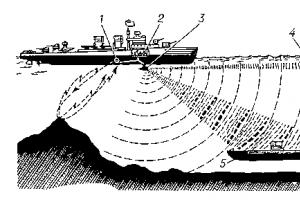
The field exists in reality and the lines of force are conditional. Electric field strength. Power lines. What is called electric current
However, in the words of the great Russian scientist Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, "science begins as soon as they begin to measure." Experiments must be planned, the results of the measurements obtained must be processed, interpreted, and then scientifically substantiated not only the purity and reliability of the research methods used, but also the reliability of measurement processing methods. In this case, it becomes necessary to use numerical methods, mathematical statistics, etc. The author, who is well acquainted with the theoretical substantiation of hypotheses, the practical setting of experiments and the numerical processing of their results, knows in practice how ungrateful this task is. Any person who is at least a little familiar with the theory of mathematical processing of measurement results or has personal experience in experimental research has great opportunity question the purity of the experiment, the processing algorithms used, the size of the statistical sample, and as a result, doubt the result as a whole.
However, there is also another side of the coin. It lies in the fact that a professionally set experiment allows you to significantly advance in understanding the phenomenon under study, to confirm or refute the hypotheses put forward, to obtain reliable and repeatable knowledge about the object of research. That is why a group of researchers led by the author for several years carried out scientific research on the properties of such a completely unscientific phenomenon as seids discovered by us.
2. How to do scientific research on seids
2.1. Essence of scientific method
In order to carry out scientific research, and not some others, we first understand what the scientific method is in general. The essence of the scientific method was quite clearly formulated by Isaac Newton in his works "Optics" and "Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy", and has not changed over the past three centuries.
The scientific method includes the study of phenomena, the systematization and correction of the acquired knowledge. Inferences and conclusions are made using the rules and principles of reasoning based on empirical (observed) and measurable data about the object of study. To explain the observed phenomena put forward hypotheses and are being built theory, on the basis of which conclusions, assumptions and forecasts are formulated. The resulting predictions are tested by experiments or by collecting new facts, and then corrected based on newly received data. Thus, the development of scientific ideas about the world takes place.
According to the scientific method, the source of data is observations and experiments. For execution scientific research first you need to choose object and subject research, property or set of studied properties, to accumulate empirical and experimental data. Then formulate one or more scientific hypotheses, perform their experimental verification, process the experimental materials, formulate the conclusions obtained, and thereby confirm, refute or correct the hypotheses put forward. After confirmation and adjustment, the hypothesis put forward becomes reliable knowledge, after refutation becomes false knowledge (delusion) and discarded.
2.2. How they write about seids
The scientific method includes methods for obtaining new knowledge about any phenomenon, incl. and about megaliths. However, in most publications about the seids of the Russian North, there is no serious reasoned confirmation of the hypotheses put forward about the properties and purpose of the seids. This applies to both official scientific and popular publications. Experimental verification is usually replaced by fairly general arguments about the unusual properties of seids. There is no clear description and systematization of the studied properties. The list of observed and studied properties can vary significantly from one region or complex to another. There is no quantitative assessment of the studied properties.
Modern methods of studying megaliths are reduced mainly to identifying artifacts, i.e. objects that do not fit into the concept of the traditional history of the development of our civilization, an emotional literary description of their unusualness, as well as a description of various kinds of myths, legends and legends, which, according to the authors of publications, have at least some relation to seids. These legends wander from one author to another without any attempt to verify and confirm them. At the same time, it is not substantiated whether the peoples from whom these legends were recorded are related to the creation of seids, or simply accidentally live in the same territory. Naturally, for different authors such "sacred knowledge" is completely different and often opposite to each other.
Professional studies of seids are not carried out by official science. The level of argumentation, even in refereed scientific publications, often leaves much to be desired. In order not to be unfounded, I will give only a few quotes from the article. " ... Statements by amateurs and journalists about the "cult" buildings on the city of Vottovaara are colored by preconceived, usually unfounded ideas about the origin and functions of these objects, although deliberate hoaxes are also possible in order to strike the imagination of gullible readers. You can't and shouldn't trust them...». « ... The intellectual drunkenness of the authors of such information is striking ...». «… We are dealing with obviously biased explanations and conjectures hidden in them, mixed with a considerable amount of fantasy.».
I remind you that this is the argumentation of a "scientific" article published in the official collection of KarRC RAS. For some reason, the authors forget to clearly state on the basis of what scientific methods of studying seids such conclusions were made. They also forget to bring the results of experimental testing of their hypotheses. But after reading this article, one gets the feeling that the next publication about the really existing, confirmed and measured properties of seids will be called heresy and the Holy Inquisition will be summoned to the author's house. And if such argumentation of "scientists" has passed scientific review and was published in the official collection of the Russian Academy of Sciences, then what can we expect from "unscientific" researchers?!
But it is precisely the lack of professional research that does not allow us to formulate sound conclusions about the real properties and purpose of megaliths. The scientific vacuum formed at the suggestion of the “scientists” of the Russian Academy of Sciences is filled with very unconvincing definitions of seids as some kind of “sacred” or “cult” complexes, the exact purpose of which defies human logic and can only be explained by the “mythological consciousness” of their primitive creators.
One of Faraday's most important achievements was his new interpretation of how force is transferred from one body to another. Instead of acting at a distance, he imagined lines of force penetrating space. In the 1830s and 1840s, Faraday continued to develop his idea of magnetic and electrical lines of force. But since this new idea did not have a mathematical form, most scientists rejected it. However, there were two important exceptions - William Thomson and James Clerk Maxwell.
Thomson gave Faraday's lines of force a mathematical interpretation and showed that the concept of lines of force was consistent with heat theory and mechanics; thus the mathematical foundation of field theory was laid. Faraday recognized the importance of being supported by these "two very talented gentlemen and eminent mathematicians"; he said: "It is a source of great pleasure and encouragement for me to feel that they confirm the justice and universality of the presentation I have proposed."
For Faraday, the idea of lines of force flowed naturally from his experiments with magnets. When he dropped needle-shaped iron filings on a sheet of paper resting on a piece of magnet, he noticed that the filings lined up in lines that went in a certain direction, depending on their position relative to the magnet.

