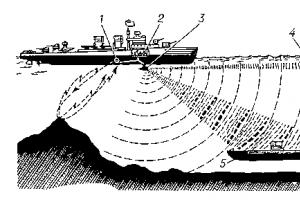
Acupressure is an ambulance for the body. How to do acupressure (acupressure) Acupressure scheme and description of points
On the human body there are points responsible for the organs that are biologically active, through which the vascular plexuses pass. The body temperature there is much higher than in other places.
And if you influence these points with the help of massage, you can easily stimulate the production of special elements that normalize, maintain and improve health, and also participate in the self-healing of the body.
Acupressure is considered an ancient method of treatment. Thanks to him, there is an effect on biological points on the human body, responsible for the organs, as well as the internal systems of the body. In addition, the method helps to improve vitality or reduce nervous and muscle tension.
The advantages of acupressure are as follows:
- No pain is felt. Therefore, the method can be easily used by people with a sensitive threshold.
- Human organs are restored.
- There are no complications, the skin is not broken, the possibility of infection is excluded.
- The first changes can be felt after the first session.
Contraindications
Acupressure is considered a simple method of restoring strength and health, activating internal systems to fight disease. To perform the massage, only the thumb and forefinger of the hand are required.
You need to click on special points to stimulate the defenses of the human body in order to promote the treatment of the disease from the inside. It is safe, but there are contraindications that must be observed so as not to harm your own body.
You should not use the method when:
- pregnancy;
- organic heart disease;
- skin and fungal diseases;
- severe fatigue.
Before using the method, it is necessary to consult a doctor and clarify whether massage will adversely affect health in each case.
Rules for influencing active points
Having learned how to massage biologically active points on the human body, which are responsible for all organs, everyone will be able to carry out treatment aimed at:
- calming the nervous system
- relieve fatigue and pain,
- slow aging,
- weight loss relief,
These points are scattered throughout the body, which are determined by pressing the finger pad on the desired area and the occurrence of pain.

Rules for influencing human biological points:
- Sit or lie on your back.
- Take a break from external stimuli and try to be in silence.
- Put the index finger on the biological point.
- It is easy to press on the skin while performing circular movements with your finger. At the same time, you cannot leave this point.
- The period of impact on the point is different and ranges from a couple of seconds to several minutes.
- The number of pressures during one session: 3 - 6 times.
The main massage techniques
Massage is a complex of techniques that affect the human body, which are performed one after another without stopping.
As a rule, the execution technique is used, which is divided into 5 main techniques:
- trituration,
- kneading,
- squeezing,
- vibration,
- stroking,
And it is done with:
- palms,
- thumbs,
- fists,
- pads of the second and third fingers,
- ulnar edges of the hand.
Stroking – massage technique, which consists in gently sliding the hands over the skin, without shifting it and pressing in different ways.
Divided into:
- planar,
- embracing,
- cruciform,
- rake,
- comb-shaped,
- pincer-shaped.
Rubbing works better than stroking because the hand shifts and shifts the skin in all directions, preparing the patient's muscles so that they are not subject to spasms as well as pain.

As a rule, it is performed:
- circular,
- zigzag,
- spirally
- longitudinally
- transversely.
Kneading is considered a difficult technique, but also the most important, as it takes up most of the execution of all manipulations and performed in the form:
- squeezing,
- push ups,
- squeezing,
- shifting,
- capture,
- grinding,
- lifting,
- felting,
- inflation,
- pinching,
- pressing,
- stretching.
Squeezing – a technique that acts on the skin of the body, on the upper layer of muscles, connective tissues and subcutaneous tissue.
Conducted:
- the base or edge of the palm,
- pads of four fingers or one thumb, slowly moving forward.
Vibration – a technique that is desirable to use when the body is already warmed up by rubbing, moreover, gently and gently:
- palms,
- fist,
- phalanges of the fingers.
Dividing on the:
- Intermittent vibration: hacking, puncturing, flogging, patting, tapping.
- Continuous vibration: chipping, pushing, shaking, planing.
Massage begins and ends with stroking, so that the muscles relax a little. And do not forget that this technique is carried out after each manipulation. The main thing is not to massage the lymph nodes.
The location of points on the human body for the treatment of the digestive system
In order to improve and normalize digestion, as well as remove toxins, it is necessary to press on the biologically necessary points on the human body that are responsible for this organ, located on the bend of the elbow, on the outside of the forearm. To do this, hold the elbow with one hand, and with the pad of the thumb, gently, with little effort, press on this point.
For colic and constipation
To relieve an attack of pain associated with colic or constipation, you need to apply a soothing acupressure, which includes four points:
- On the abdomen on both sides of the navel, at a distance of four fingers, which must be pressed synchronously and only with the index fingers.
- On the big toe, in the corner of the nail, which is turned towards the other fingers.
- On the outside of the leg, four fingers below the knee and slightly down and then forward from the head of the fibula.
- On inside legs, below the knee on the palm, in the corner of the tibia.
For diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
Every second person suffers from diarrhea. The reason for this is malnutrition, overwork, and even stress. Of course, you can take a pill, however, it is better to use acupressure, which can protect the body from chemical interference.

The point of influence is located at a distance of the width of three fingers on the side of the navel. You need to put your palm on your stomach and press hard with your fingers for a couple of minutes. It is advisable to close your eyes and try to breathe as deeply as possible.
Nausea is easily relieved when the left hand lies on the inside of the right, the little finger touches the edge of the hand, and the index finger is directed to the biological point, which should be gently pressed. This massage can also be done on the other hand. There is a similar point on the hands.
To do this, put the thumb of the left hand between the right index finger and thumb and massage. Then switch to the other hand. A point located on the inner wrist, between two tendons, three fingers wide from the base of the palm, will help get rid of vomiting.
Atlas of points on the human body for the treatment of vision
The attractiveness of each depends on the expressiveness of the eyes. To keep them clear, as well as eliminate pain, you need to use the biological points located on the head, arms and legs. Which need to be pressed gently.
Pressing on:
- The point, which is located on the border of hair growth in the frontal corners, can be used to treat vision, relieve headaches or dizziness.
- A point near the nose near the inner corner of the eyes can easily increase visual acuity, get rid of swelling and redness of the eyes, help with pain in the eyes, and also get rid of photophobia.
- The point located in the deepening of the inner edge of the eyebrows, where they converge, is used to treat any eye diseases. It also helps with hemorrhoids, headaches, nasal congestion, even during a depressive state.
- The point, on the outer side of the hand, when connecting the thumb and forefinger, you can quickly cure sore eyes, as well as get rid of toothache. And also a runny nose, swelling in the neck and sore throat.
When applying massage for the eyes, you must first of all listen to yourself, to your own feelings and immediately stop in case of overwork.

Massage has 4 effects:
- massaging the eyes with the palms,
- light stroking,
- vibrating movements,
- gentle kneading movements.
Before starting, you need to warm up your palms, rub them and immediately touch the inner surface of the eyes. The main thing is not to be cold.
Whatever technique is used, everything must be barely perceptible so that no harm can be done.
Location of points for the treatment of respiratory organs.
Knowing the location of biological points that help in the treatment of respiratory organs, you can easily cure a runny nose, cough, bronchitis and other diseases. As a rule, they are located on the head, neck, chest, arms and legs of any person.
- This point can be found between the ends of the eyebrows, which is often used for colds, as well as other respiratory organs. It also relieves headaches, hiccups and nosebleeds.
- Above the upper edge of the collarbone is a point that has a beneficial effect on the lungs, normalizes the condition of the trachea and throat.
- There is also a point under the nipple in the hypochondrium, thanks to which you can cure a cold, as well as relieve pain in the back of the head and pectoral muscles.
With a cold
You can also cure a runny nose with acupressure and preferably at the first symptoms. And it only takes a couple of minutes.
The main thing is to choose the right points and execution technique that are directly related to the nose:
- hollows near the wings of the nose,
- under the nostrils
- nose tip,
- intersection of the middle of the eyebrow line and the bridge of the nose,
- earlobes,
- near the auricle.
- from the back side of the wrist,
- on top,
- at the beginning of the neck from the back.

The main thing is to take into account the moments in which massage cannot be used:
- body temperature above 37 degrees,
- the necessary biological point coincides with the mole,
- pregnancy,
- heart disease,
- there are skin irritations.
Acupressure is performed by tapping. Bend the thumbs and gently tap the wings of the nose with the bones, as well as the bridge of the nose. Perform 30 seconds - at first, three not too strong blows on each side in turn, then one blow at a time.
Massage points only warm hands, press slowly, constantly, and in a circular motion. A runny nose will immediately pass, but we must not forget that this procedure helps if traditional methods of treatment are used at the same time.
In addition, it is desirable to use as a prophylactic agent when an exacerbation of viral diseases begins.
When coughing
As soon as a cough appears, you need to immediately consult a doctor. Well, acupressure will be a wonderful addition to this.
Before starting a cough massage, you need to find biological points, which are most often located:
- ahead, on the edge chest, at the base of the neck,
- on four fingers of the hand, except for the thumb. On the side of the palm, close to the fold, between the first and second phalanges of the fingers.
- on the side of the thumb, on the inner crook of the wrist,
- on the back of the hand, at the intersection of lines that continue the index and thumb.
The massage is done until the skin turns red and there is slight pain. When strong, the pressure is loosened and performed softer, but much more often. And preferably daily: once in the morning and twice in the evening, 5 minutes. And at the same time rotational movements clockwise.
For bronchitis and pneumonia
Thanks to massage for bronchitis and pneumonia, the patient quickly recovers. It is only required to know the healing points that really bring salvation.

They are mainly located:
- on the shoulder blades. In a recess under the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra.
- on hands. Starting from the center of the thumb pad, retreat down 3 mm.
- on the throat. Where the collarbones meet.
- on the foot. Between the second and third toes. And also in the recess on the fold between the foot and lower leg. Press strongly: 3 - 5 times, with rotational or reciprocating movements of the fingers or palms without displacement, counterclockwise for a couple of minutes. And do not carry out if the body temperature exceeds 37 degrees.
With inflammation of the lungs, acupressure is also used: light touch, stroking and deep pressure with fingertips. At the same time strictly vertically and without displacement. And daily for 10 minutes. The patient does not have to feel pain or discomfort.
The most famous are the points located on the back of the hand, at the crossroads between the index and thumb, in the center of the deepening of the jugular cavity, in the lower part of the neck.
Finish the massage, preferably kneading the end phalanges of the thumbs on the hands.
The main thing is that all this is prohibited for patients with:
- cancer and stage III hypertension.
- blood disease,
- tuberculosis
- acute febrile condition
- ulcer of the stomach or duodenum.
For asthma
With asthma, acupressure is not just a general tonic, but a wonderful prophylactic. Moreover, it complements medical treatment wonderfully.
The purpose of such a massage is to restore breathing, since the airways are too narrow and do not allow air to pass into the body normally, as a result, suffocation begins. In addition, it strengthens the immune system and muscles, improves blood circulation. It is advisable to do every day.
The methodology consists of:
- stroking,
- kneading,
- trituration,
- vibration,
- pressure,
- pushing,
- cutting,
- stabbing.
The required points are located:
- between the spine and shoulder blades, one finger below from the side of the upper edge of the shoulders,
- between the sternum and clavicle
- on the outside of the chest, three fingers down from the side of the collarbone,
- on the palm, near the thumb,
- on the crook of the wrist under the base of the thumb.
To relieve coughing, as well as reduce suffocation during an attack, it is required to press on the right and left sides of the body, between the shoulder blades, and on the back of the neck on each side and the thoracic vertebrae.

