit breakers usually includes 2 main types of releases (openers) - electromagnetic and thermal. Magnetic circuit breakers are used for electrical protection against short circuits, and thermal circuit breakers are mainly designed to protect electrical circuits for a certain overload current.
3 "Classification of automata by tripping current: B, C, D, (A, K, Z)
GOST R 50345-99, according to the instantaneous tripping current, the automata are divided into the following types:
A) type "B" - over 3 In to 5 In inclusive (In is the rated current)
b) type "C" - over 5 In to 10 In inclusive
C) type "D" - over 10 In to 20 In inclusive
Machine manufacturers in Europe have a slightly different classification. For example, they have an additional type "A" (over 2 In to 3 In). Some manufacturers of circuit breakers also have additional tripping curves (ABB has circuit breakers with K and Z curves).
4 "Classification of automata according to the type of current in the circuit: constant, variable, both.
Rated electric currents for the main circuits of the release are selected from: 6.3; 10; 16; 20; 25; 32; 40; 63; 100; 160; 250; 400; 630; 1000; 1600; 2500; 4000; 6300 A. Also, automatic machines for the rated currents of the main electrical circuits of automatic machines are also produced: 1500; 3000; 3200 A.
5 "Classification by the presence of current limitation:
a) current limiting
b) non-limiting
6 "Classification of machines by types of releases:
A) with overcurrent release
b) with independent release
c) with minimum or zero voltage release
7 "Classification of machines according to the time delay characteristic:
A) no time delay
b) with a time delay independent of the current
c) with a time delay inversely dependent on current
d) with a combination of these characteristics
8" Classification by the presence of free contacts: with contacts and without contacts.
9 "Classification of machines according to the method of connecting external wires:
A) with rear connection
b) with front connection
c) with combined connection
d) with universal connection (both front and rear).
10" Classification by type of drive: with manual, with motor and with spring.

