How to calculate hourly wages. The use of an hourly wage system - what it is, pros, cons, payroll and advance payments using examples with formulas. What is included in the calculation
Question I am paid by the hour. How to calculate hourly rate from the minimum wage? 09:24:15, Dec 3. I have an accounting period of the month 09:24:26, Dec 3. It is clear that we must increase it. , 3 Dec. I have 183 hours in December 09:24:45, 3 Dec. In January 120? I'm asking about the dependence of the hourly rate on changes in the minimum wage. Answer Answer to the question: The salary of an employee who has worked the norm of time in a month and fulfilled labor standards (labor duties) must not be lower than the minimum wage. At the same time, there are no exceptions for any wage systems in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, the salary of employees who have an hourly rate cannot be less than the minimum wage.
How to calculate wages at an hourly rate, taking into account the minimum wage
The amount of monetary compensation will not be less than 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the amounts that were not paid on time, for each day of delay. The amount of compensation is calculated based on the amount of the surcharge laid down for handing over. Example 4 Compensation for delayed payment of additional payment up to the minimum wage Salary for May 2015 of a cleaner industrial premises O.L.
Important
Vasilyeva accrued in the amount of 4816 rubles. She is entitled to an additional payment up to the minimum wage in the amount of 1149 rubles. (5965 rubles - 4816 rubles). The salary was paid on time. The company transferred the additional payment after 30 calendar days from the date of issuance of the salary. The worker has no children. She is not entitled to income tax deductions.
How much O.L. Vasilyeva need to pay monetary compensation? Decision The refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia as of the date the compensation is charged is 8.25% (Instruction of the Bank of Russia dated September 13, 2012 No. 2873-u). The amount of the surcharge minus personal income tax is 1000 rubles.
TC RF). If the salary is below the minimum wage, you need to assign an additional payment to the minimum wage (Definition Supreme Court RF dated July 23, 2010 No. 75-B10-2). For part-timers, this rule applies in a special manner. With what minimum wage to compare When calculating with employees, accountants use two indicators of the minimum wage - federal and regional.
The regional minimum wage is established in the regional agreement. Employers are required to comply with its terms, unless they within 30 days in writing refused to join it. Thus, if your region has its own minimum wage (regional), the employee's salary must be compared with it (part 1 of the article).
11 art. 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, in Moscow, the minimum wage from June 1, 2015 is 16,500 rubles. (additional agreement of the Government of Moscow, Moscow associations of trade unions and Moscow associations of employers dated May 26, 2015 No. 77-783-1).
New minimum wage
- The salary level of employees of organizations located in the districts Far North and in areas with a similar status, without taking into account the district coefficient and the allowance for work experience, it should not be lower than the minimum wage (see section 1 of the Review of Practice, approved by the Presidium of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation on February 26, 2014).
Supplement to the minimum wage for an incomplete month worked The salary may be lower than the minimum wage if:
- the employee has a part-time / part-time working week (you can learn more about the various modes of organizing working time in our article “Working hours according to the Labor Code - types and features”);
- the employee works part-time.
In these cases, since the employee is underemployed, the remuneration he receives at the end of the month may be lower than the established minimum wage.
What regulates the minimum wage rate The way to control the earnings of citizens allows the state to guarantee the maximum minimum income for the employment of each citizen, regardless of education, length of service, working conditions, work experience. The amount of earnings not lower than the minimum wage regulates labor relations in each region of the federation. Supports the subsistence level of the able-bodied population.
Making an additional payment to the employee up to the minimum wage Those.
Hourly pay
Attention
He has the right to introduce any kind of changes, provided that they do not contradict the provisions of the labor code in accordance with article 9 of the Labor Code. The employer needs to develop a list of official documentation in order to make the transition to hourly wages. It includes the provisions:
- on the wage system;
- about the bodies that deal with self-government issues, for example, the school council, the academic council, the governing council;
- on the distribution of the incentive part of the fund, from which the work of employees will be paid.
In addition to these documents, a regulatory and local act of the enterprise, a new staffing table are to be developed.
When preparing the above documentation, it is necessary to follow the requirements of legal, regulatory enactments federal significance, labor law.
Hourly wages of employees
- New minimum wage
- 502 bad gateway
- What is the dependence of the hourly tariff rate on changes in the minimum wage?