Put the patient on his back, do not use a pillow. It is required to press with the thumb on the point of the front surface, and with the other four on three points, on the back of the neck, and do it all at the same time.
It is required to put a pillow under the head and use the hands to perform circular movements, gently pressing on the chest several times, then press vertically down to facilitate exhalation and then press on the stomach.
With shortness of breath
As a rule, shortness of breath is a violation of human breathing, when it is impossible to breathe. Then a special acupressure comes to the rescue, you just need to know which points you want to use.
This point, located under the thyroid gland in the region of the collarbone, is good for shortness of breath. It takes one to two minutes to press on it. Massage is performed in your free time, but preferably daily.
In the center of the crown, where the median line of the head and the line connecting the tips of the ears intersect, there is a point with which it is easy to get rid of this disease.
It is also worth pressing the tip of the little finger at the outer edge of the nail, until it hurts, holding it with the thumb and forefinger. At the same time, pressing quickly and intermittently every day in the morning, lying in bed or when an attack occurs.
When quitting smoking
When, when quitting smoking, sometimes you still want to take a cigarette, then you should use the help of three points, thanks to which you can easily get rid of tobacco addiction. In addition, such a massage can be easily done on your own, without resorting to financial expenses or someone else's help. Do only three times during the day, 5 minutes.
- Under the thyroid gland, where the clavicle is connected, there is a point that needs to be acted upon briefly, but intensively, at least 15 times. Great for helping with shortness of breath and quitting smoking.
- There is also a point located in the deepest part of the auricle, which helps to remove dependence on a cigarette, and in order to find it, you need to feel for the external auditory opening with your index finger, then move it 1 cm towards the back of the head and start pressing. As a result, there is an aversion to tobacco smoke.
- A point located behind the line of the wrist joint, on the continuation of the axis of the little finger, also helps from tobacco addiction. At first, a light touch, and then a gradual increase in intensity.
Atlas of points on the human body for the treatment of the genitourinary system
Sometimes a person is concerned about the genitourinary system and in order to cure everything, it is necessary to use biological points on the body, thanks to which you can easily cope with this disease.

As a rule, they are on the face, back, chest, abdomen and legs, which must be gently pressed.
- In the middle of the chin-labial sulcus there is a point that helps in the treatment of the genitourinary system. It also relieves headaches, muscle tension in the back of the neck, pain in the lower jaw.
- Under the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebra there is a point used in the treatment of urinary incontinence, as well as other diseases of the genitourinary system. Also eliminates diarrhea, reduces headache, chills and fever.
- At the level of the navel, 0.5 cm, away from the midline of the abdomen, there is a point that helps in the treatment of pain in the abdomen, and also relieves bloating, vomiting and constipation.
- If you bend the knee, then in the middle of the bend there is a point, massaging which, you can cure urinary incontinence, difficulty urinating. As well as abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation and diarrhea.
With cystitis
Cystitis is considered an inflammation of the bladder. And if you simultaneously apply complex treatment and acupressure, you can quickly cure not only an acute, but also a chronic disease. It is only required to find a point located in the middle of the plexus between the big and second toes. And press on it with your thumb for 2 minutes. In this case, breathe correctly and repeat up to four times in one session.
Even during the treatment, two additional points help, on which you need to press for 2 minutes, and are located:
- Above the inner bone of the ankle, at a distance of the width of four fingers.
- On a bent knee, on the fold of a bone. The palm must move along the outside of the knee towards the foot.
With prostatitis
Moreover, during acute prostatitis, this point must be massaged clockwise, 2 minutes, three times a day. During chronic - it is also required to massage clockwise, 20 seconds, once every day.
The course of treatment is two weeks. Effective in combination with therapeutic exercises.

Another point is on the skin fold between the middle and ring fingers, which needs to be stimulated for 10 minutes, gradually increasing the pressure. You need to massage clockwise three times a day.
For urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence is a violation of the response of the bladder constrictor. And it happens if you drink a lot of liquid or freeze in a dream.
In this case, appropriate treatment is required:
- On the lumbar region on both sides there are five points that you need to press on, and then press on the three points located in the sacral region.
- On the lower abdomen, and on the area above the bladder, you should also gently press with your palms.
- It is also worth pressing on both sides of the back of the neck, on the tubercle of the occipital bone, downwards.
With congestion in the liver and gallbladder
Thanks to the liver, the functioning of the human body occurs. Therefore, to improve blood circulation, as well as reduce pain, gently massage. To complete the full course, you need to go through no more than 20 sessions.
You should start with circular stroking, around the navel, while lightly touching the fingers of your right hand. It should be done easily, the hand should not touch the stomach. Thus, the muscles of the abdominal cavity relax.
Then you need to grab your stomach with your hand for an easy warm-up. Then press on the abdominal wall with four fingers of the palm, trying to avoid sudden movements. And at the end, do the soft tissues of the abdomen, the kneading technique.
Location and massage of biological points with hearing loss
Massage of biological points quickly restores hearing, improves blood circulation, increases hearing acuity, eliminating tinnitus. It is best to carry out daily, reducing or increasing the intensity. It is required to rub the palms together so that they become warm and soft. Then sit on a chair so that your back is straight.
Work with only three fingers: thumb, index and middle. Massage gently and gently, until a state of mild pain. If performed correctly, then after the massage the patient must feel calm and light.
Allocate a couple of points that bring a person only one benefit. The main thing is to prepare internally, calm down and tune in to a positive outcome before starting the massage.
They mainly work with points located:
- between the eyebrows
- in the temporal region,
- in the area of the wings of the nose,
- in the center of the chin fossa,
- behind the ear.
Atlas of points on the human body for the treatment of the heart and blood vessels
A stressful life often leads to palpitations, discomfort and heartache. Therefore, it is required to use acupressure. The symptoms that have arisen can be easily eliminated by exposure to biological points on the head, chest, back and arms of a person.

- In the center of the crown of the head is a point that relieves dizziness and tinnitus. It also helps with shortness of breath, palpitations and arterial hypertension. In addition, it is often used for diarrhea, vomiting, urinary incontinence.
- On the chest, on the sides of the nipples, there are special points, also used for hypertension.
- In the middle of the wrist crease of the hand, you can find a point that easily relieves pain in the heart area, palpitations, and solves the problem of insomnia. Additionally, it treats colds and infectious diseases.
- There is a point at the anterior edge of the calcaneal tendon, which is often used during a strong heartbeat. In addition, it helps with diseases of the digestive system, inflammation of the throat and nosebleeds, swelling lower extremities, pain in the spine, lower back and legs.
- However, a point located on the chest between the pectoral and deltoid muscles is considered effective, which quickly heals chest pain.
With arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is divided into:
- tachycardia, when the heart rate painfully accelerates;
- bradycardia, when the heart rate slows down.
And often does not pose a threat to human life, but health suffers. And acupressure helps to improve this condition. For this, a special point is used, which is available on both hands. It is required to sit on a chair, keep your back straight. Place your left hand on your lower abdomen, palm up.
After that, with the thumb of the right hand, press the point on the left hand and, best of all, straight down, for 4 minutes. Then, without lifting the massaging finger from the point, horizontally towards the vessels, to the elbow bend, massage several times.
Massage with tachycardia begins easily and gently, slowly increasing pressure.
With bradycardia, you need to immediately press hard. Simultaneously applying vibration and kneading. Then repeat a similar massage on the right hand. A point can be saved from arrhythmia, which can be found if you count from the ankle up 6 cm, above the bone.
Press with vibration small movements for 30 seconds, 2 times a day. Among other things, as a preventive measure, this place is heated.
With cardineurosis, palpitations, yeast in the hands
With cardineurosis, palpitations, yeast in the hands, it is required to work with biological points located on the hands:
- If you bend the elbow of the hand at a right angle, then you can easily find the point used for trembling in the hands, heart pain and normalization of pressure.
- In the middle, on the skin fold of the wrist farthest from the hand, on the inside of the arm, there is a point that helps with heartbeat. And also saves from insomnia, headaches and weak immunity.
- There is a point above the crook of the wrist to help calm the outer shell of the heart. And also save from depression and insomnia.
With hypertension
Hypertension leads to undesirable consequences, which means that high pressure must be taken as seriously as possible. In this case, acupressure will help, which is considered a wonderful helper for this disease. At the same time, it quickly prevents arterial hypertension, climatic neuroses and dizziness, and also helps to get rid of tinnitus and palpitations.
 The diagram shows the location of biologically active points on the human body.
The diagram shows the location of biologically active points on the human body. You need to sit down and relax. With index fingers, gently massage the biological points on the chest a couple of times a day, for a month. Then break for 7 days and start treatment again.
It is also worth constantly working with points located behind the ear:
- In the center of the crown.
- Under the lower jaw in the place where the carotid artery pulsates.
With vegetative-vascular dystonia
During the vegetative-vascular distance, spasmodic painful contraction of the muscles occurs, and in addition, there is a deviation from the normal position of the body, causing pain and inconvenience. Besides, it's impossible to relax.
In a normal state, contraction of blood vessels is a true physiological reaction to external changes. But because of this disease, an unmotivated contraction of blood vessels occurs, causing unpredictable drops in blood pressure with pain signs: headache, lethargy and nausea.
To overcome dystonia, you need to put pressure on the point, easily finding it on your feet. You just need to take hold of the foot and press on the point with your thumb, using some effort. Perform 2 times during the day.
For hypotension (low blood pressure)
Hypotension is a disease when the pressure is below normal and is accompanied by a violation of the functions of the heart or cerebral circulation. Therefore, in order to normalize the pressure, it is necessary to press intensively on the necessary points on the human body, which are responsible for the human organs.
To do this, with the nail of the thumb, little by little, but intermittently, press the end of the little finger along the edges of the nail, which is clamped by the thumb and forefinger. It is advisable to do this in the morning in bed or when there is a feeling of lethargy. The point under the thyroid gland, where the collarbones meet, also helps. The impact must be short in time, but preferably strong.
Video about biologically active points on the human body and what they are responsible for
Massage on biologically active points on the face according to the Norbekov system:
Detailed description of reflexology:
It is very important to constantly monitor your health, undergo preventive examinations with a doctor, as well as pay attention to various pain points and symptoms of health problems in order to solve them as quickly as possible. However, there are other points - biologically active, which are responsible for certain aspects of health.
Therefore, a simple massage or pressure on such points can significantly improve health and mood. Therefore, below the site will talk about 9 biologically active points and the benefits of influencing them.
What is acupressure point massage
It is believed that each organ of our body is associated with certain points. Therefore, if you wish to improve the function of internal organs, this can be done by influencing the corresponding biologically active points.
Also, by massaging these points, you can help speed up metabolism, control appetite and energy levels. The main thing is to massage regularly (every day) and press on the points with moderate force so as not to cause pain.
Below we will look at:
- biologically active points on the head;
- biologically active points on the arms and legs;
- biologically active points on the neck and shoulders.
Biologically active points located on the head
The first biologically active point, which the site will tell you about, is located between the upper lip and nose. Regular massage of this point allows you to:
- improve memory;
- relieve pain;
- get rid of dizziness;
- improve concentration.
There are also several active points on the ear, but the most useful is the massage of the point on the earlobe, because it:
- promotes heart health;
- relieve tension headaches;

biologically active points on the arms and legs
Between the thumb and forefinger (the back of the hand) there is a point associated with various parts of the body, because its massage allows you to:
- relieve ear pain
- relieve pain or tension in the neck;
- relieve spasms and back pain.