P.S. Everything has its varieties. After all, if there were only one thing in its single copy, it would be at least just boring and too limited! The diversity is good because you can choose exactly what best suits your needs.
This article continues a series of publications on electrical protection apparatus- circuit breakers, RCDs, difautomats, in which we will analyze in detail the purpose, design and principle of their operation, as well as consider their main characteristics and analyze in detail the calculation and selection of electrical protection devices. Will complete this series of articles step by step algorithm, in which briefly, schematically and in a logical sequence, the complete algorithm for calculating and selecting circuit breakers and RCDs will be considered.
In order not to miss the release of new materials on this topic, subscribe to the newsletter, the subscription form at the bottom of this article.
Well, in this article we will understand what a circuit breaker is, what it is intended for, how it works and consider how it works.
Circuit breaker(or usually just “automatic”) is a contact switching device that is designed to turn on and off (i.e. for switching) an electrical circuit, protect cables, wires and consumers (electrical appliances) from overload currents and from short circuit currents.
Those. The circuit breaker performs three main functions:
1) circuit switching (allows you to turn on and off a specific section of the electrical circuit);
2) provides protection against overload currents by turning off the protected circuit when a current exceeding the allowable current flows in it (for example, when a powerful device or devices are connected to the line);
3) disconnects the protected circuit from the supply network when large short-circuit currents occur in it.
Thus, the automata simultaneously perform the functions protection and features management.
According to the design, three main types of circuit breakers are produced:
— air circuit breakers (used in industry in circuits with high currents of thousands of amperes);
— molded case circuit breakers (designed for a wide range of operating currents from 16 to 1000 Amperes);
— modular circuit breakers , the most known to us, to which we are accustomed. They are widely used in everyday life, in our houses and apartments.
They are called modular because their width is standardized and, depending on the number of poles, is a multiple of 17.5 mm, this issue will be discussed in more detail in a separate article.
We, on the pages of the site, will consider exactly modular circuit breakers and residual current devices.
The device and principle of operation of the circuit breaker.
The thermal release does not operate immediately, but after some time, allowing the overload current to return to its normal value. If during this time the current does not decrease, the thermal release trips, protecting the consumer circuit from overheating, melting of the insulation and possible ignition of the wiring.
An overload can be caused by connecting powerful devices to the line that exceed the rated power of the protected circuit. For example, when a very powerful heater or electric stove with an oven is connected to the line (with a power exceeding the rated power of the line), or several powerful consumers at the same time (electric stove, air conditioner, washing machine, boiler, electric kettle, etc.), or a large number of simultaneously switched on devices.
Short circuit the current in the circuit instantly increases, the magnetic field induced in the coil according to the law of electromagnetic induction moves the solenoid core, which activates the release mechanism and opens the power contacts of the circuit breaker (i.e. moving and fixed contacts). The line opens, allowing you to remove power from the emergency circuit and protect the machine itself, the wiring and the shorted electrical appliance from fire and destruction.
The electromagnetic release trips almost instantly (about 0.02 s), unlike the thermal one, but at much higher current values (from 3 or more rated current values), so the wiring does not have time to heat up to the melting temperature of the insulation.
When the contacts of the circuit are opened, when it passes through electricity, an electric arc occurs, and the greater the current in the circuit, the more powerful the arc. The electric arc causes erosion and destruction of the contacts. To protect the contacts of the circuit breaker from its destructive action, the arc that occurs at the moment of opening the contacts is directed to arc chute (consisting of parallel plates), where it is crushed, damped, cooled and disappears. When the arc burns, gases are formed, they are discharged outward from the body of the machine through a special hole.
The machine is not recommended for use as conventional switch circuit, especially if it is turned off when a powerful load is connected (i.e., at high currents in the circuit), since this will accelerate the destruction and erosion of the contacts.
So let's recap:
- the circuit breaker allows you to switch the circuit (by moving the control lever up - the machine is connected to the circuit; moving the lever down - the machine disconnects the supply line from the load circuit);
- has a built-in thermal release that protects the load line from overload currents, it is inertial and works after a while;
- has a built-in electromagnetic release that protects the load line from high short-circuit currents and works almost instantly;
- contains an arc quenching chamber, which protects the power contacts from the damaging effects of an electromagnetic arc.
We have analyzed the design, purpose and principle of operation.
In the next article, we will look at the main characteristics of the circuit breaker that you need to know when choosing it.
See The design and principle of operation of the circuit breaker in video format:
Useful articles
The development of power grid security tools has become relevant since their inception. Various overloads led not only to cable damage, but also to fires.
To date, the most popular devices of this type are circuit breakers.
They help prevent events such as fires, damage to electrical wiring. Since they are automatic, the operation occurs without human intervention. Choosing the right switch will help protect the room from accidents.
Design and principle of operation
Understanding the circuit breaker's automatic tripping mechanism will help you select the right model. Structurally, the machine includes the following key elements:
- terminals;
- toggle switch;
- electromagnetic release;
- bimetallic plate.
 Depending on the type of overload, one of two mechanisms is triggered.
Depending on the type of overload, one of two mechanisms is triggered.
When an overload of the circuit occurs with a current that exceeds the nominal value by several times, the bimetallic plate is triggered. It heats up within a few seconds, resulting in its thermal expansion. When a certain size is reached, its significant bending is carried out and the chain opens. The setting of the plate parameters is carried out by the manufacturer. For switches used in everyday life, the operating time takes 5–20 s. They are usually marked with the letters: B, C, D.
The short circuit mode (SC) is characterized by an avalanche-like increase in current, which exceeds not only the nominal value, but also its maximum permissible loads. There is no time left to heat the plate during the jump, otherwise the wiring may melt. In such a situation, an electromagnetic release is triggered. The magnetic field drives the core, which opens the circuit. Instant operation allows you to protect the premises from the consequences of a short circuit.
Classification
Electric machines differ in the following key characteristics:
- number of poles;
- time current characteristic;
- operating current;
- breaking capacity.
Number of poles
 This characteristic corresponds to the number of electrical wiring lines that can be directly connected to the machine. All output wires will be disconnected at the same time when the machine is triggered.
This characteristic corresponds to the number of electrical wiring lines that can be directly connected to the machine. All output wires will be disconnected at the same time when the machine is triggered.
Single pole machine. This is the simplest type of circuit protection device. Only 2 wires are connected to it: one goes to the load, the second is power. It mounts on a standard 18mm din rail. The power wire is fed from above, and the load to the bottom terminal. It can work in single, two or three phase power lines. In addition to the power and load wires, it has a neutral and ground, which are connected to the corresponding busbars. Such machines are not installed at the input, since the circuit will open only along the phase line. The zero wiring remains closed and, in case of failures, potential may remain on it.
A two-pole machine, its difference from a single-pole one. This type of circuit breakers allows you to completely de-energize the electrical wiring of the room. It allows you to synchronize the moment of turning off two of its output lines. The latter leads to more high level safety during electrical work. It can be used as a separate toggle switch for appliances such as a water heater or a washing machine. The connection is made using 4 cables: a pair at the input and output.
A simple question is logical: is it possible to connect two single-pole machines instead of one two-pole one? Of course no. After all, when the shutdown is automatically triggered, all output lines are turned off at the two-terminal network. For a pair of independent automata, overload may not occur on one of the lines and the de-energization will be partial. In ordinary apartments, you can connect a phase and neutral line to this machine. When opened, a complete deenergization of the entire group of devices that are powered from it will occur.
 Three and four-pole machines. All three or four phase conductors are connected to the poles of the corresponding circuit breaker. They are used when connected by a star, when the phase wires are protected from overloads, and the middle wire remains switched all the time, or by a triangle, when there is no middle central cable, and the phase wires are protected.
Three and four-pole machines. All three or four phase conductors are connected to the poles of the corresponding circuit breaker. They are used when connected by a star, when the phase wires are protected from overloads, and the middle wire remains switched all the time, or by a triangle, when there is no middle central cable, and the phase wires are protected.
If an overload occurs on one of the lines, a shutdown occurs immediately on all the others. 6 (three-phase machine) or 8 wires are connected to these machines. 3-4 at the output and the same number of lines at the output. They are mounted on din rails with a length of 54 (three-phase machine) and 72 mm, respectively. They are used most often in industrial installations, when connecting powerful electric motors.
Time current parameter
The nature of food consumption various devices varies even when power values match. Uneven dynamics of consumption during correct operation, a surge in load during turn-on - all these phenomena lead to significant changes in such a parameter as current consumption. Power dissipation can lead to false tripping of the circuit breaker.
To exclude such situations, dynamic operation parameters are introduced, called time-current characteristics of circuit breakers. Automata according to this parameter are divided into several types. Each group has its own response time. The front panel of the switch is marked with the corresponding letter from the list: A, B, C, D, K, Z.