He thought that the magnetic poles were connected by magnetic lines and that these lines were made visible by iron filings that were aligned parallel to the lines. For Faraday, these lines were real, albeit invisible. Faraday extended his idea of lines of force to electric forces; he believed that gravity could be interpreted in a similar way. Instead of saying that the planet somehow knows how it should orbit around the sun, Faraday introduced the concept of a gravitational field that controls the planet in orbit. The sun generates a field around itself, and the planets and others celestial bodies feel the influence of the field and behave accordingly. In the same way, charged bodies generate electric fields around them, and other charged bodies sense this field and react to it. There are also magnetic fields associated with magnets.
Newton believed that the main objects are particles interconnected by forces; and the space between them is empty. Faraday imagined both particles and fields interacting with each other; And this is quite a modern point of view. It cannot be said that particles are more real than fields. We usually depict fields as lines indicating the direction of the force at each point in space.
The denser the lines, the greater the force. Let's take the gravity of the Sun as an example. We can say that, coming from all possible directions, all lines of force end in the Sun. We can draw spheres of different radii centered on the Sun, with each line of force intersecting each sphere. The area of the spheres increases as the square of their radius, so the line density decreases inversely with the square of the distances.
Thus the idea of lines of force leads us directly to Newton's law of gravity (and also to Coulomb's inverse square law for an electric field of constant charge;  When using the idea of a force field (such as a gravitational field), there are a few simple rules to follow.
When using the idea of a force field (such as a gravitational field), there are a few simple rules to follow.
1. Gravitational acceleration occurs along the force field passing through the body.
2. The magnitude of the acceleration is proportional to the line density at a given point.
3. Lines of force can only end where there is mass. The number of lines ending at a given point is proportional to the mass of that point.
Now it is easy to prove the statement, on which Newton had to work hard. Comparing accelerations on the surface of the Earth and in the orbit of the Moon, Newton assumed that the Earth acts on all bodies as if all of its mass is concentrated in its center. Why?
Assume for simplicity that the Earth is perfectly round and symmetrical. Then all parts of its surface will be equally covered by incoming lines of force. According to the third) 'rule, the number of lines of force depends on the mass of the Earth. If all the mass were concentrated in the center of the planet, all these lines would continue to the center. Thus, the gravitational field of the Earth
does not depend on how the mass is distributed under its surface if there is spherical symmetry. In particular, all the mass of the Earth, concentrated in its center, creates exactly the same gravity as the real Earth.
Exactly the same reasoning applies to the electric field. But since there are two types of electric charge, positive and negative, when the sign of the charge changes, the direction of the lines of force changes to the opposite. The lines of force start at a positive charge and end at a negative one.
Topic 1.1 Characteristics and parameters of the electric field
Introduction to the discipline (the main content of the discipline, the dignity and role of electrical energy, sources of electrical energy, the use of electrical energy, the electrification of the national economy, its significance, the Leninist GOELRO plan, the formation and initial development of electrical engineering).
The concept of the electric field. The main characteristics of the electric field: strength, potential and electrical voltage. Coulomb's law.
Guidelines for the study of the topic 1.1
In the introduction, it is necessary to have an idea about the subject "Electrical Engineering and Electronics" and its place in the national economy, about the importance of electrical engineering in the development of modern industry. Literature: pp. 5-6. And also to have an idea about the electric field, its main characteristics. Know Coulomb's law. References: chapter 1, pp. 8-28.
Questions for self-examination
1. What sources of energy do you know, renewable and non-renewable?
2. What types of energy are converted into electrical energy by the electrical receivers that you have at home?
3. What measures are being taken and which can be applied in your home to save energy?
4. Are there any advantages of transmitting electrical energy on a direct current compared to its transmission on an alternating current?
