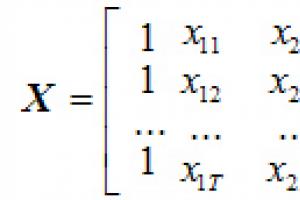Download stencils for wood milling. Homemade fixtures for a manual milling cutter. Learn how to operate a hand router. Step-by-step production of a template for furniture
In order to ensure the normal operation of the milling machine, it is necessary not only to properly handle the device used, but also to correctly use, in other words, devices for this tool to be able to form the workpiece in accordance with the requirements of the master (that is, cutting off the edges and other places of the material where it is needed, and not where "it happened"). So, it is precisely to give the processed material a clear planned form in the economy that "adaptations" for a manual milling cutter are used.
The complexity of making homemade devices
Often, manufacturers themselves complete their products at the production stage, but, alas, not every company will be able to please consumers with a complete set of all the necessary tools. And why do this if at any time you can make a suitable tool with your own hands in a garage environment. You can do this even without a preliminary drawing: their design is so primitive that even a novice master can cope with such work. To make a parallel emphasis or any other detail, it is enough to have a drawing of this device and a minimum set of tools with you. But if you want to make a homemade table for a manual router, you definitely cannot do without a drawing. It is necessary to calculate everything correctly, designate the dimensions of the table, and then proceed to work.
How to work with a manual router?
Before performing wood milling work, you need to make sure of the following:
- Is the cutter clamped in the collet.
- Whether the additional device installed on the workbench corresponds to its power and speed.
- Whether the required milling depth is set (when working with plunging devices, this indicator is measured using a special immersion limiter).
- When working with, make sure that a guide ring or bearing is installed that provides the desired trajectory of the device (in this case, the thickness of the cutter should be no more than three millimeters).

We pay attention to the supports for parts when performing work
When considering the question "how to work with a hand router" it should also be noted that the part you are processing must always have some kind of support. For example, before turning on the engine, the edge of the sole or the bearing is pressed against the guide piece or template. Only then the master turns on the machine and starts milling.
Below we will consider what are the devices for the router, and why they are special.
Parallel stop
The rip fence is one of the few devices that comes with every router. Therefore, there is simply no need for their independent development and manufacture. With regard to functions, with the help of the mentioned element, it is possible to make a reliable stop for the material being processed, thereby ensuring a rectilinear movement of the cutter relative to the base surface. The latter can act as a straight edge of a part, a guide rail or a table.

With this attachment for a handheld router, you can quickly edge and mill various grooves while holding the material almost in the “dead center” position.
Guide bar
This tool has similar functions to the previous one. Like the rip fence, the rail provides exceptionally smooth straight-line movement of the device. Working with a manual wood router using a guide rail can significantly reduce the time spent on processing a particular part. In addition, with the help of the specified equipment, it is possible to install the mechanism at almost any angle relative to the edge of the table.

In some cases, the design of the tools in question provides for the presence of special elements that facilitate certain operations (for example, it can be a function of cutting holes at the same distance opposite each other).
Copy rings and templates

Hand router fixtures such as copy rings are a round plate with a raised shoulder that can slide across the surface along the template, thereby providing an accurate path for the cutter. Often this element is attached to the sole of the workbench. There are several ways to install it:
- Screwing a ring into a threaded hole.
- Installation of special antennae of the device in the holes on the sole.
With a hand router attachment such as a template, you can also achieve more accurate and efficient work. The signified

element directly on the workpiece itself, after which both parts of the device are pressed against the machine using clamps. Upon completion of the work, experts recommend checking the condition of the ring - to see if it is securely pressed against the edge of the template or not.
Another feature of the tool under consideration is the possibility of processing not the entire edge, but only its corners. At the same time, some devices for a manual milling cutter allow you to make roundings of four different radii at once. Thus, the pattern-machining process is an excellent way to cut grooves for a part.
compasses
These home-made devices for a manual milling cutter are designed to move the entire machine along a certain circle. The design of this tool includes the main part (a compass, consisting of one rod), attached with its end to the base of the router, and a secondary one - a screw with a pin inserted into the hole of the machine. The value and is set directly by the displacement of the machine relative to the design of the device. Before starting work, it is necessary to carefully fix the tool to the base and make sure that the router is in good condition and functioning properly. It is worth noting that the most effective and easy to use is the compass, which has not one, but two rods at once.