Between the big and “index” toes there is another biologically active point, the massage of which can be done independently or entrusted to a specialist. This point has the following advantages:
- improves memory;
- helps fight headaches;
- improves concentration;
- provides a burst of energy.

Under the kneecap, closer to the outer edge of the leg, there is a point, the massage of which helps:
- improve digestion;
- fight inflammation;
- resist the accumulation of unnecessary fat .

The next point is located in the wrist area, or rather, at a distance of two fingers from the carpal crease. This point:
- helps with motion sickness;
- relieves pain in the wrist;
- helps to deal with gastrointestinal problems;
- soothes during pregnancy.

On the upper part of the forearm, at a distance of a couple of centimeters from the elbow, there is a point associated with the large intestine. Her massage:
- improves the condition of the large intestine;
- helps control appetite;
- contributes to the regulation of body temperature.

Biologically active points located on the shoulders and neck
On the back surface of the shoulder, as shown in the figure, there is a biologically active point, the massage of which:
- relieves pain in the shoulder blades;
- relieves back pain;
- helps relieve muscle tension.

On the neck, as shown in the figure below, there is a biologically active point, massaging which you can:
- relieve stress;
- relieve headaches;
- improve sleep;
- relieve tension in the neck.

In order for the massage of biologically active points to give results, it is necessary to perform it regularly on your own or with the help of a specialist. However, the site reminds that good health is ensured only by an integrated approach to the prevention and treatment of diseases.
The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the forearm above the wrist, between the tendons. Massaged like point 2.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the little finger 2 mm from the edge of the nail hole towards the ring finger. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the lower leg above the ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the foot in the deepening of the calcaneal tendon. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. The massage is carried out with a tonic method using deep pressure, rotational and vibrating stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Massage is carried out daily 1-2 times a day until the swelling disappears completely.
If the allergy is accompanied by itching, then the effect is on the next group of points (Fig. 34).
point 1. Asymmetrical, located on the spine between the spinous processes of the VII cervical and I thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward.
|
Figure 34. |
point 2. Asymmetrical, located 6 cun above the anterior border of the scalp. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the outer surface of the thigh 6 cun above the kneecap. The point is easy to determine if you lower your hands along the body: the point will be under the middle finger. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun above the outer ankle. Massaged like point 3.
Point 5. Asymmetrical, located on the spine between the spinous processes of the VII and VIII thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach.
Point 6. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen one and a half cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the lower leg below the kneecap. The patient sits with his legs bent. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the back of the leg in the middle of the popliteal fossa. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the outside of the arm at the beginning of the crease formed when the elbow is bent.
The patient sits with his arm bent at the elbow on the table. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the leg in the region of the popliteal crease. The patient sits with his legs slightly bent. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the lateral surface of the foot from the side of the big toe. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the foot in the heel area. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the inner side of the lower leg. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located 3 mm from the edge of the nail hole of the little toe towards the edge of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 5 cun above the outer ankle. The patient sits with his knees bent.
Point 16. Symmetrical, located on the border of the outer and inner sides of the hand at the level of the little finger. The patient sits with his fingers curled into a fist. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located on the border of the plantar and dorsal surfaces of the foot at the level of the heel. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. The massage is carried out with a tonic method using deep pressure and stroking with vibration and rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Massage of points 10-13 eliminates itching on the inner surfaces of the limbs and the front surface of the trunk.
3. Massage of points 14-17 eliminates itching on the outer surfaces of the limbs and the back of the body.
The method of applying acupressure in atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a vascular disease that occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, eating disorders (excessive consumption of meat, fats, alcohol), constant nervous overload, and smoking.
With atherosclerosis, memory loss, fatigue, sleep disturbance, headaches, dizziness and some other negative phenomena can be observed. In atherosclerosis, the effect is on the next group of points (Fig. 35).
 |
|
Figure 35. |
point 1. Symmetrical, located at the beginning of the fold formed when the elbow is bent, from the outside. The patient sits with his half-bent arm on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the back of the hand between the thumb and forefinger. Massaged like point 1.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the surface of the lower leg 3 cun below the patella and 1 cun outward from the anterior edge of the tibia. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located 3 cun above the inner ankle. Massaged like point 3.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the back 3 cun away from the midline between the spinous processes of the IV and V thoracic vertebrae (Fig. 36). The patient lies on his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
 |
|
Figure 36. |
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the back in the middle of the supraspinous fossa of the scapula. The point is easy to determine if you put your right hand on the right shoulder of the patient, the point will be under the index finger. Massaged like point 5.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the outer side of the lower leg 3 cun above the ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located at the level of the navel, 4 cun away from the anterior midline. The patient lies on his back, as relaxed as possible. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the upper branch of the pubic bone 4 cun away from the anterior midline. Massage like a point 8.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the hand on the middle crease of the wrist in the recess between the tendons. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the front surface of the forearm 1 cun above point 10, between the tendons. Massaged like point 10.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the shoulder 3 cun above the elbow. Massaged like point 10.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the V and VI thoracic vertebrae. Massaged like point 5.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located on the middle part of the arch of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located under the inner ankle, on the border of the dorsal and plantar surfaces. Massaged like point 14.
Point 16. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline between the spinous processes of the II and III lumbar vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach.
Notes:
1. Massage of 1-15 points is done with a soothing method using pressure and slow stroking with rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 2-3 minutes.
2. Impact on the 16th point is carried out using the techniques of tonic massage: deep pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
If atherosclerosis is accompanied by memory impairment, then massage of the following points is shown (Fig. 37).
point 1. Symmetrical, located 2-3 mm from the corner of the nail hole of the little finger of the hand towards the ring finger. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the forearm one and a half cun above the middle crease of the wrist, in a depression. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
 |
|
Figure 37. |
Point 3. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline between the spinous processes of the VI and VII thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on his back.
Point 4. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline 5 * 6 cun above the border of the scalp. The patient is sitting.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the arch of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located at the beginning of the fold formed when the arm is bent at the elbow. The patient sits with his half-bent arm on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 7. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline between the spinous processes of the VII cervical and I thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward.
Point 8. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline 5 cun above the anterior border of the scalp. The patient sits with his head tilted forward.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the V and VI thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. Massage (except for point 2) is carried out with a tonic method using deep pressure and both types of stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. The 2 point massage uses a soothing method of gentle pressure combined with a rotational stroke. The duration of exposure to the point is 4-5 minutes.
3. A full course of acupressure for atherosclerosis consists of 14 sessions daily. A second course, if necessary, can be carried out no earlier than a week later.
4. A good result is the alternation of the massage of this group with the massage of the points of the previous group.
5. Massage of the first and second groups of points can be carried out not only for the treatment, but also for the prevention of atherosclerosis.
If atherosclerosis is accompanied by dizziness, after consultation with a specialist doctor, you can massage the next group of points (Fig. 38).
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the shoulder 3 cun above the elbow, at the inner edge of the biceps muscle. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 2. Symmetrical, located half a cun away from the anterior midline and 1 cun below the navel. The patient is sitting or lying down. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the back of the shoulder, 1 cun above the elbow. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the back of the hand at the base
I phalanx of the index finger. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the back of the hand behind the head
II metacarpal. Massaged like point 4.
Point 6. Asymmetrical, located on the anterior midline 4 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back, as relaxed as possible.
Notes:
1. Massage (except point 2) is performed by a soothing method using pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
2. When massaging point 2, a tonic method is applied using deep pressure with vibration. The duration of exposure to a point is a few seconds.
3. If necessary, this massage can be alternated with massage points of the first and second groups. In this case, the full course of treatment will be 24 sessions. A repeated course of massage can be carried out no earlier than a week later.
 |
|
Figure 38. |
The method of applying acupressure in bronchial asthma
One of the most severe manifestations of bronchial asthma is severe asthma attacks, so the main task of acupressure in this disease is to activate the respiratory function of the body.
Acupressure for bronchial asthma should be carried out under the systematic supervision of a doctor. It is carried out by influencing such groups of points as (Fig. 39).
Point 1. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline between the spinous processes of the VII cervical and I thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward.
 |
|
Figure 39. |
point 2. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of II and III thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located under point 2. Massaged in the same way as point 2.
Point 4. Asymmetrical, located on the anterior midline at the jugular notch of the sternum. The patient is sitting.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located in the first intercostal space under the clavicle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the back in the center of the supraspinous fossa of the scapula. It is easy to determine the point if you put your right hand on the right shoulder of the patient: the point will be under the index finger (Fig. 40). The patient sits, slightly leaning forward, or lies on his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located in front on the inner surface of the shoulder between the beginning of the axillary fold and the elbow bend. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located in the skin fold, which is formed when the elbow joint is flexed. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 9. Asymmetric, located in the center of the sternum under point 4. The patient sits or lies on his back.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the 1st and 2nd thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward. The point is massaged simultaneously to the right and left.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located 2 cun away from the anterior midline under the clavicle. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the V and VI thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits, slightly leaning forward and putting his hands on the table. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. Massage is carried out in a soothing way using light pressure and both types of stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 3-5 minutes.
2. The impact on point 12 is during the massage of a child suffering from bronchial asthma, in addition to the previous ones. Massage of this point is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to the point is 0.5-1 min.
 |
|
Figure 40. |
If the patient is over 40 years old, then during his treatment, the massage of the first group of points should be alternated with the impact on the following points (Fig. 41).
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the lower leg 3 cun above the ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 2
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the back of the hand between the thumb and forefinger. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the back; midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes II and III belt-
Figure 41.

