How to choose the right heat pump? Heat pump for home heating: how to choose an efficient heat pump
A heat pump is a device that can provide your home with heating in winter, cooling in summer, and hot water all year round.
A heat pump uses energy from renewable sources - heated air, earth, rock or water - to produce heat energy. This transformation is carried out with the help of special substances -.
How a heat pump works
Structurally, any heat pump consists of two parts: the outer one, which "takes" the heat from renewable sources, and the inner one, which gives this heat to the heating or air conditioning system of your home. Modern heat pumps are characterized by high energy efficiency, which in practical terms means the following - the consumer, i.e. the owner of the house, using a heat pump, spends on heating or cooling his home, on average, only a quarter of the money that he would spend if there was no heat pump.
In other words, in a system with a heat pump, 75% of useful heat (or cold) is provided by free sources - heat from the earth, groundwater or heated indoors and used air thrown out into the street.
Consider how, perhaps, the most popular heat pump in everyday life, which operates due to the heat of the earth, works. The heat pump works in several cycles.
Cycle 1, evaporation
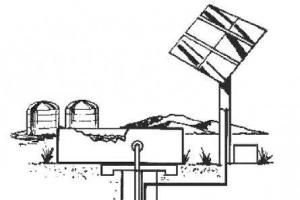
The outer part of the "earth" heat pump is a closed system of pipes buried in the ground to a certain depth, where the temperature is stable all year round and is 7-12°C. In order to "collect" enough energy from the earth, it is required that the total area occupied by the underground pipe system be 1.5-2 times the entire heated area of the house. These pipes are filled with refrigerant that heats up to ground temperature.
The refrigerant has a very low boiling point, so it can go into a gaseous state even at ground temperature. Further, this gas enters.
Cycle 2, compression
It is this compressor that consumes all the energy necessary for the operation of the heat pump, but compared, for example, with heating from, these costs are noticeably lower. We will return to the comparison of costs later.
So, heated to a temperature of 7-12°C, the gaseous refrigerant from underground pipes in the compressor chamber is strongly compressed, which leads to its sharp heating. To understand this, just remember how a regular bicycle pump heats up when you inflate tires. The principle is the same.
![]()
Note to the owner
“The heat pump is modern heating. But the real values of the efficiency of heat pumps depend on temperature conditions, i.e. on cold days, their effectiveness drops. It is about 150% at -20°C, and about 300% at a source temperature of +7°C.”
Cycle 3, condensation
After the compression cycle, we have received hot steam under high pressure, which is already supplied to the internal, “home” part of the heat pump. Now this gas can be used for an air heating system or for heating water in a water heating and hot water supply system. Also, this hot steam can be used with the "" system.
Giving heat to the heating system, the hot gas cools, condenses and turns into a liquid.
Cycle 4 expansion
This liquid enters the expansion valve, where its pressure is reduced. The low pressure liquid refrigerant is now sent back to the underground to be heated to ground temperature. And all cycles are repeated.
Efficiency of using heat pumps
For every 1 kW of electricity consumed by a heat pump to operate its compressor, on average, about 4 kW of useful heat energy is generated. This corresponds to 300% efficiency.
Comparison of heating with a heat pump with other methods.
Data provided by the European Heat Pump Association (EHPA)
|
Heating type |
Energy efficiency, % |
|---|---|
It should be understood that the performance of heat pumps differs, depending on the specific conditions in which your device operates. So, if you use an "earth" heat pump, and you have clay soil in your area, then the efficiency of the heat pump will be about twice as high as if the heat pump pipes were in sandy soil.
It should also be remembered that the laying of the underground part should be carried out below the freezing mark of the soil. Otherwise, the heat pump will not work at all.