Rated current
The differences of automata depending on the nominal values of the current are divided into several groups (12 current levels). It is directly related to the response time when the power consumption is exceeded. The operating value can be determined purely theoretically by adding up the sums of the currents consumed by each of the devices separately. In this case, a small margin should be taken. Also, do not forget about the possibilities of electrical wiring.
Machines are designed primarily to prevent damage to it. Depending on the metal of the wires and their cross section, the maximum load is calculated. The ratings of the circuit breakers for current allow such a separation.

Breaking capacity
This parameter depends on the maximum current in the event of a short circuit, provided that the machine performs a network shutdown. According to the magnitude of the short-circuit current, all automata are divided into three groups.
- The first includes devices with a nominal value of 4.5 kA. They are used in private houses intended for human habitation. The current limit is approximately 5 kA. This is due to the fact that the resistance of the system of conductive cables leading to the house from the substation is 0.05 ohms.
- The second group has rated 6 kA. This level is already used in residential apartment buildings And in public places. The current limit can reach 5.5 kA (wiring resistance 0.04 Ohm). In this case, models of types are used: B, C, D.
- In industrial plants the nominal value is 10 kA. The limit value of the current that can occur in the circuit near the substation has the same value.
How to choose the right machine
 Until recently, porcelain fuses with fusible elements were widely used. They were well suited for the same type of load of Soviet apartments. Now number household appliances became much larger, as a result of which the probability of getting a fire with old fuses increased. To prevent this, it is necessary to carefully approach the choice of a machine with the correct characteristics. Excess power reserves should be avoided. The final choice is made after a few simple steps.
Until recently, porcelain fuses with fusible elements were widely used. They were well suited for the same type of load of Soviet apartments. Now number household appliances became much larger, as a result of which the probability of getting a fire with old fuses increased. To prevent this, it is necessary to carefully approach the choice of a machine with the correct characteristics. Excess power reserves should be avoided. The final choice is made after a few simple steps.
Determining the number of poles
When determining this switch parameter, one should be guided by simple rule. If you plan to secure sections of the circuit with devices that have low power consumption (for example, lighting devices), then it is better to leave your choice on a single-pole machine (usually class B or C). If you plan to connect a complex household device with significant power consumption (washing machine, refrigerator), then you should install a two-pole machine (class C, D). If the equipment is small production shop or a garage with multi-phase propulsion systems, then a three-pole option (class D) is worth choosing.
Power consumption calculation
As a rule, by the time it is planned to connect the machine, the wiring to the room has already been connected. Based on the cross section of the cores and the type of metal (copper or aluminum), you can determine the maximum power. For example, for a copper core of 2.5 mm 2, this value is 4–4.5 kW. But the wiring is often summed up with a large margin. Yes, and the calculation should be done before the start of all installation work.
 In this case, you will need a value about what the total power will be used by all devices. It is always possible to turn them on at the same time. So, in an ordinary kitchen, the following appliances are often used:
In this case, you will need a value about what the total power will be used by all devices. It is always possible to turn them on at the same time. So, in an ordinary kitchen, the following appliances are often used:
- fridge- 500 W;
- Electric kettle- 1700 W;
- microwave– 1800 W
The total load is 4 kW and a 25 A machine is enough for it. But there are always consumers who turn on sporadically and can create factors that contribute to the operation of the switch. Such devices can be a combine or a mixer. Therefore, you should take the machine with a margin of 500-1200 watts.
Rated current calculation
Since the power in single-phase networks is equal to the product of voltage and current, it is easy to determine the current as a quotient of power and voltage. For the above example, this value is easy to calculate, knowing that the mains voltage is 220 V. The current consumption is 18.8 A. With a margin of 500-1200 V, it will be 20.4-23.6 A.
In order for the work not to stop even with such short-term excesses of the load, the rated current for the machine can be taken equal to 25 A. Approximately the same value corresponds to the rating, based on a copper cable with a cross section of 2.5 mm 2, which is enough with a margin for such loads. A machine with a rated current of 25 A will work before it starts to heat up.
Determination of the current characteristic time
 This parameter is determined by a special table that lists the starting currents and their flow time. For example, for a household refrigerator, the starting current ratio is 5. With a power of 500 W, the operating current is 2.2 A. The starting current will be 2.2 * 7 \u003d 15.4 A. Data on the frequency is also taken from a special table.
This parameter is determined by a special table that lists the starting currents and their flow time. For example, for a household refrigerator, the starting current ratio is 5. With a power of 500 W, the operating current is 2.2 A. The starting current will be 2.2 * 7 \u003d 15.4 A. Data on the frequency is also taken from a special table.
Table No. 1. Starting currents and pulse durations for household appliances
For the selected device, this characteristic does not exceed 3 s. The choice becomes obvious: for such a consumer, it is necessary to take a type B circuit breaker. It is permissible to make a choice of the machine according to the load power. You can skip the last step by opting for a class B switch. For domestic needs, the characteristics of class B and C electrical switches are most often sufficient.
What is a circuit breaker?
Circuit breaker(automatic) is a switching device designed to protect the electrical network from overcurrents, i.e. against short circuits and overloads.
The definition of "switching" means that this device can turn on and off electrical circuits, in other words, switch them.
Circuit breakers come with an electromagnetic release that protects the electrical circuit from short circuits and a combined release - when, in addition to the electromagnetic release, a thermal release is used to protect the circuit from overload.
Note: In accordance with the requirements of the PUE, household electrical networks must be protected from both short circuits and overload, therefore, to protect home electrical wiring, machines with a combined release should be used.
Circuit breakers are divided into single-pole (used in single-phase networks), two-pole (used in single-phase and two-phase networks) and three-pole (used in three-phase networks), there are also four-pole circuit breakers (can be used in three-phase networks with a TN-S grounding system).
The device and principle of operation of the circuit breaker.
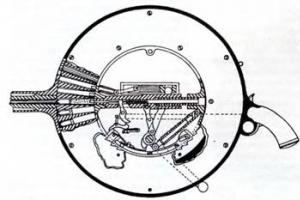
The figure below shows circuit breaker device with combined release, i.e. having both electromagnetic and thermal release.