vertebrae. The patient sits, slightly leaning forward, or lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Note:
massage is carried out with a tonic method using deep pressure with rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
Massage of the next group of points is used in the period between attacks of suffocation in order to prevent them (Fig. 42).
 |
|
Figure 42. |
point 1. Coincides with point 8 of the first group.
Dot 2. Symmetrical, located on the forearm one and a half cun above the middle crease of the wrist, on the side of the thumb. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the front surface of the wrist 1.5 cm below the crease, on the side of the thumb. Massaged like point 2.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the border of hair growth. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Coincides with point 3 of the first group.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located in the depression between the calcaneal tendon and the outer malleolus. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot at the narrowest point of the gap between the I and II metatarsal bones. Massaged like point 6.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located at the inner end of the popliteal crease. Massaged like point 6.
Point 9. Coincides with point 11 of the first group.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the XI and XII thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits, slightly leaning forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 11. Coincides with point 12 of the first group.
Point 12. Coincides with point 2 of the second group.
Notes:
1. The massage is performed with a soothing method using pressure with rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 3-5 minutes.
2. At the beginning of the course, massage is carried out every other day, then after 2-3 days, and at the final stage - once a week.
The technique of acupressure for sinusitis
Sinusitis usually occurs as a result of acute infection or chronic cold. Its main signs are fever and severe headache, which radiates simultaneously to the cheek, temple and jaw.
With sinusitis, there is an impact on points such as (Fig. 43).
Point 1. Symmetrical, located 12 mm below the lower eyelid. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from
midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes III and IV
thoracic vertebrae. The patient is sitting or lying down. The point is massaged at the same time
at both sides.
 |
|
Figure 43. |
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the occipital region of the head. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Asymmetrical, located 1 cun above the border of the scalp. The patient is sitting.
Point 5. Symmetric, located half a cun above the inner beginning of the eyebrow. The patient is sitting or lying down. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the outer surface of the forearm above the middle crease of the wrist. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Notes:
1. The massage is carried out with a soothing method using rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
2. A full course of massage is carried out for 10-12 days, gradually increasing the number of daily procedures from one to three.
The method of applying acupressure for hemorrhoids
With hemorrhoids, the enlarged venous plexuses of the rectum form nodes: external (under the skin) and internal (under the mucous membrane of the rectum), which, increasing, cause pain and bleeding.
Hemorrhoids are usually found in people leading sedentary image life, in women during pregnancy and as a result of chronic constipation.
With hemorrhoids, the following group of points is affected (Fig. 44).
Point 1. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline 5.5 cun above the border of the scalp. The patient is sitting.
point 2. Asymmetrical, located in the middle between the coccyx and the anus. The patient is squatting.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located in the recess, which is formed in the middle of the sole when the fingers are bent. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the arch of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the forearm one and a half cun above the middle crease of the wrist in the region of the styloid process of the radius. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Point 6. Asymmetrical, located on the head, on the posterior midline, above point 1. The patient is sitting.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun above the inner ankle. Massaged like point 4.
 |
|
Figure 44. |
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the foot in the recess between the calcaneal tendon and the outer ankle on a line passing through its center. Massaged, point 4.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located 3 mm outward from the corner of the nail socket of the little toe of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the IV and V lumbar vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located in the recess in the middle of the back surface of the wrist. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the outer surface of the lower leg 4 cun above the center of the outer ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located on the second toe at -3 mm from the angle of the nail hole towards the third toe. Massaged like point 12.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located in a recess on the front side of the ankle joint. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the abdomen 2 cun away from the navel. The patient lies on his back. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 16. Symmetrical, located on the neck at the level of the lower edge of the thyroid cartilage. It is massaged like point 14, but very carefully, without strong pressure.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located in a recess on the highest part of the dorsum of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 18. Symmetrical, located on the abdomen 4 cun away from the anterior midline at the level of the navel. The patient lies on his back. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 19. Symmetrical, located 4 cun away from the anterior midline at the level of the superior branch of the pubic bone. Massaged like point 18.
Point 20. Symmetrical, located in a recess on the back of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 21. Symmetrical, located on the border of the dorsal and plantar sides of the foot behind the head of the first metatarsal bone. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 22. Asymmetrical, located on the lumbar region of the back between the spinous processes of II and III lumbar vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach.
Point 23. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen in the anterior midline, 2 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back.
Point 24. Symmetrical, located 3 mm from the inner corner of the nail hole of the big toe. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. Massage is carried out by a soothing method (except for points 14, 17, 22, 24) using light pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 3-5 minutes.
2. Massage of points 14, 17, 22, 24 is carried out with a tonic method using deep pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
4. The course of massage consists of 12 sessions held daily. If necessary, a second course is carried out no earlier than a week later.
If the patient has cracks in the mucous membrane anus, then the impact on the following points can alleviate his condition (Fig. 45).
#Point 1#. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen in the anterior midline 4 cun above the navel. The patient sits or lies on his back.
#Point 2#. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen, 1 cun below point 1. Massaged like point 1.
#Point 3#. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen in the anterior midline one and a half cun below the navel. Massaged like point 1.
# Note#. The massage is performed in a soothing way using light pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 3-5 minutes.
 |
|
Figure 45. |
The method of applying acupressure for diabetes
Diabetes mellitus occurs as a result of malnutrition, excessive alcohol consumption, and frequent nervous overload. Middle-aged people are especially susceptible to this disease.
Signs of diabetes are dry mouth, intense thirst, frequent and copious urination, decreased performance.
An indispensable condition for the appointment of acupressure in diabetes - the patient should not take insulin. During massage, the following points are affected (Fig. 46).
Point 1. Symmetric, located half a cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the X and XI thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
 |
|
Figure 46. |
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the back, one and a half cun away from the posterior midline. Massaged like point 1.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located near the inner corner of the eye 2-3 mm towards the nose. The patient sits with his elbows on the table and his eyes closed. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located in a recess near the outer corner of the eye, 5 mm towards the ear. Massaged like point 3.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the outside of the arm, at the beginning of the fold formed when the elbow is bent. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun below the patella and 1 cun back from the anterior edge of the tibia. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located in a depression on the lower leg 2 cun below the patella and one and a half cun outwards. The patient sits with his knees bent at an angle of 90 degrees. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located in the heel area, in the depression between the calcaneal tendon and the outer ankle at the level of its center. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located at the border of the intersection of the plantar and dorsal sides of the foot with the calcaneal tendon. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the border of the plantar and dorsal surfaces of the foot. Massaged like point 9.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 2 cun above the inner ankle. Massaged like point 9.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the big toe 3 mm towards the second finger from the angle of the nail hole. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located on the dorsum of the foot between the heads of the I and II metatarsal bones. Massaged like point 12.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located on the anterior surface of the lower leg 6 cun below the patella and one and a half cun outward from the anterior edge of the tibia. Massaged like point 12.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located in a recess above the collarbone. Massaged like point 12.
Point 16. Symmetrical, located in the depression between the calcaneal tendon and the medial malleolus. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located on the border of the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot behind the head of the first metatarsal bone. Massaged like point 16.
Point 18. Symmetrical, located to the right of point 17 from the side of the heel. Massaged like point 16.
Point 19
Point 20. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the forearm 1 cun above the lower crease of the wrist, on the side of the first finger. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 21
point 2 2. Symmetrical, located on the foot at the point of attachment of the calcaneal tendon to the calcaneus. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 23. Symmetrical, located in a recess on the highest part of the back of the foot. Massaged like point 22.
Notes:
1. Massage is performed with a tonic method (except for points 9 and 20) using deep pressure. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. The massage of points 9 and 20 is performed in a soothing way using light pressure and rotational stroking, gradually slowing down its pace. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
3. The massage course consists of 12 sessions every day. If necessary, a second course is carried out after consultation with the attending physician not earlier than in a week.
The method of applying acupressure in vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia, as a rule, occurs as a result of nervous stress. Under the influence of atmospheric changes, physical and emotional stress, the patient experiences a strong heartbeat, increased sweating, his hands and feet become cold.
Point 1. Symmetrical, located almost in the center of the plantar surface of the foot in the depression formed when the fingers are bent. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the big toe 3 mm from the angle of the nail hole towards the adjacent toe. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot at the narrowest point of the gap between the I and II metatarsal bones. Massaged like point 2.
 |
|
Figure 47. |
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun above the inner ankle. Massaged like point 2.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the front surface of the lower leg 3 cun below the kneecap. Massaged like point 2.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the arch of the foot. Massaged like point 1.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the border of the back side and the sole of the foot between the I metatarsal bone and the main phalanx of the big toe. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot between the heads of the I and II metatarsal bones. Massaged like point 7.
Point 9
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the front of the thigh 3 cun above the patella. Massaged like point 9.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 6 cun above the outer ankle between the bone and muscles. Massaged like point 9.
Notes:
1. Massage of points 1, 2, 6, 7, 9 is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure and both types of stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Massage of points 3-5, 8, 10,11 is performed with a soothing method using light pressure. The duration of exposure to each point is ~ 4-5 minutes.
3. The massage course consists of 12 sessions held every other day. If necessary, the massage course can be repeated, but not earlier than in a week.
If the patient's hands are getting cold, then massage of the following points can help him (Fig. 48).
 |
|
Figure 48. |
Point 1. Asymmetrical, located on the back on the posterior midline between the spinous processes of the VII cervical and I thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits with his head tilted forward.
Point 2. Symmetrical, located on the thumb 3 mm outward from the corner of the nail hole. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the middle finger 3 mm from the corner of the nail hole towards the index finger. Massaged like point 2.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the little finger of the hand 3 mm from the corner of the nail hole towards the ring finger. Massaged like point 2.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the palm at the base of the I metacarpal bone. Massaged like point 2.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the palm between the III and IV metacarpal bones. Massaged like point 2.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the palm in the widest part of the gap between the IV and V metacarpal bones. Massaged like point 2.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the outer surface of the forearm one and a half cun above the middle crease of the wrist in the fossa at the styloid process of the radius. Massaged like point 2.
Notes:
1. Massage of points 1, 5-7 is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure and both types of stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Points 2-4 are massaged in a soothing way using light pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 2-5 minutes.
3. The massage course consists of 12 sessions every day. If necessary, you can conduct a second course, but not earlier than in a week.
If the patient experiences a burning sensation in the area of \u200b\u200bthe soles, then the following points should be massaged (Fig. 49).
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the sole of the foot in a depression formed when the fingers are bent. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
point 2. Symmetrical, located at the inner end of the popliteal crease between the tendons. The patient sits with his knees bent. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located under point 2. Massaged like point 2.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot between the heads of the II and III metatarsal bones. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot between the heads of the IV and V metatarsal bones. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot next to the little toe. Massaged like point 5.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the lower leg 2 cun below the kneecap. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
 |
|
Figure 49. |
Notes:
1. The massage is performed in a soothing way using light pressure and slow rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 3-5 minutes.
2. The course of massage is 12 sessions held daily. If necessary, a second course is carried out, but not earlier than in a week.
The method of applying acupressure for stuttering
Stuttering is a speech disorder resulting from mental trauma. The use of acupressure in this type of disease does not lead to a complete cure, but the impact on the following points can greatly alleviate the patient's condition (Fig. 50).
 |
|
Figure 50. |
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the arm on the wrist between the tendons. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the forearm 2 cun above the middle crease of the wrist. Massaged like point 1.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the outer side of the shoulder 1 cun above the elbow crease of the unbent arm. The patient sits with his hand down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun below the patella and 1 cun back from the anterior edge of the tibia. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the V and VI thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits, slightly leaning forward. The point is massaged simultaneously to the right and left.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the face in a recess above the zygomatic arch at the base of the ear. The patient sits with his elbows on the table. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun above the inner ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the forearm one and a half cun above the middle crease of the wrist, in a depression. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 9. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline on the lower border of the scalp. The patient sits with his head tilted slightly.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the hand on the border of the inner and outer sides of the palm at the little finger. The patient sits with a slightly bent hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Notes:
1. Massage (except point 10) is performed with a soothing method using light pressure. The duration of exposure to each point is 3 minutes or more.
2. Point 10 is massaged with a tonic method using deep pressure. The duration of exposure to the point is 0.5-1 min.
3. The massage course consists of 12 sessions every day. If necessary, you can conduct another 2-3 courses with an interval of one week.
The method of applying acupressure for impotence
Impotence occurs as a result of excessive use of alcohol, sleeping pills and some other medications. It can also be caused by diabetes, obesity, spinal injury or mental trauma.
 |
|
Figure 51. |
Acupressure is carried out after a mandatory consultation with the attending physician. The impact is on the following points (Fig. 51).
point 1. Asymmetrical, located on the back in the lumbar region between the spinous processes of II and III lumbar vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline near point 1. The patient lies on his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae. Massaged like point 2.
Points 4-7. Symmetrical, located on the back in the region of the intervertebral foramina of the I-IV sacral vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach. Each point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the abdomen at the level of the navel. The patient lies on his back. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 9. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen 3 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back.
Point 10. Asymmetrical, located on the anterior midline in the pubic region. The patient lies on his back.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the inner thigh. The patient lies on his back. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the back of the leg at knee level. The patient lies on his back or sits with his leg bent. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun above the inner ankle. Massaged like point 12.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located on the foot in the area of the calcaneal tendon. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the lower leg 2 cun below the kneecap. Massaged like point 14.
Point 16. Symmetrical, located on the pubic region half a cunning away from the anterior midline. The patient lies on his back, as relaxed as possible. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located on the abdomen 4 cun below the navel and half a cun away from the anterior midline. Massaged like point 16.
Point 18. Symmetrical, located on the shoulder 7 cun above the elbow. The patient sits with his arm bent at the elbow on the table. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Point 19. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the arch of the foot (massaged with insufficient erection). The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 20. Symmetrical, located on the big toe next to the nail hole. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 21. Asymmetrical, located on the back on the posterior midline between the spinous processes of I and II thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach or sits, slightly leaning forward.
Point 22. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen one and a half cun below the navel. Massaged like point 8.
Point 23. Asymmetrical, located on the back in the lumbar region between the spinous processes of the IV and V lumbar vertebrae. Massaged like point 1.
Notes:
1. Massage of points 1-7, 13-15, 18-21 is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. The massage of points 8-12, 16, 17 is performed with a soothing method using light rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
3. It is not necessary to massage all of the above points at each session, you can limit yourself to half, choosing the points so that the tonic effect is combined with a calming one.
4. The massage course consists of 14 sessions every day (2-3 procedures daily). If necessary, a second course is carried out in a week.
If impotence in a patient is accompanied by dizziness and an unbalanced state, then the following points can be massaged (Fig. 52).
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 2 cun above the inner ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
 |
|
Figure 52. |
point 2. Symmetrical, coincides with point 2 of the first group. The patient lies on his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the big toe 3 mm from the nail hole towards the second finger. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, coincides with point 16 of the first group.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located in the depression between the calcaneal tendon and the inner ankle at the level of its center. Massaged like point 3.
Point 6. It is located on the lower leg at the inner end of the popliteal crease.
Note: massage carried out by the tonic method using deep pressure and rotational stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
With premature ejaculation, the following points are massaged (Fig. 53).
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot between the heads of the I and II metatarsal bones. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 2. Coincides with point 19 from the first group.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot in front and below the inner ankle, in a recess. Massaged like point 2.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the abdomen 2 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back, as relaxed as possible. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 8 cun above the inner ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
 |
|
Figure 53. |
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the border of the dorsal and plantar sides of the foot under the I metatarsal bone. Massaged like point 5.
Point 7. Coincides with point 9 of the first group.
Point 8. Coincides with point 22 of the first group.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the forearm 2 cun above the middle crease of the wrist. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the border of the dorsal and plantar sides of the foot behind the head of the first metatarsal bone. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 11. Coincides with point 13 of the first group.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 6 cun below the kneecap. Massaged like point 11.
Point 13. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen in the anterior midline, 4 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back.
Point 14. Coincides with point 2 of the first group.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the back in the region of the sacrum half a cun away from the posterior midline. The patient lies on his back, a pillow is placed under his stomach.
Notes:
1. Points 1-9 are massaged with a tonic method using deep pressure with rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. The massage of points 10-15 is performed with a soothing method using light stroking. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
The method of applying acupressure in case of insufficient lactation
Lack of milk is observed, as a rule, in women after the first birth. Massage of the following points can help with this (Fig. 54).
Point 1. Symmetrical, located on the outer side of the forearm half a cun above the middle crease of the wrist, in a depression at the styloid process of the radius. The patient sits with her hand on the table. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
 |
|
Figure 54. |
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the index finger 3 mm from the corner of the nail hole towards the thumb. Massaged like point 1.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the back of the hand at the base of the index finger. Massaged like point 1.
Point 4. Asymmetrical, located on the anterior midline in the chest area. The patient is sitting.
Point 5
Point 6. Symmetrical, located 4 cun away from the anterior midline at the level of the fifth rib. Massaged like point 5.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the little finger of the hand 3 mm from the corner of the nail hole. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the VII and VIII thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on her stomach, a pillow is placed under her stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the back under point 8 at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the IX and X thoracic vertebrae. Massaged like point 8.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the back of the hand between the I and II metacarpal bones. The patient sits with her hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
point 1 1. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the forearm 2 cun above the middle crease of the wrist, between the tendons. The patient sits with her hand on the table, palm up. It is massaged alternately on the right and left.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located 4 cun away from the anterior midline. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. Massage is performed with a tonic method, using deep pressure with vibration. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Massage sessions are held every day for 2 procedures daily.
The method of applying acupressure for migraine
Migraines are prolonged attacks of pain that occur in a specific area of the head and are especially common in women.
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the outer surface of the forearm 2 cun above the upper crease of the wrist, in a depression. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
 |
|
Figure 55. |
point 2. Symmetrical, located in the temple area on the border of the scalp. The patient sits with his elbows on the table and his head resting on them. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located in the recess at the outer corner of the eye. Massaged like point 2.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located in a recess at the base of the ear above the zygomatic arch. Massaged like point 2.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located in the recess at the outer end of the eyebrow. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the face at the inner corner of the eye 2-3 mm towards the nose. The patient sits with his elbows on the table and his head resting on them. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the back of the hand between the I and II metacarpal bones. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately left and right.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located at the end of the fold, which is formed when the arm is bent at the elbow joint. The patient sits with a slightly bent arm on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left,
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the foot 3 mm from the nail hole of the thumb towards the second finger. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun above the inner ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot between the II and III fingers. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the second toe 3 mm back from the nail hole. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located on the back of the foot between the heads of the IV and V metatarsal bones. Massaged like point 12.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located on the face at the bridge of the nose above point 6. Massaged like point 12.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the foot 3 mm back from the corner of the nail hole of the little finger. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 16. Symmetrical, located on the foot under the inner ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located on the temporal part of the head. To find it, you need to bend your ear forward: the point will be at the very top of the ear. Massaged like point 16.
Point 18. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen one and a half cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back, as relaxed as possible.
Point 19. Asymmetrical, located 6 cun above the navel, above point 16. Massaged like point 18.
Notes:
1. Massage (except for points 15, 16, 18) is performed with a soothing method using light stroking and rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
2. Massage of points 15, 16, 18 is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure and rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
3. Massage can be done between attacks or during them.
4. During the session, you can not massage all the points, but only those, the impact on which gives the maximum analgesic effect.
The method of applying acupressure in cardiovascular diseases
The use of acupressure can have a beneficial effect on such manifestations of heart disease as sudden attacks of increased heart rate and pain in the heart area. With an increased heartbeat, the following points are affected (Fig. 56).
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the IV and V thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits, slightly leaning forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 2. Symmetrical, located one vertebra below point 1. Massaged like point 1.
Point 3. Asymmetrical, located on the anterior midline at the level of the fourth intercostal space. The patient lies on his back.
 |
|
Figure 56. |
#Point 4#. Asymmetrical, located on the anterior midline under point 3. Massaged like point 3.
#Point 5#. Symmetrical, located on the back 3 cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the V and VI thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits, slightly leaning forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the wrist in a depression between the tendons on the middle carpal crease. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the forearm 5 cun above the middle crease of the wrist between the tendons. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged with the index finger alternately to the right and left.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the forearm, between points 6 and 7. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged with the middle finger alternately on the right and left.
Notes:
1. The massage is performed in a soothing way using a light rotational stroke, the pace of which gradually slows down. The duration of exposure to each point is 2-5 minutes.
2. Points 7-8 are massaged simultaneously.
It is advisable to alternate the massage of points 1-8 with the impact on subsequent points (Fig. 57).
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the lower border of hair growth one and a half cun away from the posterior midline. The patient sits with his head slightly tilted forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
 |
|
Figure 57. |
Point 10. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the occipital cavity. Massaged like point 9.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the II and III thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits or lies on his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the 1st and 2nd thoracic vertebrae. The patient sits or lies on his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located on the back to the left of point 12. The patient sits or lies on his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located 6 cun away from the anterior midline in the third intercostal space. Massaged with the thumb, like point 13.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the inner surface of the arm in the area of the elbow. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 16. Symmetrical, located on the front surface of the lower leg 3 cun down from the lower edge of the patella. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the forearm 3 cun above the middle crease of the wrist, between the tendons. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 18. Symmetrical, located 2 cun away from the anterior midline. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged with the thumbs simultaneously on both sides.
Point 19. Symmetrical, located on the back away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the IV and V thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Acupressure can lower blood pressure and improve the general condition of the patient. In this case, a sequential massage of several groups of points is performed.
The first group includes the points described below (Fig. 58).
point 1. Asymmetrical, located on the anterior line 5 cun above the upper border of the scalp in the region of the crown. The patient is sitting.
point 2. Asymmetrical, located on the posterior midline 3 cm above the lower border of hair growth. The patient is sitting.
 |
|
Figure 58. |
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the back in the middle of the supraspinous fossa of the scapula. The patient lies on his stomach or sits, slightly leaning forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 5 cun above the inner ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the outer surface of the hand at the end of the fold, which is formed when the arm is bent at the elbow, from the side of the thumb. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the V and VI thoracic vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach or sits, slightly leaning forward. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the back under point 6 at the level of the prom.
between the spinous processes of the VII and VIII thoracic vertebrae. massaged,
like point 6.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located in the lumbar region of the back on the same vertical line with points 6 and 7. Massaged like point 6.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun above the inner ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously" on both sides.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 5 cun above the inner ankle. Massaged like point 9.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the sole of the foot in a small depression formed when the fingers are bent. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Notes:
1. Massage (except points 4, 11) is performed with a soothing method using light pressure with rotation, the pace of which gradually slows down. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
2. The massage of points 4 and 11 is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure with vibration. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
3. A particularly good effect is given by frequent exposure to point 11.
The second group includes the following points (Fig. 59).
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the forearm 1 cun above the middle crease of the wrist. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the shoulder 3 cun above the elbow. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
 |
|
Figure 59. |
Point 14. Symmetrical, located in the middle of the arch of the foot. sick si
dit. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the border of the rear and sole of the foot. Massaged like point 14.
Point 16. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the forearm on
2 cun above the middle crease of the wrist, between the tendons. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the hand on the wrist, between the tendons . Massaged like point 16.
Point 18. Symmetrical, located on the abdomen 4 cun away from the front
midline at the level of the umbilicus. The patient lies on his back. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Dot
19.
Symmetrical is located 4 cun away from the anterior median line at the level of the superior branch of the pubic bone. Massaged like point 18. Point 20. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the arm on the middle Notes:
1. Massage should be carried out in combination with medical treatment prescribed by a doctor. As blood pressure decreases, the use of medications can be limited, and acupressure sessions can be continued until the pressure is completely normalized. 3. During the entire massage course, it is necessary to systematically monitor blood pressure. Figure 60.
warehouse
crease of the wrist in the depression between the tendons. The patient sits, laying on
table hand palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
point 1. Asymmetrical, located 5 cun above the upper border of the scalp in the parietal region. The patient is sitting.
point 2. Asymmetrical, located 3 cm above the lower border of the scalp. The patient is sitting.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 5 cun above the inner ankle. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the hand 1.5 cm below the lower crease of the wrist from the side of the thumb. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged with the thumb alternately on the right and left.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the outside of the wrist in the recess, which is formed when the hand is extended, between the tendons. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged with the index finger alternately to the right and left.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the wrist in line with the middle finger, in a recess. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged with the thumb alternately on the right and left. ;
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the wrist, between the tendons. The patient sits with his hand on the table. The point is massaged with the middle finger alternately on the right and left.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located at the end of the fold, which is formed when the arm is bent at the elbow, from the side of the thumb. The patient sits with a slightly bent arm on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the foot at the point of attachment of the calcaneal tendon to the calcaneus. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located under the inner ankle on the border of the rear and sole of the foot. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 11. Symmetrical, located on the middle finger 3 mm from the angle of the nail hole towards the index finger. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the wrist from the side of the little finger, in a recess. Massaged like point 11.
Point 13. Symmetrical, located on the border of the back side and the sole of the foot under the I metatarsal bone. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 14. Symmetrical, located on the outer side of the forearm one and a half cun above the middle crease of the wrist at the styloid process of the radius. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm down. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 15. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 3 cun below the patella and 1 cun outward from the anterior edge of the tibia. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 16, Symmetrical, located half a cunning away from the anterior midline at the level of the upper edge of the pubic bone. The patient lies on his back. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 17. Symmetrical, located in the chest in the subclavian fossa. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. Massage (except for point 3) is carried out with a tonic method using deep pressure with vibration. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Point 3 is massaged in a soothing way using light strokes. The duration of exposure to the point is 2-5 minutes.
3. Point 4 with point 5 and point 6 with point 7 are massaged at the same time.
4. When performing a massage, you can limit yourself to influencing only those points that give the maximum effect in this patient.
5. Usually acupressure sessions are held every 2 months.
The method of applying acupressure for varicose veins
The cause of this disease is insufficient outflow of blood through the veins. It occurs, as a rule, as a result of a long stay on the legs or during pregnancy in women. Patients may experience itching, a feeling of heaviness and numbness in the legs, fatigue.
Acupressure in the treatment of varicose veins is best used at the initial stage of the disease - then its effect will be most effective. With varicose veins, the following points are affected (Fig. 61).
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the foot under the ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 4 cun above the ankle. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 3. Symmetrical, located 2 cun above the kneecap. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. Point 1 massage is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure. The duration of exposure to the point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Massage of points 2, 3 is performed with a soothing method using pressure. The duration of exposure to each point is 3-4 minutes.
 |
|
Figure 61. |
3. The massage course consists of 12 sessions every day. After consulting with a doctor, you can repeat the course in 1-2 weeks.
If there are ulcers on the lower leg, act on the points listed below.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located 2 cun away from the anterior midline above the superior ramus of the pubis. The patient lies on his back. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the abdomen in the area of \u200b\u200bthe XI rib. The patient lies on his side, stretching out one leg and pressing the bent other leg to the stomach. The point is massaged first from the healthy side, and then from the side on which the ulcer is located.
Notes:
1. Massage is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. The course of treatment for leg ulcers consists of 10-12 sessions every day. A second course can be done in 1-2 weeks.
The method of applying acupressure for enuresis
Enuresis - involuntary urination during sleep - is most common in children suffering from any chronic disease.
With enuresis, the following points are affected (Fig. 62).
point 1. Asymmetrical, located in the lower abdomen on the anterior midline, 3 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back.
 |
|
Figure 62. |
point 2. Asymmetrical, located under point 1 above the upper edge of the pubic bone. Massaged like point 1
Point 3. Symmetrical, located on the lumbar region of the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the back 3 cun away from the posterior midline near point 3. Massaged like point 3.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline in the sacral region. Massaged like point 3.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the front surface of the leg 3 cun below the patella, 1 cun outward from the anterior edge of the tibia. The patient sits with legs stretched out. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located at the point of attachment of the calcaneal tendon to the calcaneus. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Asymmetrical, located on the abdomen 4 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back.
Notes:
1. The massage is performed in a soothing way using light pressure with rotation, the pace of which gradually slows down. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
2. It is desirable to conduct sessions 2 times a day.
For the treatment of enuresis in the elderly, massage of the following points is used (Fig. 63).
 |
|
Figure 63. |
point 1. Symmetrical, located on the lumbar region of the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the IV and V lumbar vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
point 2. Symmetrical, located on the back of the neck one and a half cun away from the posterior median line at the border of hair growth. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously to the right and left.
Dot 3. Symmetrical, located on the foot on the border of the rear and sole at the base of the fifth metatarsal bone. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 4. Symmetrical, located on the foot 2 mm from the corner of the nail hole of the little finger. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 5. Symmetrical, located in the center of the lateral surface of the foot from the side of the big toe. Massaged like point 4.
Point 6. Symmetrical, located on the lower leg 2 cun above the inner ankle. Massaged like point 4.
Point 7. Symmetrical, located on the lateral surface of the foot in the heel area. The patient is sitting. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 8. Symmetrical, located near point 7 on the border of the outer and plantar surfaces of the foot. Massaged like point 7.
Point 9. Symmetrical, located on the inside of the arm in the area of the elbow joint in the fold from the side of the thumb. The patient sits with his hand on the table, palm up. The point is massaged alternately to the right and left.
Point 10. Symmetrical, located on the back one and a half cun away from the posterior midline at the level of the gap between the spinous processes of the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Point 11. Asymmetrical, located in the lower abdomen on the anterior midline, 2 cun below the navel. The patient lies on his back.
Point 12. Symmetrical, located on the back in the area of the shoulder blades. The patient lies on his stomach, a pillow is placed under his stomach. The point is massaged simultaneously on both sides.
Notes:
1. Massage (except points 7, 8, 9, 11) is performed with a tonic method using deep pressure with rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 0.5-1 min.
2. Points 7, 8, 9 and 11 are massaged in a soothing way using light stroking with rotation. The duration of exposure to each point is 4-5 minutes.
3. During the massage, it is necessary that the patient strictly observe the diet.
CHAPTER 3. CONNECTIVE TISSUE MASSAGE
Studies by many Russian and foreign scientists have shown that diseases of the internal organs are often associated with dysfunction of the connective tissue. As a rule, this disrupts the mobility of the skin, subcutaneous tissue in relation to the fascia, in addition, the relief of the skin over the foci of the disease is disturbed. When you touch these areas, pain occurs, they look compacted and swollen.
To restore the function of connective tissue, connective tissue massage should be performed, which helps to normalize metabolism and improve blood circulation.
Connective tissue massage is recommended for pathology of the musculoskeletal system and diseases of some internal organs. Before starting it, an examination of the segmental zones and palpation should be carried out to identify areas with increased tension, seals, and swelling. Such areas during massage can be painful, the skin in these places during the massage procedure may turn red or turn pale.
Connective tissue massage brings a greater effect in combination with water procedures when the patient's muscles are as relaxed as possible. The water temperature should be 37 degrees C.
Connective tissue massage technique
When massaging, the tissues should move in relation to the muscles, tendons and bones. The main method of connective tissue massage is tissue displacement. It is more convenient to capture tissue with the thumb and forefinger. The duration of the massage is from 5 to 15 minutes.
Connective tissue massage should begin with healthy tissues and gradually approach painful points. At first, the movements should be superficial, but gradually (as tension and pain are relieved), the massage should become deep.
Movements are made along the edges of the tendons, along the location of muscle fibers, as well as the places of attachment of muscles, fascia and joint capsules.
When massaging the back and chest, movements should be directed towards the spine, while massaging the limbs, movements are directed to the proximal sections (Fig. 64).
The procedure must be started from the sacrum (paravertebral zone of the back) and gradually move up to cervical region spine. After that, you need to massage the hips, legs, and only then - the patient's shoulder girdle.
 |
|
Figure 64. |
When massaging reflexogenic zones, in order not to cause sharp pain and worsen the general condition of the patient, the movements of the massage therapist should be directed along the border of these zones.
The order of the procedure and the areas of influence on the connective tissues in certain diseases
At headache it is necessary to act on the back of the head, on the interscapular region and on the region of the muscles of the forearm.
For diseases spine you need to act paravertebral on the lumbar region and move smoothly to the cervical spine.
At lumbago produce impact in the lumbar region, sacrum and behind the ilium.
At sciatica massage is performed on the lumbar region, intergluteal fold, popliteal fossa, back of the thigh and calf muscle.
For diseases shoulder joint And shoulder should act on the area between the spinal column and the scapular region, on the costal arches and on the front of the shoulder.
For diseases elbow joint, forearm and hand it is necessary to influence the area between the spine and the scapula, the area of the costal arches, the elbow bend, the inner surface of the forearm and the radio-metacarpal joint.
For diseases hip and thigh it is necessary to act on the buttocks, along the gluteal fold, inguinal region, as well as on the hip joint area.
For diseases knee joint and shins massage is performed on the buttocks, along the gluteal fold, on the inguinal region, on the hip joint and on the popliteal fossa.
CHAPTER 4. PERIOSTAL MASSAGE
Many years of research by specialists have shown that many diseases of the internal organs of a person are accompanied by changes in bone tissue. To restore it, a so-called periosteal massage should be carried out.
Periosteal massage is a type of massage that has an effect on altered painful points that have a reflex connection with various human organs. It is recommended for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, joints, skeletal system and some internal organs. This type of massage has a beneficial effect on blood and lymph circulation, metabolic and trophic processes. This is because when pressure is applied to pain points, highly sensitive interoreceptors of the periosteum, as well as the walls of extraosseous venous vessels, are irritated. When conducting a periosteal massage session, it is necessary to take into account the topography of the nerves and the Zakharyin-Ged zone.
Periosteal massage should be done in those pain points in which painful sensations were localized. In this case, it is necessary to take into account: how severe the patient's pain is. In the event that the pain is very strong, the procedure must begin with exposure to the areas surrounding the painful point and gradually approach its focus. If the procedure is performed on the patient's chest, it is imperative to observe the rhythm of breathing. So, during exhalation, one should press on the chest, and during inhalation, let go.
In the process of massage, one should act on the skull, on the spinous processes of the vertebrae, the exit points of the nerve trunks. The middle sacral scallop, patella and clavicles are not affected.
When massaging the skull, the impact is carried out on the mastoid processes and the occipital protuberance. In the pelvic region, the iliac crests should be affected. When massaging the joints, the actions should be directed to the greater trochanter, tuberosity of the tibia, near the joint space. On
metacarpal bones are massaged in the hands. In the region of the spine, areas near the spinous and transverse processes are massaged. On the ribs, massage is performed near the corner of the rib. The area of the acromial process is massaged on the collarbones.
In case of lumbago (backache), the area of the pubic articulation, the ischium, the ilium and the sacrum should be affected.
With sciatica, the main points of influence are the areas of the sacrum, ischium, greater trochanter and pubic joint.
In the treatment of diseases associated with changes in the joints and muscles of the arms and legs, it is recommended to act on various areas.
1. During the procedure in the area of the shoulder and shoulder joint, it is necessary to press on the spine of the scapula, on the acromion of the clavicle and on the external and internal condyles of the shoulder.
2. During the procedure in the area of the elbow joint, forearm and hand, the spine of the scapula, the acromial part of the clavicle, the internal and external condyles of the shoulder, the styloid process of the radius and ulna, as well as the metacarpal bones should be massaged.
3. During the procedure in the area of the hip joint and thigh, it is necessary to act on the iliac crest, sacrum and pubic joint.
4. During the procedure in the area of the knee joint and lower leg, pressure should be applied to the sacrum, pubic joint, greater trochanter and tibial crest.
In the treatment of osteochondrosis, deforming spondylosis and other diseases of the spine, the areas of the sacrum, ischium, ribs, scapula, sternum, pubic articulation of the spinous processes of the vertebrae should be massaged.
Contraindications for periosteal massage: osteoporosis, bone tuberculosis.
Periosteal massage technique
During the procedure, one or more fingers should rhythmically press on the periosteal point, located not far from the course of the nerve trunks, or on the periosteal point of the periosteum. Press on this point should be 1 time per second, without taking your fingers off the massaged area. The patient should be in a sitting or lying position. He should relax his muscles as much as possible. Massage should be done on exposed areas.
The duration of massaging one point, as a rule, is from 1 to 3 minutes. After that, you should massage other points. When pressing on the point, the fingers should not tremble and vibrate.
Periosteal massage can be carried out in the form of independent procedures and in combination with hydroprocedures and physiotherapy. Periosteal massage should be carried out 2-3 times a week.
East Asia has long been distinguished by a special culture and medicine. Great importance is given to the state of mind of a person, the energy of "qi". The presented side of the world is the birthplace of acupuncture. No less interesting to study the direction that was formed there is acupressure (acupuncture) massage.
Introduction to the theory of Chinese medicine, points on the body for weight loss
Acupressure is a type of massage in which fingers or a brush produce a mechanical effect on body points associated with human organ systems, thereby providing a therapeutic or prophylactic effect.
It can be compared with a massage, in which the human body is divided into sections (segmental). Both require complex and individual treatment. Only if in acupuncture massage they act on certain points, then in segmental massage - on entire areas.
There is a fairly popular opinion among people that acupuncture massage helps with weight loss. Is it really? The short answer is yes, there are weight loss points on the body.
This statement is worth exploring in more detail. But before proceeding to clarify this issue, you need to learn basic knowledge about acupuncture massage.