Most often, this tool is made of transparent plexiglass. A small metric scale is additionally applied to its surface. It is worth noting that some models of compasses can have a circumference up to 150 centimeters long. With the help of such a device, you can easily make a round table top for several people.
However, back to the principle of operation. By means of the angular lever with an exact scale copying on preparation is carried out. Here you have the opportunity to center the ring directly under the cutter. The angle arm, which is complemented by a special support plate, also ensures precise edge milling.
The whole structure of this fixture consists of a base plate, a set of probes and a chip protection device.
Devices for copying identical devices and parts
This characteristic refers to a set of tools, consisting of an angle lever and special copy probes, which are needed to manufacture a batch of identical parts. Most often, such equipment is used in cases where there is a need to replicate small wooden devices. But before starting work with such a router, it is necessary to prepare in advance the scale of the angle lever (scale division - 1/10 mm).

After the scale is set, you will be 100 percent sure that the thrust ring is correctly centered under the cutter, the location of which depends on the values set on the angle arm. Also, this adjusting element can be equipped with a base plate and a special mechanism that protects the surface of the device from chips. The use of such parts will significantly speed up and secure the processing of the edges of products.
For full-fledged work with a manual router, in addition to the tool itself, the material and the corresponding set of cutters, it is necessary to have one more component - fixtures. In order for the cutter to form the workpiece in accordance with the master's intent - cutting the material exactly where it is required - it must be in a strictly defined position relative to the workpiece at any given time. To ensure this, numerous devices for a manual milling cutter serve. Some of them - the most necessary ones - are included in the instrument delivery set. Other milling devices are purchased or made by hand. At the same time, home-made devices are so simple that for their manufacture you can do without drawings, using only their drawings.
Parallel stop
The most used device, which comes with the kit for almost every router, is a parallel stop, which ensures the rectilinear movement of the cutter relative to the base surface. The latter can be a straight edge of a workpiece, a table or a guide rail. The parallel stop can be used both for milling various grooves located on the face of the workpiece, and for processing edges.Parallel stop for a manual router: 1 - stop, 2 - rod, 3 - router base, 4 - rod stop screw, 5 - fine adjustment screw, 6 - movable carriage, 7 - movable carriage stop screw, 8 - pads, 9 - screw stop stop.

To set the device in working position, it is necessary to push the rods 2 into the holes of the frame 3, providing the necessary distance between the support surface of the stop and the axis of the cutter, and fix them with the locking screw 4. For precise positioning of the cutter, you need to release the locking screw 9 and turn the fine adjustment screw 5 set the cutter to the desired position. For some models of the stop, the dimensions of the supporting surface can be changed by shifting or expanding the support pads 8.
If one simple part is added to the parallel stop, then with its help it is possible to mill not only straight, but also curved grooves, for example, to process a round workpiece. Moreover, the inner surface of the bar located between the stop and the workpiece does not have to have a rounded shape, repeating the edge of the workpiece. It can also be given a simpler form (Figure "a"). In this case, the trajectory of the cutter will not change.

Of course, the usual parallel stop, thanks to the recess in the center, will allow you to orient the router along the rounded edge, however, the position of the router may not be stable enough.
The guide bar is similar in function to the rip fence. Like the latter, it provides a strictly rectilinear movement of the router. The main difference between them is that the bar can be set at any angle to the edge of the workpiece or table, thus providing any direction of movement of the router in the horizontal plane. In addition, the tire may have elements that simplify the performance of certain operations, for example, milling holes located at the same distance from each other (with a certain step), etc.
The guide rail is attached to the table or workpiece with clamps or special clamps. The tire can be equipped with an adapter (shoe), which is connected to the base of the router with two rods. Sliding along the profile of the tire, the adapter sets the rectilinear movement of the cutter.
Sometimes (if the distance of the tire from the router is too close), the bearing surfaces of the tire and the router may be in different planes in height. To align them, some routers are equipped with retractable support legs that change the position of the router in height.
Such a device is easy to do with your own hands. The simplest option is a long bar fixed to the workpiece with clamps. The design can be supplemented with side stops.

By placing a bar on two or more aligned blanks at once, they can be grooved in one pass.

When using a bar as a stop, it is inconvenient to place the bar at a certain distance from the line of the future groove. This inconvenience is devoid of the following two devices. The first is made from boards and plywood fastened together. In this case, the distance from the edge of the stop (board) to the edge of the base (plywood) is equal to the distance from the cutter to the edge of the router base. But this condition is met only for a cutter of the same diameter.. Thanks to this, the device quickly aligns with the edge of the future groove.