5. What are the areas of application of DC electrical devices?
6. The figure shows a model of a hydrogen atom. In what region of space does electric field:
a) in the area
b) in area C?
7. Which of the following statements do you think is correct?
a) the field and lines of force really exist;
b) the field exists in reality, and the lines of force are conditional;
c) the field and lines of force exist conditionally.
8. What is the potential of the electric field?
a) vector; b) scalar.
Topic 1.2 Properties of conductors, semiconductors and electrical insulating materials
Conductors and dielectrics in an electric field. Electro insulating materials and their properties. electrical capacity. Capacitors. Capacitor connections. Varnishes and insulating materials for electrical work.
Guidelines for the study of the topic 1.2
Have an understanding of conductors and dielectrics in an electric field, electrical insulating materials and their properties. What is a capacitor. Unit of measure for electrical capacitance. How can capacitors be connected? What varnishes and insulating materials are used for electrical work.
Questions for self-examination
1. When parallel connection three capacitors connected to the power source, one of them (C 3) turned out to be broken. How will the voltage across the capacitors change and what will be their total capacitance?
a) U = const; C total \u003d C 1 + C 2;
b) U = 0; C total = ¥.
2. Three capacitors connected to the power supply are connected in series. How will the voltage be distributed across the capacitors?
a) U 1 > U 2 > U 3;
b) U 3 > U 2 > U 1;
c) there is not enough data to answer the question.
3.Three capacitors can be connected in series, parallel, and mixed connection. How many connection circuits can be built from three capacitors of the same capacitance C and which one has the smallest equivalent capacitance?
Section 2. MAGNETIC FIELD
Topic 2.1 Characteristics and parameters of the magnetic field
General information about the magnetic field. Basic properties and characteristics of the magnetic field. Force action of a magnetic field. Law of Ampère, Lenz. Inductance.
Guidelines for the study of the topic 2.1
Have an understanding of the magnetic field, its properties and characteristics. What is the force exerted by a magnetic field. Know the law of Ampere, Lenz, the concept of inductance and its units of measurement.
Questions for self-examination
1. What field arises around moving electric charges?
a) magnetic;
b) electrical;
c) electromagnetic.
a) B = 200 Wb;
b) B \u003d 0.25 × 10 -3 Wb.
3. What characteristic of the magnetic field corresponds to the dimension of a henry per meter (G/m)?
4. What is the magnitude of the magnetic flux Ф?
a) vector;
b) scalar.
5. What is the value of the magnetic voltage U m?
a) vector;
Electric field potential. equipotential surfaces.
Conductors and dielectrics in an electric field.
Electrical capacity. Units of electrical capacity. Flat
Capacitor.
Electric field. Coulomb's law.
Electric field strength.
field lines.
According to modern scientific concepts, matter exists in two forms: in the form of matter and in the form of a field. There are not so many fields in nature. There are only these fields:
A) gravitational
B) electrical
B) magnetic
D) nuclear
E) field of weak interactions.
And there are no more fields in nature and cannot be.
All information about other types of fields (biological, torsion, etc.) is false, although the supporters of these fields are trying to bring some kind of “scientific” theory under these concepts of non-existent fields, but as soon as the principle of the presumption of provability is used, then these pseudoscientific theories suffer complete crash. This should be taken into account by all medical specialists, since supporters of pseudoscientific theories brazenly speculate with the concepts of non-existent fields: they sell all sorts of useless devices for big money, which allegedly cure all diseases by the method of “correction of the biofield or torsion field”. All sorts of "torsion field generators", "charged" amulets and other completely useless items are on sale. And only a solid knowledge of physics and other natural sciences will make it possible to cut the ground from under the feet of those who profit from the deception of the population.
In this lecture, we will consider one of the real fields − electric field.
As you know, the field does not affect our senses, does not produce sensations, but nevertheless, it really exists and can be detected by appropriate instruments.
In what way does it manifest itself?