The historical essence of the method
The peoples of the East believe that human life directly depends on the state of internal energy. The name of this matter is the energy "qi". It fills the human body from the cellular level. If biological fluids move through the vessels, then this energy moves along the meridians, setting the blood and lymph in motion.
For example, if a disease occurs, this indicates some kind of obstacle that impedes the normal movement of energy.
The method of classical acupuncture or acupressure removes all blocks, and the flow resumes, the disease disappears. Knowing the places to influence makes it easy to correct human ailments.
There are points in the human body that have the following properties:
- Reduced resistance to electrical current.
- High voltage potential.
- Increased skin temperature.
- High pain threshold.
Parts of the body corresponding to these parameters are called vital, or, as noted in the scientific literature, biologically active points.
The yin-yang theory is also associated with point effects on the body. According to the theory, the human body is a combination of two oppositely charged principles: yin and yang.
The first beginning is the maternal essence, associated with black, cold, damp, depressive, it corresponds to a negative charge. The second type of energy is a warm, cheerful, bright beginning, it corresponds to a positive charge. In order for the body to be normal, the harmony of the two principles must be achieved. By influencing vital points, this harmony can be achieved.
At the moment, there are about 360 biologically active points.
Important: the point does not have to be in the area of the organ being treated. Simply put, if the stomach hurts, this does not mean that you need to put pressure on the epigastric region. Perhaps you should work on the earlobe or the outer part of the foot.