The following fixture can be used with cutters of different diameters, plus when milling, the router rests with its entire sole, and not half, as in the previous fixture.


The stop is aligned along the edge of the hinged board and the center line of the groove. After fixing the stop, the folding board leans back, making room for the router. The width of the folding board, together with the gap between it and the stop (if any), must be equal to the distance from the center of the cutter to the edge of the router base. If you focus on the edge of the cutter and the edge of the future groove, then the device will work with only one cutter diameter.
When milling grooves across the fibers, at the exit from the workpiece, when milling an open groove, cases of wood scuffing are not uncommon. The following devices will help minimize scuffing, which press the fibers at the exit of the cutter, preventing them from chipping off the workpiece.


Two boards, strictly perpendicular, are connected with screws. Different cutters are used on different sides of the stop so that the width of the groove in the fixture matches the width of the groove of the part to be milled.
The other open slot milling fixture can be pressed tighter against the workpiece to further minimize tearing, but it only fits a single diameter cutter. It consists of two L-shaped parts connected on the workpiece with clamps.


Copy rings and templates
A copy ring is a round plate with a protruding collar that slides along the template and provides the necessary trajectory for the cutter. The copy ring is attached to the sole of the router in various ways: it is screwed into a threaded hole (such rings are in the photo below), the antennae of the ring are inserted into special holes on the sole or screwed.

The diameter of the copy ring should be as close to the diameter of the cutter as possible, but the ring should not touch the cutting parts of the cutter. If the ring diameter is larger than the cutter diameter, then the template must be smaller than the finished parts to compensate for the difference between the cutter diameter and the copy ring diameter.

The template is fixed on the workpiece with double-sided tape, then both parts are pressed with clamps to the workbench. When you have finished milling, check that the ring is pressed against the edge of the template during the entire operation.
You can make a template for processing not the entire edge, but only for rounding the corners. In this case, using the template shown below, it is possible to make roundings of four different radii.


In the figure above, a cutter with a bearing is used, but the template can also be used with a ring, only either the ring must exactly match the diameter of the cutter, or the stops should make it possible to move the template away from the edge by the difference in the radius of the cutter and the ring. This also applies to the simpler version shown below.


Templates are used not only for milling edges, but also for grooves on the plate.

The pattern can be adjustable.


Template milling is a great method for cutting grooves for hinges.


Devices for milling round and elliptical slots
Compasses are intended for the movement of a milling cutter on a circle. The simplest device of this type is a compass, consisting of one rod, one end of which is connected to the base of the router, and the other has a screw with a pin at the end, which is inserted into the hole that serves as the center of the circle along which the cutter moves. The radius of the circle is set by the displacement of the rod relative to the base of the router.
It is better, of course, that the compass was made of two rods.

In general, compasses are a very common device. There are a large number of branded and home-made devices for circumferential milling, differing in size and ease of use. As a rule, compasses have a mechanism that provides a change in the radius of the circle. Usually it is made in the form of a screw with a pin at the end, moving along the groove of the device. The pin is inserted into the center hole of the part.



When it is necessary to mill a circle of small diameter, the pin must be located under the base of the router, and for such cases other devices are used that are attached to the bottom of the base of the router.

Ensuring the movement of the cutter in a circle using a compass is quite simple. However, one often has to face the need to perform elliptical contours - when inserting mirrors or oval-shaped glasses, arranging arched-type windows or doors, etc. Device PE60 WEGOMA (Germany) is designed for milling ellipses and circles.


It is a base in the form of a plate, attached to the surface using vacuum suction cups 1 or screws, if the nature of the surface does not allow fixing with suction cups. Two shoes 2, moving along intersecting guides, ensure the movement of the router along an elliptical path. When milling a circle, only one shoe is used. The fixture kit includes two mounting rods and a bracket 3, with the help of which the router is connected to the plate. The grooves on the bracket allow you to install the router in such a way that its supporting surface and the base of the plate are in the same plane.
As you can see from the photos above, the milling cutter was used instead of a jigsaw or band saw, while, due to the high speed of the cutter, the quality of the machined surface is much higher. Also, in the absence of a manual circular saw, the router can replace it.
Devices for milling grooves on narrow surfaces
Grooves for locks and door hinges, in the absence of a milling cutter, are performed using a chisel and an electric drill. This operation - especially when making a groove for an internal lock - takes a lot of time. Having a milling cutter and a special device, it can be done several times faster. It is convenient to have such a fixture that allows milling slots of a wide range of sizes.To make grooves in the end, you can make a simple fixture in the form of a flat base attached to the sole of the router. Its shape can be not only round (according to the shape of the base of the router), but also rectangular. On both sides of it, you need to fix the guide pins, which will ensure the rectilinear movement of the router. The main condition for their device is that their axes are in line with the center of the cutter. If this condition is provided, the groove will be located exactly in the center of the workpiece, regardless of its thickness. If it is necessary to move the groove to one side or another from the center, a bushing with a certain wall thickness must be put on one of the pins, as a result of which the groove will shift in the direction from which the pin with the bushing is located. When using a router with such a device, it must be driven in such a way that the pins are pressed on both sides to the side surfaces of the part.

