Using a heat exchanger in a heating system
Heat exchangers are among the main elements of the heating system. The functions of such a heating unit are numerous and very important, because the purpose and design of the boiler used directly depends on this device.
Through the heat exchanger, the generated energy is directly transferred from the combustible to the heat exchanger itself.
What is a modern heat exchanger made of?
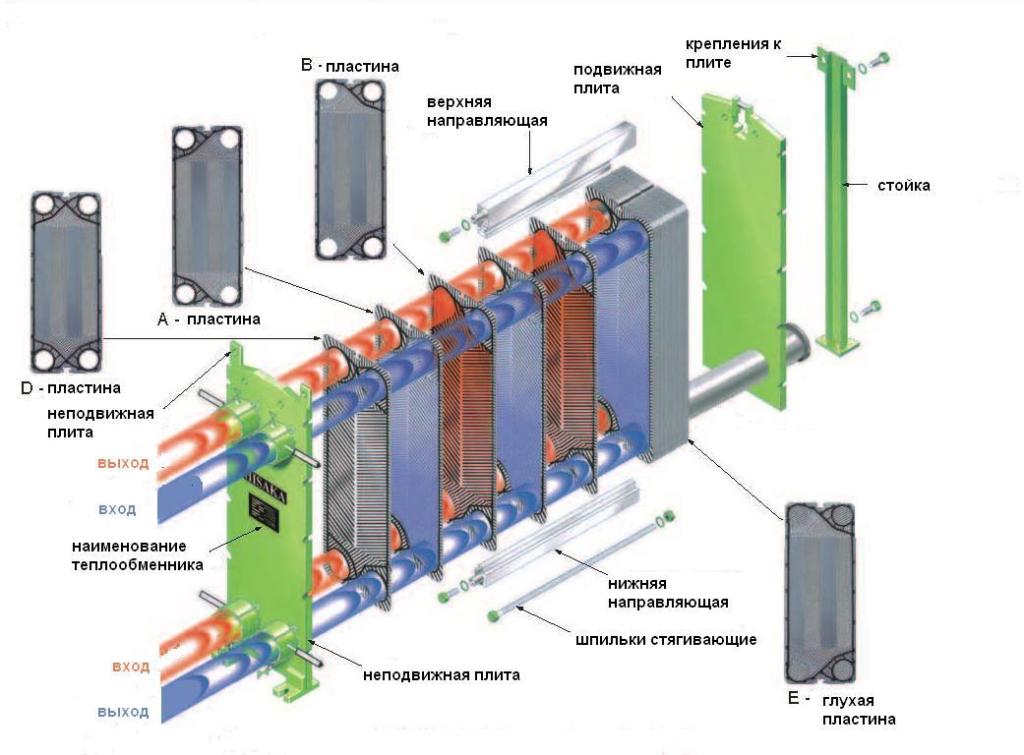
A modern type heat exchanger consists of several parts, each of which plays its own important role:
- a fixed plate, to which all inlet pipes are connected;
- pressure plate;
- heat transfer plates with inserted gaskets of sealing type;
- top and bottom guides;
- rear rack;
- threaded pins.
This image shows a shell and tube heat exchanger.
Thanks to this unique design, the heat exchanger is able to provide the most efficient layout of the entire surface of the heat exchanger used, which makes it possible to create a small heating apparatus. Absolutely all the plates in the assembled package are the same, only some of them are turned to the other at an angle of 180 degrees. That is why channels must be formed during the necessary contraction of the entire package. It is through them that during the heating process the working fluid flows, which takes part in heat transfer. Thanks to this arrangement of the elements of the system, the correct alternation of channels is achieved.
Today, we can safely say that plate-type heat exchangers are more popular due to their technical characteristics. The key element of any modern heat exchanger is the heat transfer plates, which are made of steel that is not subject to corrosion, the thickness of the plates is in the range from 0.4 to 1 mm. For production, a high-tech stamping method is used.
During operation, the plates are pressed against each other, thereby forming slotted channels. The front side of each of these plates has special grooves, where a rubber contour gasket is specially installed, which ensures complete tightness of the channels. There are four holes in total, two of them are necessary to ensure the supply and removal of the heated medium to the channel, and the other two are responsible for preventing cases of mixing of the heating and heated media. In the event of a break in one of the small circuits, the plate heat exchangers are protected by drainage grooves.
If there is a large difference in the flow rate of the media and a very small difference in the final temperatures, then it is possible to reuse the heat exchange process, which will occur through a loop-like flow direction.
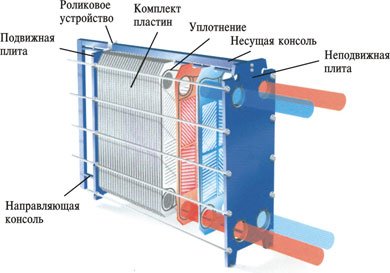
Used heat transfer scheme
Scheme of the device of a plate-type thermal unit.
Plate heat exchangers provide such a heat exchange scheme in which the liquids move towards each other, that is, in a constant countercurrent. In those places where they flow, as a rule, a steel plate or a special double rubber seal is installed. So you can achieve a complete elimination of mixing of liquids.
The type of plate corrugation used, as well as their required number, which is installed in the frame, depends on the operational requirements for a plate heat exchanger. The material used to make the gaskets can vary. It depends on the conditions of use of the heat exchangers themselves. Usually, various polymers are used in the manufacture, which are based on synthetic or natural rubbers.
Plate Heat Exchangers: Applications
Plate heat exchangers are used in the home heating system, hot water supply, air conditioning systems in large cottages, schools, gardens, swimming pools, in entire microdistricts, as well as in the heating system of rural houses. Plate heat exchangers are widely used in the food industry.
Heat exchangers for heating have a number of undeniable advantages compared to other devices used to create a suitable microclimate.
Such heating devices have a number of advantages over other types.
Positive traits
Among the main positive qualities of a device that provides heating, the following can be noted:
- high level of compactness;
- plate heat exchangers have a high heat transfer coefficient;
- the heat loss coefficient is as low as possible;
- pressure losses are at a minimum;
- installation and adjustment, repair and insulation works require low financial costs;
- in case of possible clogging, this device can be disassembled, cleaned and reassembled by just two workers in 4-6 hours;
- it is possible to add power to the plates.