Theoretical explanation of acupuncture massage
The basis for both acupuncture and massage is the knowledge of vital points on the surface of the human body. The number of points known in the east is in the thousands, but about two hundred have acquired practical significance.
Sizes range from 0.2-5 mm.
Properties that these points have:
- The fibers in the loose connective tissue are arranged in the form of a grid.
- More receptor endings.
- Groupings of mast cells that secrete biologically active substances that affect the metabolic processes of the body.
According to the provisions of Oriental medicine, the energy "qi" penetrates into the body, through biologically active points together with food, from the environment. It moves sequentially through all organs, making a complete revolution in a day. This theory is very similar to the doctrine of biological rhythms, which is gaining popularity in the modern world.
Scientists of the world do not always fully agree with the arguments of Eastern doctors regarding the energy of life, but the impact that acupressure has makes it necessary to study this issue more deeply.
In practice, the dependence of the impact on certain areas of the body and organ systems has been revealed:
- On the autonomic system of the cervical region - points from the seventh cervical to the first thoracic vertebra.
- On nervous system- points of the mutual spectrum of influence.
- Systems of internal organs - points of certain segments.
- Effect on peripheral nerve endings - points on the paravertebral line.
The human body is divided into so-called meridians. On each of them, six classical points are distinguished:
- Exciting.
- Braking - activates braking activity.
- Mediator - enhances excitation or inhibition.
- Stabilizer - point-adapter of energy from systems.
- Empathy point - same function as 3.
- An alarm point is used to diagnose diseases.
Advantages of acupressure
The benefits of acupuncture massage are as follows:
- Treatment of the disease is carried out without medical intervention.
- Easy to perform.
- It is selected for each disease individually.
- Has a relaxing effect.
Among other things, acupuncture massage helps with weight loss. Interestingly, in addition to a direct effect on the body due to points on the body for weight loss, it also has an indirect effect on this process.