If you attach a second parallel stop to the router, you will also get a device for milling grooves in the edge.

But you can do without special devices. For the stability of the milling cutter on a narrow surface, boards are fixed on both sides of the part, the surface of which should form a single plane with the surface to be machined. When milling, the router is positioned using the parallel stop.

You can make an improved version that increases the area of \u200b\u200bsupport for the router.


Device for processing balusters, pillars and other bodies of revolution
The variety of work that is performed by a manual milling cutter sometimes dictates the need for independent manufacture of devices that facilitate the performance of certain operations. Branded devices are not able to cover the entire range of work, and they are quite expensive. Therefore, home-made fixtures for a router are very common among users who are fond of working with wood, and sometimes do-it-yourself fixtures either outperform branded counterparts or have no branded counterparts at all.Sometimes there is a need to mill various grooves in the bodies of revolution. In this case, the device shown below may be useful.




The device is used for milling longitudinal grooves (flutes) on balusters, poles, etc. It consists of a body 2, a movable carriage with a milling cutter 1, a disk for setting the angle of rotation 3. The device works as follows. The baluster is placed in the body and fixed there with screws 4. Turning to the desired angle and fixing the workpiece in a strictly defined position is provided by disk 3 and locking screw 5. After fixing the part, the carriage with the router is set in motion (along the guide rails of the body), and milling a groove along the length of the workpiece. Then the product is unlocked, rotated to the required angle, locked and the next groove is made.
A similar fixture can be used instead of a lathe. The workpiece must be slowly rotated by an assistant or a simple drive, for example, from a drill or a screwdriver, and excess material is removed by a milling cutter moving along the guides.
Stud milling fixtures
Tenon cutters are used for milling the profile of tenon joints. In the manufacture of the latter, greater precision is required, which is almost impossible to provide manually. Tenoning devices allow you to quickly and easily complete the profile of even complex joints such as dovetails.
The figure below shows an industrial sample of a tenoning device for the manufacture of three types of connections - "dovetail" (deaf and through version) and through connection with a straight tenon. Two mating parts are installed in the fixture with a certain shift relative to each other, controlled by pins 1 and 2, then they are processed. The exact path of the cutter is set by the shape of the groove in the template and the copying ring of the router, which slides along the edge of the template, repeating its shape.