- How to pay extra to the minimum wage when combining and part-time (non-grebetskaya o.v.)
- Supplement to the minimum wage from 2018
- Hourly pay
- Is the district coefficient included in the minimum wage?
- Making additional payments to the employee up to the minimum wage
New minimum wage At the moment, I can offer the following reflection in the service: Set a monthly salary for employees - in proportion to the number of shifts / hours set by him for a month.
The procedure for additional payment to the minimum wage in 2018 (nuances)
For a non-lawyer: This means that the regional cost of living figure is not required when compiling staffing? The most important thing is that the monthly salary should not be lower than the regional minimum wage? Even if the regional minimum wage is below the regional subsistence level? #11 IP/Host: 10.214.28. Date of registration: 02/09/2015Posts: 17,889 Re: Wage below the minimum wage with a schedule of "day after three" Does this mean that the figure of the regional subsistence minimum is not required when drawing up the staffing table? Yes. as well as the minimum wage is optional when compiling the SHR. The most important thing is that the monthly salary should not be lower than the regional minimum wage? Yes, if the month is fully worked out.
Even if the regional minimum wage is below the regional subsistence level? Yes. And there is no magic in the world, baby. There is only sensitivity, kindness and sensitivity, and also the ability to see through (s).
Additional payment up to the minimum wage in order to comply with legal requirements
Question: At the beauty salon, employees go out on appointment, they do not work all day. Is it possible to pay them an hourly rate of 100 rubles per hour. If we calculate the cost of an hour based on the minimum wage for Moscow = 15,000 rubles (minimum wage) / 160 working hours = 93.75 rubles.
minimum hourly rate. Monthly wages will be based on hours worked. In some cases, the monthly amount, if the master has worked a small number of hours, may be less than the Moscow minimum wage. Wouldn't this be a violation of the law? Answer: With time / hourly wages, the employee's earnings are determined based on the time actually worked by him and the tariff rate (salary). The tariff rate is understood as the amount of remuneration for labor per unit of time (hour, day, month). To record the working time of employees with hourly pay, it is necessary to establish a summarized time record.
In this case, the amount of the surcharge will be different every month. The algorithm for calculating it is simple: first, the amount of salary for the month is determined based on the work performed, hours worked, etc. actual data, and the system of remuneration adopted in the organization. Then the resulting size wages compared with the established minimum wage.
If the minimum wage is higher, the additional payment is determined as the difference between the amount of the salary received and the minimum wage. Details in the materials of the System Personnel: 1. Magazines and books: Salary July 7, 2015 Payments to employees How to pay extra to the minimum wage when combining and part-time O.V. Negrebetskaya, an expert of the Zarplata magazine - Two indicators of the minimum wage - Important differences between part-time jobs and part-time jobs - How to calculate the additional payment to the minimum wage when combining and part-time jobs The Labor Code has a rule - if an employee has fully worked for a month, his salary must be at least the minimum wage (part 3 Art.
18.03.2016
Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that, with properly executed legal acts and prescribed terms of the agreement, each employee has the right to arrange work with payment for one hour, day and month. The employee has the right to receive payment calculated on the basis of established criteria, without any restrictions.
The minimum hourly minimum wage will determine the minimum allowable cost of one hour of work.
The issue of the minimum hourly wage has not been resolved by law. The practice of labor law and judgments has long required changes to the minimum wage and the calculation methodology, and in particular the methodology for calculating hourly wages.
How much is the hourly minimum wage
The planned hourly minimum wage will be 100 rubles. and is planned for use since 01/01/2017, but when it will be accepted is not clear. It is also possible to adjust this indicator according to territorial, sectoral and professional criteria.
If the minimum wage for one hour significantly exceeds the minimum wage per month, it is not clear how to proceed in this case, but the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not limit the maximum payments.
History issue in government
- In 2017, the draft law on the hourly MTROT was rejected by the Government of the Russian Federation, so, when setting a monthly salary for an employee, it will turn out that its size will not depend on the number of working hours in a month, however, the cost of an hour of his working time will change monthly. Therefore, since monthly tariff rates and salaries are more common, it is more rational to apply the monthly minimum wage.
- In June 2017, amendments were made to the labor code: norms according to which an employee working on a part-time basis can be set an irregular working day only if an agreement between the parties to the employment contract establishes a part-time working week, but with a full working day.