It was noted above that acupressure has a relaxing effect. In other words, it relieves stress, and stress is known to be one of the causes of rapid weight gain. It stimulates not to solve the problems that have arisen (due to which the stress hormone rises), but, for example, to seize them (compensate).
So a vicious circle is formed: stress - jamming - weight gain - stress about weight gain - jamming, etc.
Acupressure helps to calm down and relax. In this state, there is much more chance of acceptance right decisions: a sober-minded person will judge that it is more logical not to go to the refrigerator for another portion of cakes, but to start solving the problem that caused the stressful state.
Contraindications
Before taking a course of such a massage, it should be noted that it cannot be used in the presence of the following health features:
- Changes in the body.
- Diseases of the blood system.
- Diseases of an infectious nature.
- Necrosis of the heart muscle.
- Tendency to form blood clots.
- Sudden weight loss.
- Physical overload.
- Ulcers in gastrointestinal tract.
- Pregnancy.
- Inflammatory processes in the musculoskeletal system.
- Menstruation.
- Drunk state.
Also, during the course of acupressure, it is forbidden to drink coffee, tea, strong drinks.
Even if a person does not have any of the above contraindications, a specialist consultation is still necessary.
Techniques and types of massage
The main types of acupuncture massage that helps with weight loss:
- Cosmetic.
- Therapeutic.
- Prophylactic.
- Restorative.
In order to qualitatively do acupuncture massage of any kind, you need to know the main points on the body that contribute to weight loss, and methods of influencing them.
You can find points using:
- Knowledge of the main anatomical lines and landmarks.
- Possession of the technique of tsunei. Cun - measure. Each person has their own. It calculates the location of certain points.
Basic Methods
- Classic pressure. The massage therapist puts pressure on one of the points on the body for weight loss for four seconds.
- Repeat pressure. The first exposure lasts about five seconds, then the pressure is not completely removed and immediately follows a second one. Repeat 3 times.
- Simultaneous impact with two thumbs.
- Simultaneous pressure with crossed thumbs.
- rotation method.
- Reception of oscillatory-tremulous movements.