When using the content of this site, you need to put active links to this site, visible to users and search robots.
To expand the functionality of a hand-held power tool, to make its use more convenient, comfortable and safe, devices for a manual milling cutter allow. Serial models of such devices are quite expensive, but you can save on their purchase and make devices for equipping a wood router with your own hands.
Different kinds of devices can make a truly versatile tool out of a hand router.
The main task that the devices for the milling cutter solve is to ensure that the tool is located in relation to the surface to be machined in the required spatial position. Some of the most commonly used attachments for milling machines are included as standard with such equipment. The same models that have a highly specialized purpose are purchased separately or made by hand. At the same time, many devices for a wood router have such a design that making them with your own hands does not present any particular problems. For home-made devices for a manual milling cutter, drawings will not even be required - their drawings will be quite enough.
Among the devices for a wood router, which you can make yourself, there are a number of popular models. Let's consider them in more detail.
Rip fence for straight and curved cuts
It is possible to ensure the stability of the router when processing narrow surfaces without special devices. This problem is solved with the help of two boards, which are attached on both sides of the workpiece in such a way as to form one plane with the surface on which the groove is made. The milling cutter itself, when using this technological method, is positioned using a parallel stop.
Probably, there is no such furniture maker who did not make a corner kitchen. Therefore, it’s not news to anyone that you can’t just join two countertops end-to-end. The fact is that the kitchen countertops - postforming - have a rounded front edge, and the rest are flat. If you attach a flat edge to a rounded one, you get a rather wide and deep seam.
To connect the worktops, there are special aluminum connecting strips. Such a bar has one side concave and the other flat, which ensures a snug fit to the postforming. All inexpensive kitchens use just such a connection. It is quite reliable, easy to install and inexpensive. But it is not without drawbacks, namely:
- The strap length is limited.
- A raised edge is formed on the table top.
- The aesthetic appearance leaves much to be desired.
That is, if we make the kitchen "above average", then the aluminum connecting bar will not be very useful. In this case, it is better to connect the countertops without a plank. Any reputable store offers countertops on just such a connection. But in order to connect them, you will have to cut at an angle of 45 degrees so that the front face converges, and this is also not very convenient for the following reasons:
- A sink can often be planned in the corner, requiring a single piece of slab.
- Explicit waste of material by as much as 600 mm (after all, you need to slaughter two parts, to the corner).
To avoid cutting parts along the entire bisector of the angle, you can (and should) apply the following trick: start the cut at an angle of 45 degrees, and after passing the bulge, turn it at a right angle. This can be done on a saw by fitting one part to the second, but it is more convenient to use a manual router and a special template.
Such templates are sold in hardware and tool stores and cost about 230 USD (for example, Virutex PFE60 furniture template for worktops). A little pricey for such a simple device. Therefore, we decided to try to create this furniture template with our own hands. A drawing and a file for a CNC machine were prepared. Then a test sample of MDF, 8 mm thick, was made on a CNC router. What came of it - watch the video.
In general, although not on the first try, I was more than satisfied. For 7 USD, we got a furniture template that allows you to trim the tabletops no worse than the firm one for 230 USD! At the moment, we have taken into account the revealed shortcomings, and the new drawing was made already taking them into account.
If you liked the template and would like to make something similar for yourself, I will explain how to do it.
- We measure the diameter of the ring on the router and the diameter of the cutter.
- Draw two lines intersecting at an angle of 135 degrees. The corner is smoothed with an arc. The arc must have the cutter radius minus the difference between the ring and cutter radii. That is, R1 = Rf-(Rk-Rf), where
Rf - cutter radius;
Rk is the radius of the cutter ring.
This will be the inner arc along which we mill the straight end of the postforming. When the ring passes along such a radius, the cutter, in turn, will describe an arc equal to its diameter. - From the lines we set aside two parallel lines, at distances equal to the diameter of the router ring plus 5 millimeters (it doesn’t matter how much, but a little more than the diameter), in the direction from the center of the previous arc, that is, as if outward.
- The intersection of the created lines is smoothed by an arc with a radius equal to the radius of the router stop ring. Moving along this contour, the cutter will no longer describe any arc. But since the contour will now be on the other side, and the cutter will be inside the corner, then in the place where it changes the trajectory, an arc will remain, with a radius equal to the radius of the cutter, that is, this contour will repeat the contour from point 2.
- The main part - the coincidence of radii and angle - is. Now you can draw two rectangles symbolizing the countertops and put them on this corner, and lengthen the lines as much as you need. It should be noted that the router ring is larger than the cutter, so the groove should decently extend beyond the countertops.
- You can put marks on the template so as not to suffer with a tape measure. Please note that the beginning of the upper and lower arcs of the contour do not match, so the marks for each part should be applied with an offset.
- The depth of entry of the contour into the countertop is 20 mm.
Well, such a general principle that allows you to create a furniture template for milling countertops. Please note that there is a play between the supporting char and the contours, so when milling, you need to press the router against the desired contour. We recommend milling in two passes, at half the depth.
If you are reluctant to develop a furniture template yourself, we suggest downloading ready-made drawings. These drawings of the furniture template are designed for a cutter with a diameter of 15.4 mm, and a thrust ring with a diameter of 23 mm. Unfortunately, this drawing will not work for other sizes, but if necessary, it can be taken as a basis. So, we offer the following files according to the template:
- Furniture template drawing in PDF format.
- Furniture vector template in CDR.
- Template model in T-Flex. By the way, in T-Flex the main dimensions - radii and some dimensions - are specified through variables. Therefore, those who work in this program can easily customize the furniture template for themselves by changing just two radii values in the variable table.
By the way, the drawings and files are submitted without taking into account the diameter of the cutter, which will make a template for countertops. But the machine operator himself will make all the corrections.
You can download the drawings and files of the furniture template for countertops from the link at the top of the page available to registered users.
Devices for a manual router
For many people, a router accessory is like a TV remote that has many buttons and functions, but most people only use a small portion of these buttons because they don't know or understand the many button options. The same position is with the milling cutter. Often this versatile tool is not fully utilized. Let's look at some of what a manual milling machine is capable of.
Indispensable assistants for a manual router
Fraser instead of a chisel
Usually, samples are made with a chisel. But if you have a milling cutter, then the selections can be made with a spiral cutter. Install the guide bush in the base of the router base according to the diameter of your cutter. Fix the template on the workpiece, and then slowly and with a not deep immersion of the cutter, moving the router smoothly, make a selection in the workpiece. It is troublesome, it is important that the conductor is constantly parallel to the workpiece, and for this, make a fixture, as shown in the photo.
Router guide
Usually, ready-made fixtures are already included with the router. One of them is a set of guide rods and a parallel stop. It serves both for making grooves, spikes, giving decorative patterns on the edges of the product and for many other purposes. In our case, oval recesses are made on the casing at the same distance between them, resembling antique columns in shape. The use of this conductor is simple and consists in parallel and perpendicular movement of the router on the workpiece. Setting up the conductor includes loosening the screws on the stop and router, setting the router in the right place, tightening the screws. Immerse the cutter to the desired depth and move the cutter with the stop to make a selection.