The amendments also affected Art. 152 and 153 of the Code, they specify the procedure for accounting for work performed in excess of the norm of working time on weekends and non-working holidays, when calculating the duration of overtime work payable at an increased rate.
Time / hourly wages are not prohibited
With time / hourly wages, the employee's earnings are determined based on the time actually worked by him and the tariff rate (salary). This type of activity refers to a time-based type of earnings and is also subject to mandatory official registration and regular payment of funds. The peculiarity of this type of work is that the calculation of wages is made from the actual number of hours worked. Such a condition is mandatory prescribed in the contract, based on the provisions of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The tariff rate is understood as the amount of remuneration for labor per unit of time (hour, day, month).
To record the working time of employees with hourly pay, it is necessary to establish a summarized time record. When setting the length of working time for the accounting period (month, quarter or other periods, but not more than a year), it should be borne in mind that it should not exceed the normal number of working hours - 40 hours per week.
Accounting period: month, quarter, half year, year, the employer needs to set it on his own.
In which case does it apply
Hourly pay is ideal for part-time employees. It is suitable for employees whose workload varies on different working days. We recommend not hiring with hourly pay, but hiring under GPC agreements, for a certain type of work, and it is more profitable in terms of taxes.
How to reflect
Before applying the hourly wage system, it is necessary to fix this rule in the following documents:
- labor agreement;
- staffing table;
- order.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the hourly payment system:
- for the employer- cost savings when employees receive money only for the hours actually worked, the ability to track and monitor the effectiveness of working hours, the convenience of settlements with part-time workers;
- for employees- convenient for employees of certain professions, as it allows you to take into account their uneven workload.
Minuses:
- for employers- the complexity of the financial calculation of wages, the need to strictly control the amount of time worked by employees;
- for employees- the absence of bonuses and bonuses, the possibility of abuse by an unscrupulous employer who will set unrealistic amounts of work for one hour.
Hourly payment in accordance with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation can be:
- Simple. This system is most often used in the public sector. Only the amount of time worked is paid.
- Premium simple. The amount of payment of funds includes both the time worked and the quality of the tasks performed. The amount depends on the rate and calculation of the premium.
- Normalized. This type of payment of funds is based on the fulfillment of the established norm.
Note that the norm of working hours in each month is different, it is determined by the production calendar.
So, for example, in May the norm of working hours is 143 hours, in June - 167 hours. It is for the norm of working hours according to the production calendar that the salary should be set not less than the regional minimum wage. But this applies only if the employee has fulfilled the established norm of working hours.
If the employee has worked fewer hours. In this case, the employee's salary is determined in accordance with his qualifications and the number of hours worked.
It should be emphasized that the minimum wage is provided to an employee who has fully worked out the norm of working time. Part-time wages may be less than the minimum wage.
If an employee wants to work and receive a salary for each period worked, on the basis of Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, he has the legal right to draw up an agreement with payment for each hour. To do this, the employer and employee must establish and prescribe the features of this type of earnings on a mutual basis.
The correct way to complete the contract is as follows:
- The tariff rate for hourly activity is fixed, taking into account the minimum wage indicators.
- The level of income is prescribed in the process of multiplying the rate and the hours worked.
- Information is registered that relates to holidays, weekends and sick days.
) the calculation of the salary paid to the employee for the performance of a certain amount of labor duties (labor standards) at the specified time is made. This type payment is fixed and is the minimum guaranteed amount accrued for work. It is fixed at the request of the law in the employment contract, along with other conditions.
Tariff rates depending on the time period are divided into monthly, daily and hourly.
Dear readers! Each individual case is individual, so you can check with our lawyers for more information.Calls to all numbers are free.
What might be needed?
May be needed for:
- calculation of salaries for employees with summarized working hours;
- calculation of payment for;
- determining the amount of payments on weekends and holidays;
- payment ;
- payment calculation for .
The calculation of the hourly tariff rate is necessary for the summarized accounting of working hours.
Such accounting is used for a shift work schedule introduced by the organization, when it is impossible to interrupt production activities for general weekends.
At the same time, each employee has a work schedule and an hourly rate, which he must work out in a certain period of time. Schedules and norms are reflected in production calendar. The time of work in such a schedule is measured in hours, so it is most convenient to calculate the minimum wage for work exactly per hour. In the case when the employee exceeded his norm (worked large quantity hours), it is necessary to calculate the hourly tariff rate and make the corresponding surcharges.