Classification of massage by pressure force
According to the force of pressure that the master exerts on a particular point, massage is divided into:
- Strong. It is an analgesic and relaxing procedure.
- Average. Has a braking effect.
- Weak. It has an exciting effect.
Usually, several techniques are used in one massage session. So it turns out to have a complex effect, influencing pressure on the acupuncture points on the human body for weight loss.
Session time - no more than ten minutes. In various diseases, the effect on mechanoreceptors can either be reduced or increased.
Often, acupressure is used to relieve feelings of fatigue, as well as after exposure to stressful factors.
Massage rules
The basic rules for performing a massage include:
- It is necessary to establish the purpose of the procedure.
- Massage is carried out exclusively with warm hands.
- The pressure should be applied with such force that it is felt, but not painful.
- Clicking on vital points should not be long.
- Sharp jerks are contraindicated, they can leave hematomas.
It is very important to note again: before taking a course of acupressure for weight loss, it is imperative to consult with a specialist. Only a doctor will be able to correctly assess whether it is possible to prescribe acupuncture massage to a given patient who wants to lose weight.
Massage algorithm
You need to perform the procedure in the following sequence:
- Place the tips of the middle fingers at the right points for weight loss on the human body, which are usually symmetrical.
- After finding the desired point, press it and gradually increase the pressure.
- The duration of exposure is not more than thirty seconds.
- An experienced massage therapist should feel when the pressure on the point no longer affects the body, and stop it, moving to another area or finishing the procedure.
The sequence of impact on the points is determined depending on the purpose of the procedure being performed.
The direction of acupressure in order to reduce weight
This method weight loss has been practiced for quite a long time, so a lot of points on the human body for weight loss are known.
By acting pointwise on the human body, you can:
- Reduce the desire to eat. Massage produces serotonin, which is a good mood hormone that distracts the body from the desire to aimlessly consume food.
- Stimulate blood flow to the circulatory organs, thereby ensuring rapid absorption and distribution of energy.
- Normalize metabolic processes.
- Activate fat metabolism.
- Reduce the amount of glucose in the blood.
- Remove metabolic products from the body.
- Activate the liver and urinary system.

The main benefits of acupressure for weight loss
- The general condition of the body improves.
- There is no age limit.
- There are no side effects and few contraindications.
- No allergic reactions.
Some points on the body for weight loss:
- External fossa of the knee. Apply for about fifteen minutes. Perform the procedure while sitting.
- 3 mm from the outer edge of the thumbnail.
- Between the sixth and seventh cervical vertebrae. Produce mass while sitting.
- The area below the navel is 7-9 cm. Reduces appetite.
What points on the body are responsible for losing weight yet?
- Center between upper lip and nose. It is necessary to massage for a couple of minutes if there is a desire to “seize” stress.
- The middle of the tragus of the auricle is the point of appetite.
- On the arm, bent at the elbow, there is a point on the outside on the top of the bend, the massage of which improves bowel function.
- The point is 5 cm higher than the inside of the ankle. Massage of this point helps to get rid of excess weight.
A photo of points on the body for weight loss is presented below. This is one of the possible sites of influence on the body. True, it is worth remembering that these are not the only areas that can be influenced in order to achieve the desired result.

Acupuncture massage and points on the body for weight loss. Reviews
After analyzing the reviews, we can say that the majority of people using this procedure are satisfied with the effect obtained. True, weight loss is noticeable only in the long term. You should be prepared for this. If you want to achieve a good result, you do not need to stop working on the acupuncture points on the body for weight loss after one or two sessions.
Evidence of effectiveness, detailed technique, we influence the point of longevity - in the article.
The main advantage of shiatsu
The possibility of self-massage in any situation and place (at home, at work, in a car).
Having mastered the basic techniques of pressure and having learned to find the right acupuncture points, we are able to independently:
- overcome fatigue,
- get rid of mental overload,
- remove or reduce any pain,
- reduce the unpleasant symptoms of diseases,
- normalize blood pressure
- increase energy,
- improve health,
- provide emergency assistance
- improve sleep and overall well-being.
Shiatsu Evidence
Let us refer to the publication of the results of experiments in well-known international publications.
Sleep quality and relaxation
July 2004, the study was conducted in England and Germany. In an in-depth interview, 14 practitioners and 15 long-term clients testified to the positive effects of shiatsu massage on falling asleep, sleep patterns, and body relaxation.
Journal of Integrative Medicine(Journal of Integrative Medicine):
year 2014. Difficulty falling asleep is a common problem for people suffering from pain. Individuals with musculoskeletal pain and sleep problems were selected to participate in the study (Canada). They were taught self-massage of the hands and interviewed after 8 weeks.
Participants noted a long-term increase in uninterrupted sleep time, more than during nocturnal awakenings. None of the participants reported adverse effects of the intervention.
Thus, shiatsu can be beneficial to apply during nocturnal awakenings as well as before bed.
Reducing pain, chronic fatigue, stress
Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine(official journal of the Acupuncture Research Society, USA):
2008, the study covered 948 people from England, Austria, Spain. They received shiatsu therapy for 6 months.
Indications: pain in the joints and muscles, chronic fatigue, fatigue, stress.
633 subjects provided complete information on treatment effects.
Result:
- all respondents improved their health, decreased pain, stress and fatigue.
- 80% have made positive changes in their lifestyle after introducing shiatsu into their daily routine.
- 16-22% have reduced their use of traditional medicine.
- In a third, drug dependence has decreased.
Signs of chronic fatigue, causes, risk group, provoking factors, how to avoid illness.
Increasing vitality
International Journal of Palliative Care(International Journal of Palliative Nursing):
September 2013 This qualitative 6-month study was designed to evaluate the impact of shiatsu on clients attending hospice day services. Three overlapping groups of eleven patients with progressive disease received 5 weeks of shiatsu therapy.
The results of the analysis revealed significant progress in levels of energy, relaxation, confidence, mental clarity and mental stability.
The effect lasted in some cases for several hours, but in most cases exceeded the 5-week treatment regimen.
Reducing anxiety and stress
World Journal of Plastic Surgery(World Journal of Plastic Surgery):
in 2013 (Tehran), 60 patients with burn injuries (10-45%) and associated severe post-traumatic nervous disorders received a 20-minute shiatsu massage (each hand was massaged for 10 minutes).
As a result, the degree of anxiety and pain was significantly reduced, recovery came faster.
It is explained by the fact that the pressure on the points causes the production of serotonin and dopamine hormones, which reduce anxiety, muscle tension also disappears, the heartbeat slows down, blood pressure and metabolism normalize.
Reducing back pain
Journal of Holistic Care(Journal of Holistic Nursing):
year 2001. 66 patients with low back pain received four sessions of shiatsu and reported their feelings 2 days after each session. All noted a significant reduction in pain and anxiety.
Massage technique
Active participation in shiatsu hand massage gives a predictable therapeutic effect: in the hands, fingers and in those organs with which the pressure zones are associated, the metabolism is also stimulated.
In addition, the fingers are connected directly to the brain by numerous nerve endings, and therefore shiatsu perfectly calms and relieves mental fatigue.
For pressure use:
the entire area of the fingertips
- large ones (Tokujiro considered them the most important and powerful tool of influence);
- three put together (index, middle and nameless);
- two fingers superimposed one on the other.
Palms.
Clicks do strictly perpendicular to the skin, without displacement and sticking, without "smearing".

"PRESSURE, not rub or massage!" - Namikoshi succinctly described the difference between his technique.
Pressing force
Moderate. The response should not cause discomfort and severe pain.
If you are massaging someone, take a position so that, if necessary, you can control the pressure with your own weight.
Feel
If the execution technique is correct, then numbness, aches, warmth or slight soreness occurs at the place of pressure.
Press duration
depends on the area of the body, health status and specific instructions for the procedure. Most often, single 3-second pressures are applied in the neck area, 5-7 seconds on other parts of the body.
Another option is also used: pressing lasts 1-3 breaths. Repeat the pressure 2-10 times.
How to find the right point
Anatomical landmarks are: bony protrusions and depressions, hair growth boundaries, skin folds, gaps between muscles and tendons, places where pulses can be felt on the arteries, etc. The point can be palpated by a tubercle or fossa.
Response sensations in it differ from other parts of the body.
Aches, numbness, tingling (like a weak current discharge), soreness, stiffness - these feelings are an indicator of the correct definition of a biologically active point.
Pain in BAT may indicate a pathology in the organ associated with it.
Preparing for a massage
Warm up your hands well: rub your palms and fingers together.
If you touch the body with cold hands, there are distorted reactions that can aggravate the condition of the disease. Cold is one of the most disease-causing factors.
It is undesirable to massage on an empty stomach (fainting is possible) and immediately after eating.
Longevity Point ZU-SAN-LI
Restorative paired point, belongs to the meridian of the stomach.
Synonyms: gui-se, xia-lin.
The miraculous properties of zu-san-li are mentioned in ancient medical treatises. This point is deservedly called the point of longevity, since it affects three levels of the body at once, which in ancient China correlated with Man, Heaven and Earth.
Through these three energy levels, with the help of very thin hormonal connections, all systems and organs are influenced, recovery processes are launched in them.
The list of indications is huge:
Zu-san-li - emergency point for fainting, postpartum shock, cerebral hemorrhage, sunstroke.
Located at the junction of the tibia and fibula.
How to find: put the center of the palm on the center of the patella, press your fingers to the lower leg (under its pad).
To make sure that the point is correctly determined, pull the foot up, a muscle tubercle should form under the ring finger. Lower your foot and a depression will appear under your toe. You have to click on it.

How to massage: press simultaneously on the points on both legs for 5-7 seconds, release for 2-3 seconds, repeat 3-4 times.
It is desirable to work with zu-san-li in the first half of the day, preferably before 10 am, when the stomach channel is most active. Massage in the afternoon and especially in the evening can provoke insomnia.
Even experts in oriental medicine advise using the first 8 days of the growth of the moon
Massage zu-san-li for a long time can increase pressure. Therefore, people prone to hypertension can be advised to massage the Yang Ling Quan point for similar purposes.
Summary
Shiatsu acupressure is an amazing technique: very simple, affordable and effective. Having mastered simple tricks, we can help ourselves in time and restore our health.
Watch for skin reactions, if in some place the skin starts to hurt, then there is a problem in the organ corresponding to this area.
Put your hand there and try to find the most painful point. This does not require an acupuncture atlas, the body itself indicates its location.
It is enough to apply 5-7 seconds of pressure with repetition a couple of times and throughout the day for the pain to subside. And this means that the process of self-healing is started.
And finally, advice from Tokujiro Namikoshi, who lived 95 years:
“To live a long and fulfilling life, avoid prolonged overwork and get enough sleep. While we are young, an 8-hour sleep removes the most severe fatigue like a hand.
Be sure to pay attention to - they are sure signs of prolonged fatigue and lack of sleep, which lead to serious health problems.
Be healthy!
Sources:
- Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine,
- US National Library of Medicine,
- Top10HomeRemedies.com
- P.V. Belousov "Acupuncture points of Chinese Zhenjiu therapy"
Elena Valve for the Sleepy Cantata project
In preparation: shiatsu for immunity, youthfulness of the face, for various problems.