Inlay and application of text inscriptions
To write a variety of text and inlay with a router, you first need to apply marking lines, and then mill along the recess lines with a firm hand. One slip and you have the good fortune to start all over again. With the help of templates, a cutter with a guide bearing or a guide (copy) bush, you eliminate the possibility of deviating from the intended course, as shown in these photos.

Device for cutting inlay inserts.

Device with letter templates.
Milling cutter instead of a jigsaw
To cut a perfect circle with a router, make a small tool with a knife. The router is mounted on plywood with a "long arm" that rotates around a fixed point, as shown in the photo.

Having a milling machine, cutting round blanks without a jigsaw is not difficult.
Grooving tool
The design of the device for making grooves is shown in the photo.



With the help of this device, you can make grooves of the required size.
Calibration templates for milling cutters
Imagine a situation where you need to change the cutter, and then to continue the work you need to restore the height of the cutter. Make two calibration templates for cutters to be replaced.

You can make templates from medium density chipboard or hardwood. The thickness of the template must correspond to the thickness of the part of the product and have a length of at least one meter. Next, we insert a milling cutter into the router to make the first calibration template and do test milling. Having received a satisfactory result, make a template. Having the first calibration template available, install the second cutter in the router and substituting the first calibration template under it, raise the router to the desired height.

By changing the height of the router up or down, achieve the full coincidence of the router bit with the contours of the template, as shown in the photo and fix the height at the router. Check the settings made on the test rail, check the accuracy of the match between them. Having a satisfactory result, make a second calibration template.
Parallel Milling Attachment
If you need a large number of dovetail slots, or simple slots spaced at regular intervals, as shown in the picture, then a parallel milling fixture will come in handy.

This fixture saves time when setting slot spacings and will help you get more accurate cutter passes by fitting the fixture into the newly created slot. An important parameter in the settings is the manufacture of the first slot, it will ensure a uniform arrangement of all the slots.
Parallel milling fixture made of 12mm plywood. Cut the workpiece in the shape of a square measuring 200 x 200 mm. In the center of the workpiece, the auxiliary base, drill a hole for the cutter. Determine and mark the groove for the runner rail. The distance from the edge of the cutter to the slider will be the distance between the slots on the product. The rack-runner for adaptation is made of deciduous breeds of a tree.
For dovetail slots, first make the groove with a smaller diameter straight cutter, then finish the slot with a dovetail cutter.
Stop milling by stop block
It happens that it is not necessary to mill chamfers, profiles along the entire length of the part, and sometimes it is necessary to stop milling exactly in a certain place. For these purposes, a simple device is used - stop block, which can be installed on any workpiece.

Determine the distance to the point where milling on the workpiece will stop, determine the bearing radius, and add it to the extreme point. Install the stop block and press it against the edge of the workpiece as shown in the figure.
Control over fine details in milling
It is difficult to hold small parts in your hands when milling a product if the hole for the cutter does not match the diameter of the cutter, there is also a possibility that the workpiece will fall through and you can damage your fingers with the cutter.
First decision- drill a hole slightly larger than the diameter of the cutter, which will prevent the workpiece from falling into the hole.
Second decision- clamp the workpiece into the clamp. When clamping the workpiece, make sure that it does not have slopes and that it lies firmly on the milling table.