Also in ancient greece it was found that amber, worn with wool, began to attract various small objects to itself: specks, straws, dry leaves. If you rub a plastic comb on clean and dry hair, then it will begin to attract hair. Why was the hair not attracted before rubbing against the comb, but after rubbing it began to be attracted? Yes, after friction, a charge appeared on the comb after friction. And they named him electric charge. But why was there no such charge before friction? Where did he come from after friction? Yes, the field exists around all bodies that have an electric charge. Through this field, the interaction between objects removed at some distance is transmitted.
Further research showed that electrically charged bodies can not only attract, but also repel. From this it was concluded that there are two types of electric charges. They were tentatively named positive (+) And negative (-). But these designations are purely arbitrary. With the same success they could be called, say, black and white, or top and bottom, etc.
Like charges repel, and unlike charges attract. The unit of electric charge in international system SI units is pendant (Cl). This unit is named after the French scientist C. Coulomb. This scientist experimentally deduced the law that bears his name:
F = k( q1q2)
F- force of attraction or repulsion between charges
q1 And q2 - charges
R- distance between charges
k- coefficient of proportionality, equal to 9*10 9 Nm 2 / Kl 2
Is there a smallest charge? It turns out that yes, there is. There is such an elementary particle, the charge of which is the smallest and less than which does not exist in nature. In any case, according to modern data. This particle is electron. This particle is located in the atom, but not in its center, but moves in orbit around the atomic nucleus. The electron has negative charge and its magnitude is q \u003d e \u003d -1.6 * 10 -19 Cl. This value is called elementary electric charge.
We now know what an electric field is. Now consider the question: in what units should it be measured so that this unit is objective?
It turns out that the electric field has two characteristics. One of them is called tension.
To understand this unit, let's take a charge of +1 C and put it in one of the points of the field and measure the force with which the field acts on this charge. And the value of this charge will be the field strength.
But, in principle, it is not necessary to take a charge of 1 C. You can take an arbitrary charge, but in this case, the intensity will need to be calculated using the formula:
Here E is the strength of the electric field. Dimension - N/Cl.
Why not “caloric” or “phlogiston” of past centuries (http://gravitus.ucoz.ru/news/ehlektricheskij_zarjad/2014-09-06-30)?
Just think: "electronic liquid", "electronic gas", "electronic cloud" ...
How can electrons flow from body to body, creating an electrifying effect?
It is a well-known fact that electric current flows through a conductor at the speed of light. This has been repeatedly proven by experiments. In the process of electrization of bodies, as in the process of electric current, the field interaction between atoms is leading. Since the atom is a two-component vortex, the force lines of the family of hyperbolas are closed at the speed of light. Conductors differ from dielectrics in that a single circuit of the form is formed on the entire conductive section: 
In a dielectric, a single circuit is not formed, since it is periodically interrupted by interactions of the form: 
According to the postulates of N. Bohr, an atom must somehow react to the detachment of an electron and generate an electromagnetic perturbation quantum. Have the results of the observed experiments with electrification been published anywhere? No. Electrification is not accompanied by such an effect. Moreover, the electrification of matter occurs at the speed of light. There is no process inertia. In addition, if the charge is carried by electrons at the speed of light, then at the opposite point from the place where the charge enters, an anomaly should occur due to the colliding electron beams. Something like the point of convergence of colliding beams of like-charged particles (electrons), which is implemented in accelerators. With all the effects that accompany this process. However, no such effects have ever been observed. Consequently, there is no "electronic fluid" flowing from body to body (and even at the speed of light!), does not exist.
As follows from the electromagnetic theory of gravity, the visibility of charges is formed by variants of the closure of the vortex lines of force. This explains even the Volta series: any body, when it touches any of the bodies further in this row, is electrified positively, and when it touches any of the bodies preceding it, it is electrified negatively. That is, one vortex in relation to others can be both a "spray gun" and a "vacuum cleaner". As in astronomy: the Earth in relation to the Sun is a "vacuum cleaner", and in relation to the Moon - a "pulverizer". The potential difference is the difference between a "spray gun" and a "vacuum cleaner". The vortices are reoriented: 