In state-owned enterprises, employees often receive 13 salaries. How its size is determined, you can find out from.
Calculation methods
Depending on the norm of working hours in a month
The formula applied is:
T/h = tariff rate per month: norm of hours (per month)
The norm of hours per month must be taken from the production time sheet-calendar.
Inshina N.N. works in OAO Topol as a salesman on a shift schedule. The salary per month is 20,000 rubles. The production calendar indicates the hourly rate per month - 160 hours. In October 2015, she worked 166 hours.
In order to calculate wages, it is necessary to take into account processing.
- First, the hourly rate is calculated according to the formula: 20,000 rubles: 160 hours = 125 rubles per hour.
- We calculate processing time: 166 - 160 = 6 hours.
For these six hours worked overtime, Inshina needs to accrue a salary supplement. According to labor law, the first two hours of processing are paid with a coefficient of 1.5, the next - in double the amount:
125 rubles × 2 × 1.5 + 125 rubles × 4 × 2 = 375 rubles. + 1000 rub. - overtime pay. We add them to the salary and get Inshina's salary for October: 20000 + 1375 = 21375 rubles.
If, for one reason or another, an employee has worked fewer hours than the norm, then the daily working rate is calculated and multiplied by the number of hours worked.
Kulagin K.K. at work on a shift schedule has a monthly salary of 15,000. In June, its norm is 150 hours. He worked 147 hours this month.
In order to calculate salaries, the accountant makes calculations:
- Determines the hourly rate: 15,000 rubles: 150 hours = 100 rubles/hour.
- Now you just need to multiply the resulting amount by the number of hours actually worked: 100 rubles per hour * 147 = 14,700 rubles.
This is a fairly simple calculation, however, it has a drawback. The tariff rate depends on the hourly rate, which can be different every month. And the lower the rate of hours, the higher the hourly rate. It turns out that the employee worked less in one month than in another, and will receive a higher salary than in the month in which he worked more.
Savushkin L.L. works as a security guard. He has a flexible work schedule. His salary is 19,000 rubles a month. In accordance with the production calendar, in February the norm of hours is 150, in March - 155 hours. In February, Savushkin worked 149 hours, in March - 151 hours.
February salary will be:
- We determine the hourly tariff rate: 19,000 rubles: 150 hours = 126.66 rubles per hour.
- We multiply the result by the time worked: 126.66 rubles / hour * 149 hours = 18872 rubles 34 kopecks.
March salary:
- Hourly rate: 19,000 rubles: 155 hours = 122.58 rubles / hour
- 22.58 rubles / hour * 151 hours = 18509 rubles 58 kopecks.
It turns out that Savushkin, in fact, worked two hours less in February than in March, but his salary turned out to be 362 rubles 76 kopecks.
Depending on the average monthly number of working hours per year
The formula applied is:
T/h = tariff rate per month / norm of working hours per year: 12 months
The norm of working hours is also taken from the production calendar.
Seller Lavrova E.N. works by . The monthly salary is 21,000 rubles. According to her schedule, she worked 120 hours in July 2015.
- We calculate the tariff rate per hour according to the formula: 21,000 rubles / 1890 hours: 12 months = 133 rubles 33 kopecks.
- We determine the salary for July: 133.33 rubles * 120 hours = 15999 rubles 60 kopecks.
This method of calculation allows you not to calculate the hourly rate on a monthly basis, but only once a year. And she will not change all this time. So the employee will receive an amount that directly depends on the amount of time actually worked.
Watchman Kravtsov P.P. works in shifts. His salary is 12,000 rubles a month. In March 2015, the watchman worked 120 hours, in April - 130 hours, in May - 110 hours. The norm of working hours for 2015 is 1800 hours.
The calculation of wages at any commercial or state enterprise occurs in accordance with the legislative acts in force at a given time. Its amount depends on the official salary prescribed in the employment contract, the hours worked during a certain period and other details. The amount due for payment is calculated by the accountant on the basis of a number of documents.
What is included in the calculation?
To date, two types of payment are most often practiced:
- Time . The first provides for a salary determined by the contract for the hours worked - an hour, a day, a month. Often a monthly rate is practiced. In this case, the total amount depends on the time worked during a certain period of time. It is mainly used in the calculation of salaries for employees who do not depend on the amount of the created product - accountants, teachers, managers.