1.2 - respectively, the lower and upper screw terminals for connecting the wire
3 - moving contact; 4 - arc chute; 5 - flexible conductor (used to connect the moving parts of the circuit breaker); 6 - electromagnetic release coil; 7 - the core of the electromagnetic release; 8 - thermal release (bimetallic plate); 9 - release mechanism; 10 - control handle; 11 - latch (for mounting the machine on a DIN rail).
The blue arrows in the figure show the direction of current flow through the circuit breaker.
The main elements of the circuit breaker are electromagnetic and thermal releases:
Electromagnetic release provides protection of the electrical circuit against short circuit currents. It is a coil (6) with a core (7) located in its center, which is mounted on a special spring, the current in normal operation passing through the coil according to the law of electromagnetic induction creates an electromagnetic field that attracts the core inside the coil, however, the forces of this electromagnetic field not enough to overcome the resistance of the spring on which the core is installed.
In the event of a short circuit, the current in the electrical circuit instantly increases to a value several times greater than the rated current of the circuit breaker, this short circuit current passing through the coil of the electromagnetic release increases the electromagnetic field acting on the core to such a value that its pulling force is enough to overcome the resistance springs, moving inside the coil, the core opens the movable contact of the circuit breaker, de-energizing the circuit:

In the event of a short circuit (i.e., with an instantaneous increase in current by several times), the electromagnetic release switches off the electrical circuit in a fraction of a second.
Thermal release provides protection of the electrical circuit against overload currents. An overload can occur when electrical equipment is connected to the network with a total power exceeding the allowable load of this network, which in turn can lead to overheating of the wires, destruction of the insulation of the electrical wiring and its failure.
The thermal release is a bimetallic plate (8). Bimetallic plate - this plate is soldered from two plates of different metals (metal "A" and metal "B" in the figure below) having different coefficient expansion when heated.

When a current exceeding the rated current of the circuit breaker passes through the bimetallic plate, the plate begins to heat up, while the metal "B" has a higher coefficient of expansion when heated, i.e. when heated, it expands faster than metal "A", which leads to the curvature of the bimetallic plate, bending it acts on the release mechanism (9), which opens the moving contact (3).

The operating time of the thermal release depends on the magnitude of the excess current of the power supply network of the rated current of the machine, the greater this excess, the faster the release will operate.
As a rule, the thermal release trips at currents 1.13-1.45 times the rated current of the circuit breaker, while at a current 1.45 times the rated current, the thermal release will turn off the machine after 45 minutes - 1 hour.
The operating time of circuit breakers is determined by their
With any disconnection of the circuit breaker under load, an electric arc is formed on the moving contact (3), which has a destructive effect on the contact itself, and the higher the disconnected current, the more powerful the electric arc and the greater its destructive air. action. To minimize the damage from the electric arc in the circuit breaker, it is directed to the arc chute (4), which consists of separate, parallel plates, falling between these plates, the electric arc is crushed and damped.
3. Marking and characteristics of automatic switches.

BA47-29— type and series of circuit breaker
Rated current- the maximum current of the electrical network at which the circuit breaker is able to operate for a long time without emergency shutdown of the circuit.
Standard values of rated currents of circuit breakers: 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 8; 10; 13; 16; 20; 25; 32; 35; 40; 50; 63; 80; 100; 125; 160; 250; 400; 630; 1000; 1600; 2500; 4000; 6300, Amp.
Rated voltage — maximum voltage network for which the circuit breaker is designed.
PCS- ultimate breaking capacity of the circuit breaker. This figure shows the maximum short circuit current that is able to turn off this circuit breaker while maintaining its performance.
In our case, the PKS is indicated as 4500 A (Amps), which means that with a short circuit current (short circuit) less than or equal to 4500 A, the circuit breaker is able to open the electrical circuit and remain in good condition, if the short circuit current exceeds this figure, it becomes possible to melt the moving contacts of the machine and weld them to each other.
Tripping characteristic- determines the operating range of the electromagnetic release of the circuit breaker.
For example, in our case, an automatic machine with a characteristic “C” is presented, its response range is from 5 I n to 10 I n inclusive. (I n - rated current of the machine), i.e. from 5 * 32 \u003d 160A to 10 * 32 + 320, this means that our machine will provide instant circuit shutdown already at currents of 160 - 320 A.

Note:
- The standard response characteristics (provided by GOST R 50345-2010) are characteristics "B", "C" and "D";
- The scope is indicated in the table according to established practice, however, it may be different depending on the individual parameters of specific electrical networks.
4. Circuit breaker selection
Note: Read the full methodology for calculating and selecting circuit breakers in the article: "