For example, the Sun is an obvious "pulverizer": in its bowels there is an actively working thermonuclear furnace.
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune (giant planets with a low density of matter) have fusion furnaces operating in a smoldering mode. They clearly lack something to move into the category of stars. Can they be classified as "vacuum cleaners"? I think yes. Isn't that how atoms work?
It follows from the electromagnetic theory of gravity (EMTG) that an EM vortex has two components: electric (family of hyperbolas) and magnetic (family of ellipses). Its instantaneous two-component "cut" in the plane can be represented in the figure:

Consider the electrical component of the vortex: 
And let's pay attention to the direction of the arrows that characterize the movement of the field-ether along the channels-lines of force.
And now - the most interesting: let's consider how the direction of the arrows on the lines of force changes when the picture is rotated in the XY plane.
Rotate the drawing 90 degrees:

As you can see, the direction of the arrows has changed to the opposite.
Let's rotate the drawing 180 degrees: 
The direction of the arrows is the same as the original.
Accordingly, when the pattern is rotated 270 degrees

the direction of the arrows will be the same as when the pattern is rotated 90 degrees.
And now I want to remind you that the families of hyperbolas and ellipses are related. As the electrical component rotates, the magnetic component also rotates.
As you can see from the picture:
Rotating a family of ellipses by 360 degrees does not have symmetry, as is the case with a family of hyperbolas. Therefore, the overall pattern with two components is also not symmetrical when it is rotated through 360 degrees.
And now we rotate both families around the Y axis by 360 degrees.
It is obvious that the family of ellipses is symmetrical under such a rotation and the direction of the arrows will not change.
For a family of hyperbolas, when rotated by 180 degrees, the direction of the arrows changes to the opposite. BUT! As it is easy to see from the drawings for the electrical component, in contrast to the three-dimensional spatial symmetry of the family of ellipses, the three-dimensional spatial symmetry of the family of hyperbolas is NOT POSSIBLE. The family of hyperbolas is two-dimensional. Only in the process of a certain dynamics is its three-dimensional functioning realized. But this already applies to the essence of EMTG.
Sunday, November 02, 2014 3:55 pm ()When creating the electromagnetic theory of gravity, it was found that there are no electric charges in nature. All EM field generators can be conditionally divided into "pulverizers" and "vacuum cleaners". For example, the interaction of a "pulverizer" with a "vacuum cleaner" is similar to the effect of attraction of two opposite charges, two "pulverizers" create a repulsive effect, and two "vacuum cleaners" create a neutrality effect. Let's take a short excursion into history and see how the concept of electric charge was formed in physics.
The first serious scientific work in the field of electricity was carried out by Benjamin Franklin (1706 - 1790).
In 1746-54. he carried out a number of experimental studies that brought him wide fame. Franklin explained the action of the Leyden jar, built the first flat capacitor, consisting of two parallel metal plates separated by a glass layer, invented a lightning rod in 1750, proved in 1753 the electrical nature of lightning (experiment with kite) and the identity of terrestrial and atmospheric electricity. In 1750, he developed a theory of electrical phenomena - the so-called "unitary theory", according to which electricity is a special thin fluid that permeates all bodies. Each uncharged body, according to Franklin, always contains a certain amount of "electric fluid". If for some reason an excess of it appears in the body, then the body is charged positively, when it is lacking - negatively.
Here we see that Franklin approaches the phenomenon of electricity from a macroscopic point of view, i.e. empirically and by "electric fluid" up to sign one should understand simply electrons. This name arose for the reason that the amount of this “mysterious liquid” in the bodies could be smoothly changed: reduced or added.
In this Franklin theory, the concept of positive and negative electricity was first introduced. Based on his theory, he explained the phenomena he observed. Franklin's unitary theory contained the law of conservation of "electric fluid" or electric charge in the modern sense.
These were the first macroscopic, experimental ideas about electric fields. Subsequently, these macroscopic representations were transferred to microparticles. By analogy with macroscopic bodies, physicists began to imagine microparticles only as charged with some “electric fluid”, which until recently remained a mystery.
Thus, we see that historically the concept of "electric charge" was introduced at a time when the carriers of electrical phenomena - electrons, positrons and other elementary particles were not yet known. At the same time, the charge was perceived macroscopically as some continuous substance like a liquid, which can be added or removed on the surface of dielectrics, i.e. how to “charge” or “discharge” the surface of glass, amber, etc. Analogues of the concept of "electric charge" can be called "caloric" or "phlogiston", which were in use at a time when physicists had a very vague idea of thermal phenomena in substances. This also includes the most common moisture, which can also be applied to the surface. solids.
Since electrical and magnetic phenomena have not been fully understood until recently, even now the concept of “electric charge” is perceived macroscopically, i.e. Physicists “charge” even elementary particles with this “liquid”. Searching for a charge on an electron, a positron, or inside a proton and a neutron is just as ridiculous a task as searching for moisture inside a H2O water molecule.
It is enough to recall the history of caloric in the Middle Ages to understand how absurd this is. After all, when we talk about electromagnetic phenomena, we are not really talking about some kind of charges, but about force interactions between particles that are carried out through an intermediary. In this case, any conventions are removed, and we directly pass to the real mechanisms of interactions. It remains only with a logical sequence to analyze the various possible options similar interactions.
http://forum.etherdynamic.ru/showthread....-
Consider two EM vortices with two types of field lines.