- piecework . Depends on the amount of product created for a certain period. Often used in factories. It has several subspecies, which we will consider a little later.
So, time wages provide that the head of the enterprise or other executive are required to maintain and complete a time sheet. It is issued in the form No. T-13 and is filled out daily.
It should note:
- the number of working hours worked during the day;
- exits "at night" - from 22:00 to 6:00;
- out of hours (weekends, holidays);
- omissions due to various circumstances.
Piecework payment includes route map or order for a certain amount of work. In addition, the following are taken into account: sick leave, orders for bonuses, orders for the issuance of material assistance.
After hiring, each accountant must keep an analytical record of wages and record it in the form No. T-54. This is the so-called personal account of the employee. The data specified in it will be taken into account when calculating hospital payments, vacation and other types of benefits.
You can find out how vacation pay is calculated.
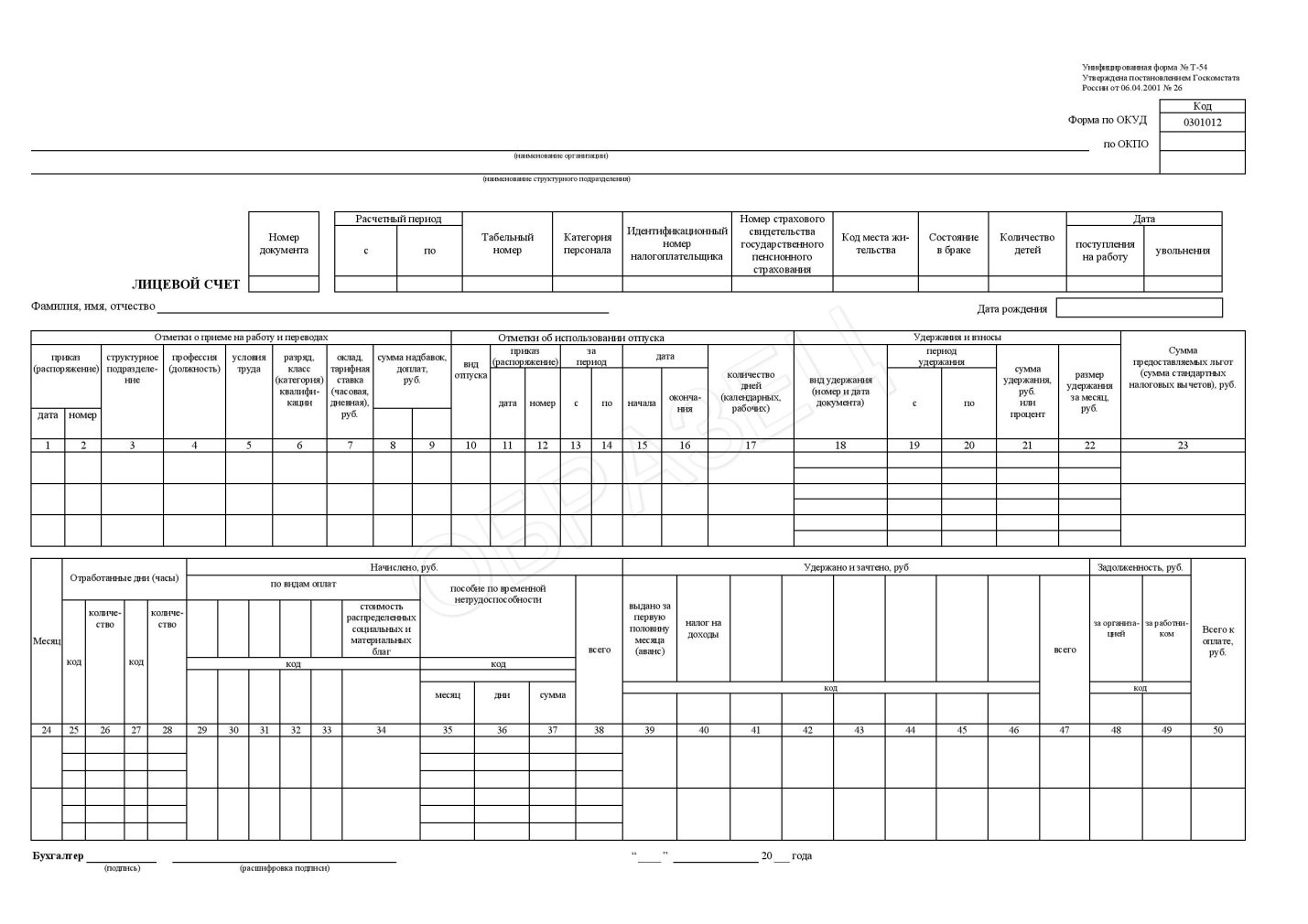
Calculation formula and examples
Hourly pay provides for remuneration according to the time worked and the salary of the employee.