Narrow Edge Milling Attachment

Narrow edges are very inconvenient to mill with a manual router. To facilitate the work, make inserts-clamps. They can be made from waste wood. Place the fixing inserts on both sides between the shelves and squeeze them with clamps. Now you can mill any edge on all shelves.

If the router is not stable on the edges, place additional intermediate inserts inside the box and firmly clamp it again with clamps.
Device for marking and selecting grooves and slots
This attachment will help you quickly make router settings and cut grooves and slots exactly to size using a straight cutter of any diameter.
This fixture is made from two parallel strips of plywood or 3/4″ medium density chipboard. The size of the narrow strip is the length from the edge of the cutter to the edge of the sole of the router.

Lay the strips side by side and connect them with hinged loops. Install a straight cutter of the desired diameter in the router. Adjust the insertion depth of the cutter to the same depth as the slot. Now, on the working surface of the workpiece, with a pencil, mark the line of the beginning of each groove.

Align the mark and fixture with the folded strip on the workpiece and press firmly with clamps. Turn the strip over and mill the first slot. By setting the fixtures to the second mark, it will repeat the milling process.
Slider for quick settings
Two guides fixed on the rail-runner will serve you in the case when you need to restore all the settings after changing the cutter on the milling table. Let's say that a perfectly tuned fence was forced to move due to a change in the cutter. Save time on restoring the settings of the stop, the height of the bearing, you can easily do with this tool.

Before making any adjustments, install the slider in the slot on the table, align the movable rails with the stop and tighten the fastening nuts. Then remove the fixture from the table, move the stop and replace the cutter. Install the fixture parts in the slot, adjust the stop to align it with the guides and tighten the stop nuts. If your router table does not have a slider slot, use the front edge of the tabletop. Put the milled edge of the workpiece on the table, changing the height of the cutter to match the cutter and the pattern on the product.
Methods for adjusting the exact immersion of the cutter
Usually, restoring the old settings is troublesome and not rewarding, I offer two quick and easy ways to always accurately adjust the depth of cut on the milling machine.
First way. For settings, you can use drills of various thicknesses and accurately set the insertion depth of the cutter.

The second way. Make two slats of the same height and equal to the depth of the cutter.

Place the router on the rails and lower the router down until it touches the table top, tighten the stop rod on the router.
Insulating tape will increase the width of the groove
Sometimes, the width of the groove may differ slightly from the size of the cutter, and in order to widen the groove, it is necessary to adjust the distances of the fixture or ruler each time. As a rule, this creates big problems. Instead of these adjustments, I suggest adding strips of electrical tape to the edge of the base of the router. This will move the edge of the cutter slightly away from the edge of the slot and give you the opportunity to widen the slot if necessary. Four layers of blue tape will suffice.

How to make beautiful oval edges
Sometimes, for various reasons, it can be difficult to keep the base of the router even and without tilting in relation to the product, to create smooth and even edges, as shown in the figure.

An auxiliary stand for a router, fixed in any way possible, will help to make beautiful oval edges.

How to make beautiful oval corners
Rounding the corners on the product using a manual router does not always give a positive result. To get a nice, even oval, let's look at one of the ways, using an oval cutter with a small radius, and how to set it to always be at the same height for milling.
The same cutter radius on the milling table can be set using the fixture shown in the figure.

The device consists of two parts: a wooden corner, the edge of which is beveled for a specific cutter and a supporting block.
The corner and the block are fastened together with a clamp. By changing the height of the cutter above the table, achieve its exact match in height with the corner. Then set the fence flush with the milling guide bearing.
Start pin for smooth and safe milling
The hard and unsafe start of freehand milling can be changed using the start pin. It will help to smoothly bring the workpiece to the cutter at the beginning of milling.
The starting pin is set at a distance of 2? from the cutter. It can be made from brass or aluminum rod and securely mounted on the router table.

Prepare the part for milling and lay it on the table with one edge pressed against the pin, then slowly turn it towards the cutter with the bearing. When the cutter has completely milled the edge of the workpiece, continue to mill the entire workpiece, pressing it lightly against the start pin.
Use this method for milling small parts as well.
Enlargement of holes in two steps
You may need to enlarge the hole, or make a sweat over the round hole. This method can be used when you need to make a hole larger than the largest Forstner drill.
The hole enlargement method is performed in two steps:
Step 1. It is necessary to increase the size of the hole with a cutter for cutting quarters, the width of the quarter corresponds to the radius of the cutter, minus the radius of the bearing on the cutter. The bearing is in contact with the old edge of the hole.