It follows from the electromagnetic theory of gravity that the field line of the EM field is a channel for the movement of the ether-field (http://gravitus.ucoz.ru/news/silovye_linii_ehm_polja/2014-08-27-27). Just as there are channels in the Benard vortex:

Consider the electrical components (families of hyperbolas) of two synchronously functioning vortices:
Let's designate the source of the channels-field lines with the sign "+", and the drain - with the sign "-"

and connect "+" with "-"

It turns out that the lines of force of the family of hyperbolas close with each other and begin to contract into an ellipse, which creates an attraction effect:

Now let's look at how the repulsion effect works.
Consider two vortices operating in antiphase:

Let's see how their sources and sinks are located:

Channels-power lines will be connected according to the following scheme:

In this case, when the families of hyperbolas are closed, a conjugation point will appear, dividing the channels-field lines into two independent closed channels, through which the field-ether circulates in opposite directions. Two ellipses with specific dimensions and other parameters will begin to form, which will lead to repulsion:

As a result, two closed electrical components having a junction point turn into two independent magnetic components.
In general, the Earth is like an electrical circuit with a source, a load, an inductor and a capacitor. That is - an oscillatory circuit, or a generator of a high-frequency alternating EM field. It is impossible to single out something important: all elements are constituent parts one common circuit. The result of this electrical circuit is an EM vortex. All natural field generators have a similar structure: an atom, a star, a galaxy, etc. There are no black holes in nature. There is no nucleon packing in the nucleus of an atom. No charges. The structure of the micro-world is similar to the structure of the macro-world. Quantum mechanics works both in the micro-world and in the macro-world. Occam's razor should cut off all unnecessary entities.
So what is a "vacuum cleaner" and a "spray gun"?
The modern explanation of the essence of electric charges is no different from the ancient explanations of thousands of years. The electrification of bodies was undoubtedly known to the ancient man, who observed the attraction of dust particles with a piece of amber: 
And this one ancient man said that an invisible liquid is poured from body to body, responsible for this effect. The modern explanation of electrization has been concretized: they say that these are electrons, like an ancient magic liquid, flowing from one body to another. The body that has donated some of its electrons will be positively charged, and the body that has acquired them will be negatively charged. And then there is BUT! The rest mass of an electron is 1837.14 times less than the mass of a hydrogen atom. Let us assume that the mass of an electron in an average atom is 10^(-4) of the mass of the atom. IN solar system this corresponds (roughly) to the mass of the planet Uranus. Let's mentally pull Uranus out of the SS with great speed. Will the Sun react to this? According to the postulates of N. Bohr, the atom must also respond to the detachment of an electron and generate an electromagnetic perturbation quantum. Have the results of the observed experiments been published anywhere? No. Electrification is not accompanied by such an effect. Moreover, the electrification of matter occurs at the speed of light (example? the same capacitor). There is no process inertia. And this means that electrification has a field nature. There is no "electronic fluid" flowing from body to body. The vortices are reoriented: 

But in the first picture, the field-ether moves along the lines of force in one direction, and in the second - in the opposite direction. Let us recall the Volta series: any body, when it touches any of the bodies further in this row, is electrified positively, and when it touches any of the bodies preceding it, it is electrified negatively. That is, one vortex in relation to others can be both a "spray gun" and a "vacuum cleaner". The Earth in relation to the Sun is a "vacuum cleaner", and in relation to the Moon - a "pulverizer". The potential difference is the difference between a "spray gun" and a "vacuum cleaner". However, we have come to the next question: what is the potential difference?
| Tags: |