It is calculated as follows:
For monthly salary:
ZP \u003d O * CODE / KD, where
- O - fixed monthly salary;
- CODE - days worked;
- CD is the number of days in a month.
For hourly/daily fixed salary:
ZP \u003d KOV * O, where
- ZP - wages excluding taxes;
- KOV - the amount of hours worked;
- O - salary per unit of time.
Consider an example:
Tatyana Ivanovna has a monthly salary of 15,000 rubles. There were 21 working days in a month, but since she took a vacation at her own expense, she worked only 15 days. In this regard, she will be paid the following amount:
15,000*(15/21)=15,000*0.71= 10,714 rubles 30 kopecks.
Second example:
Oksana Viktorovna works with a daily salary of 670 rubles. This month she worked 19 days. Her salary will be:
670 * 19 \u003d 12,730 rubles.
As you can see, the formula for calculating wages for this type of payment is very simple.
Piecework payment - how to calculate?
With piecework wages, the amount of work performed is paid. At the same time, prices are taken into account in the ratio of the volume of work.
With piecework wages, wages are calculated according to the following formula:
ZP \u003d RI * CT, where
- RI - prices for the manufacture of one unit;
- CT - the number of products produced.
Consider the following example:
Ivan Ivanovich produced 100 engines in a month. The cost of one engine is 256 rubles. Thus, in a month he earned:
100 * 256 \u003d 25,600 rubles.
piece-progressive
It is worth considering separately such a type of payment as piecework-progressive, in which the price depends on the number of products produced for a certain period.
For example, if an employee produces 100 engines per month, then he receives 256 rubles for each. If it exceeds this norm, that is, it produces more than 100 engines per month, the cost of each engine produced in excess of the norm is already 300 rubles.
In this case, earnings for the first 100 engines and separately for subsequent ones are considered separately. The amounts received are cumulative.
For example:
Ivan Ivanovich made 105 engines. His earnings were:
(100*256)+(5*300)=25,600+1,500= 28,100 rubles.
Other payment systems and their calculation
Depending on the specifics of the work, payment can be:
- chord . Often used when paying for the work of the brigade. In this case, the salary of the brigade as a whole is calculated and issued to the foreman. The workers divide the amount received among themselves according to the agreement existing in their brigade.
- Payment based on bonuses or interest . A bonus or commission system is applied to employees on whom the company's revenue depends (see also). Quite often it is applied to sales consultants, managers. There is a constant, fixed rate and a percentage of sales.
- shift work . The shift method of work provides for payment according to the employment contract - that is, by the time or for the amount of work performed. In this case, there may be interest allowances for difficult working conditions. For exits on non-working days, holidays, payment is calculated in the amount of at least one daily or hourly rate on top of the salary. In addition, an allowance is paid for the shift method of work from 30% to 75% of the monthly salary. The interest rate depends on the region in which the work takes place. For example, Ivan Petrovich works on a rotational basis. His monthly rate is 12,000 rubles, the allowance for work in this region is 50% of the salary (O). Thus, his salary will be 12,000 + 50% O \u003d 12,000 + 6,000 \u003d 18,000 rubles per month of work.
Payment for holidays and night shifts
When working in shifts, each shift is paid depending on the tariff rate of each shift. It is either established by an employment contract or calculated by an accountant.

At the same time, it should be borne in mind that weekends and holidays are paid at a higher rate - an increase in the rate by 20%. In addition, exits at night from 22:00 to 06:00 are also subject to a rate increase of 20% of the cost of an hour of work.
payroll taxes
When calculating wages, do not forget about taxes. Thus, the employer is obliged to pay 30% of the amount of calculated wages to the insurance premium fund.