Step 2 Turn the workpiece upside down and, using a straight cutter with a bearing, remove the rest of the edge until the bearing comes into contact with the new edge, as shown in the figure.

Part Support Block
The supporting block can be used as a perpendicular, stop and block. It will not only increase the accuracy of the cut, but also help to make perpendicular cuts, and also do the job of a trimming fixture.

The dimensions of the supporting block are shown in the figure.

Compound curve milling attachment
Templates help milling not only in a straight line, but also in curved milling. Templates will help you process complex oval shapes on the product, but for this, the bends of the template must match the radius of the guide bushing of the router.

Shown here is a fixture that allows you to mill a mirror image of a template onto a workpiece. The template is made of plywood or chipboard 12 mm thick. The size and shape of the roundings of the template are matched to the radius of the copying sleeve. The template on the workpiece is attached in any way possible. Then select the cutter with which you are going to make a copy of the template. It can be a straight cutter, an oval cutter or a combination of cutters.

This picture shows routing with the same template on a door infill. The same template will help you create patterns on the top of a table or countertop. There is only one requirement: The workpiece must have at least one straight edge to align the template.
Template for making pin holes
Drilling holes for shelf pins is a tricky job in any project. Having a template with marked holes, a router with a guide sleeve and a drill of the required diameter, it is not a problem to get exact copies of the holes. The template is made from a smooth double-sided strip of hardened hardboard 12 mm thick. The width and length of the template is made according to the size of the workpiece and the base of the router. Make markings on the template from lines for future holes. Make markings for the holes with a slight offset.
For example, the distance between the lines is 75 mm, the distance on the template, to the hole on the line, from one edge will be 1 1/4?, and from the other edge - 1 3/4?, which means the distance to the hole on one side of the workpiece , which we drill, will be equal to 1 1/4?, and on the other side, the holes already drilled are located at a distance of 1 3/4? respectively, as shown in the figure.

Then, using a drilling machine, drill evenly holes with a diameter of 3/4?, after drilling, fix the template on the product. Next, install a 3/4″ gauge bushing on the base of the router, install a 1/4″ straight cutter. into your router, set the drilling depth on the router. Insert a guide sleeve into each hole of the template and plunge the drill into the hole until it stops sinking. When you finish drilling a hole, move on to the next hole and repeat the steps until you are done.
Additional mounting plate for router
Mounting fixtures on a router or extending the base on a router requires precise positioning of the mounting holes.

Remove the plastic smooth overlay from the router, copy its dimensions and holes onto plywood or chipboard 12 mm thick. With a drill of smaller diameter, according to the marks of the holes for the bolts, drill the mounting holes. Check the size of the copy with the base size, if the copy and the original do not match, increase the diameter of the drill step by step until the holes match exactly. In the case when an exact copy is made, drill holes of the desired diameter.
Jointing on a milling table
A thin plastic (laminate) is attached to the receiving side of the router stop and works in the same way as the jointer receiving table. Adjust the laminate stop to be flush with the cutting edge of the cutter. Clicking on the part in the right half of the fence, move it in the direction of the cutter. With your left hand, press on the cut piece, against the laminate, to mill the workpiece.

Spacers for pattern milling
Milling the entire edge of the panel with a large cutter, in one pass, is a risky business. Gaskets glued to the stop on the milling table will help to gradually, without constant adjustments, get a beautiful and accurate pattern on the part. Adjust the stop in relation to the cutter so that this is the last milling step. Then make eight spacers from plywood with a thickness of not more than 5 mm, glue them with double-sided tape on both sides on the stop.

You need to mill all four edges of each panel, then separate the gasket from each side of the stop, as shown in the figure. Continue milling each panel until all spacers are removed. The last step is to mill the products without spacers on the fence.
Edge Removal Tool
This device will help to mill the remaining edges on the part, without the risk of damaging the workpiece.
We cut out a square base measuring 200 x 200 mm and 18 mm thick. Then, with a circular saw, make a cut in the center of the base, but with a depth of no more than half the thickness of the base. Make a rectangle measuring 100 x 200 mm. The thickness of the workpiece for stability can be increased. Glue it to the base flush with the cut as shown in the picture.

Drill a hole in the center of the base to match the diameter of the straight cutter you are using. Insert the cutter into the router and set to a shallow insertion depth. Make sure when test milling that a thin layer of edge remains on the surface. Clamp the workpiece in a vise, turn on the router and cut off the overhanging edge of the strip. Remove residue with a knife blade and sand with sandpaper.