In addition, employees are charged 13% of their wages in personal income tax. Let's take a look at how taxes are calculated.
First of all, the tax is charged on the entire amount of wages, except for cases in which there is a tax deduction. So, a tax deduction is calculated from the total amount of wages, and only then the tax rate is calculated on the resulting value.
The right to a tax deduction has a number of socially unprotected categories, the list of which is prescribed in article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These include:
- Veterans of the Great Patriotic War, invalids, whose activities were connected with nuclear power plants. The tax deduction is 3000 rubles.
- Disabled people, participants of the Second World War, military personnel - 500 rubles.
- Parents who are dependent on one or two children - 1,400 rubles.
- Parents who are dependent on three or more children - 3,000 rubles.
The last two categories are restricted. So, after the amount of wages received from the beginning of the calendar year reaches 280,000 rubles, tax deduction does not apply until the beginning of the next calendar year.
Example:
Ivan Ivanovich's monthly salary was 14,000 rubles, since he worked for a full month. He received a disability while working at a nuclear power plant. Thus, his tax deduction will be 3,000 rubles.
The personal income tax is calculated for him as follows:
(14,000 - 3,000) * 0.13 = 1430 rubles. This is the amount that must be withheld when receiving wages.
Thus, he will receive in his hands: 14,000 - 1430 \u003d 12,570 rubles.
Second example:
Alla Petrovna is the mother of two minor children. Her salary is 26,000 per month. By December, the total amount of wages paid to her will be 286,000 rubles, therefore, no tax deduction will be applied to her.
Payment procedure and calculation of delays
According to all the same legislation, wages must be paid at least 2 times a month. Allocate an advance, which is issued in the middle of the month and the actual salary.

The advance payment averages from 40 to 50% of the total amount of payments, at the end of the month the rest of the payments are issued. Usually this is the last day of the month, if it falls on a weekend - the last working day of the month. In case of untimely calculation of wages, the employer is obliged to pay a fine.
In addition, compensation is provided for the employee, which is issued at his request and amounts to 1/300 of the rate for each day of delay.
Video: Simple payroll
Familiarize yourself with the basic nuances of calculating and calculating wages. An experienced accountant will tell you how to correctly calculate wages, depending on the wage system you choose.
The calculation of wages is made by an accountant on the basis of a number of documents. There are two main systems of remuneration: piecework and time. The most popular is the time-based wage system - it is quite simple and is used in most industries.
The system of remuneration in the company is established by collective agreements, industry and regional agreements, local regulations, regulations, in accordance with labor law.
The division of wage systems into subspecies is rather conditional. Usually there are several forms of wage systems:
Time-based - the salary of an employee depends directly on the hours worked. Fixed rate can be hourly, daily or monthly;
- Piecework - the salary of an employee depends on the amount of work that he performed;
- Commission is a remuneration system in which an employee receives a commission (percentage) from a fixed indicator. For example, 10% of the outlet's revenue per day;
- A floating salary system is a system in which an employee's salary can be changed periodically - for example, once a quarter or once a month. Changes may depend on the implementation of the work plan or other indicators;
- Piece-by-piece - when using such a system of remuneration, the employee's salary will depend on the set of works performed by him (in accordance with the piece-by-piece task) for a certain period of time.
Hourly wages are one of the options for hourly wages. The wages of a worker depend on the number of hours the worker actually worked.
Which employees should be paid hourly wages?
Under certain conditions, the use of hourly wages is very beneficial for the employer: only the time that the employee is directly engaged in work is paid, it is convenient to calculate wages for part-time workers.
For example, these could be:
- Workers with an uneven workload - for example, promoters involved in work at a particular facility
- Workers whose working time is difficult to standardize - for example, teachers who lead extra classes in training centers;
- Flexible workers who combine multiple jobs;
- Employees whose labor productivity is required to be determined high costs or very difficult.
Employers should take into account that if an employee has worked the norm of working time for a month (based on 40 hours per week), then the salary of this employee cannot be less than the established minimum wage.
How do you calculate hourly wages?
If the employee is "sitting on a salary", then his salary is fixed subject to the worked time norm (usually a 40-hour work week). The employee will receive a salary of a certain amount for the worked time norm, regardless of the number of working days according to the schedule according to