The actual efficiency values of heat pumps depend on temperature conditions, i.e. on cold days, their effectiveness drops. It is about 150% at -20 °C, and about 300% at a source temperature of +7 °C. But technology does not stand still - modern models are more energy efficient, and this trend continues.
Heat pumps for home cooling
By its principle of operation, a heat pump is similar to or. Therefore, in the summer, it can be used not for heating the house, but for cooling or air conditioning. Recall that, if we are talking about an "earth" heat pump, then the temperature of the soil is stable within 7-12 ° C all year round. And with the help of a heat pump, it can be transferred to the premises of the house.
The principle of operation of a cooling system using a heat pump is similar to a heating system, only radiators are used instead. With passive cooling, the coolant simply circulates between the fan coil units and the well, i.e. cold from the well directly enters the air conditioning system, but the compressor itself does not work. If passive cooling is not sufficient, the heat pump compressor is switched on, which additionally cools the heating medium.

Types of heat pumps
Household heat pumps are of 3 main types, differing in external heat source:
- "ground" or "ground-water", "ground-air";
- "water" or "water-water", "water-air";
- "air" or "air-to-water", "air-to-air".
Ground source heat pumps
The most popular are heat pumps that use the heat of the earth. They have already been discussed above. These are the most effective, but also the most expensive of all types. Pipes going underground can be located vertically or horizontally. Depending on this, "ground" heat pumps are divided into vertical And horizontal.
Vertical heat pumps require immersion of pipes through which the refrigerant circulates to a considerable depth: 50-200 m. True, there is an alternative - to make not one such well, but several, but more “shallow”. The distance between such wells must be at least 10 m. To calculate the drilling depth, one can roughly estimate that a 10 kW heat pump will require wells (one or more) with a total depth of about 170 m. It should also be remembered that it is useless to drill very shallow - less 50 m - wells.
At horizontal laying expensive drilling to great depths is not required. The depth of laying pipelines with this method is about 1 m, depending on the installation region, this value can either decrease or increase. With this method, the refrigerant pipe is laid so that the distance between adjacent sections is at least one and a half meters, otherwise heat collection is not effective.
![]()
Note to the owner
“If you live in a temperate zone - for example, in the Northwest - then the most efficient option for you is a heat pump that uses the heat of the earth. Moreover, it is better to install a vertical version of the heat pump - especially if your house is located on rocks.
To install a heat pump with a capacity of 10 kW, a total buried pipe length of about 350-450 m is required. If you take into account the restrictions associated with the proximity of different sites to each other, then you will need a plot of land with dimensions of 20 by 20 meters. Whether there is such a free site available is a big question.
How to choose the right heat pump
If you live in a temperate zone - for example, in the Northwest - then the most efficient option for you is a heat pump that uses the heat of the earth. Moreover, it is better to install a vertical version of the heat pump - especially if your house is located on rocks, where it is problematic to find a free large plot of land. But this type of heat pump is the most expensive in terms of capital costs.
In a mild climate zone - for example, in Sochi - it is possible to install an air-to-water heat pump, which does not require excessive capital costs and is especially effective in areas where seasonal temperature fluctuations are relatively small.
Depending on the principle of operation, there are and. Electric models are more popular.

One more important note. A good idea is combined models of heat pumps, which combine the classic version of the heat pump with a gas or electric heater. Such heaters can be used in adverse weather conditions when the efficiency of the heat pump is reduced. As already mentioned, a decrease in efficiency is especially characteristic of air-to-water and air-to-air heat pumps.
The combination of these two heat sources reduces the cost of capital expenditures and increases the payback period of the heat pump installation.
Advantages and disadvantages of heat pumps
The main advantage of heat pumps is their low operating costs. Those. the cost of heat or cooling produced to the end user is the lowest compared to other heating/cooling methods. In addition, the heat pump system is practically safe for the home. Consequently, the requirements for the ventilation systems of its premises are simplified and the level of fire safety increases. This also has a positive effect on the cost of installing these systems.
Heat pumps are easy to operate and very reliable, and yet - almost silent.
Another plus is that you can easily switch the heat pump from heating to cooling if necessary. You just need to have at home not only heating, but also fan coil units.
What is a heat pump for home ✮Large selection of heat pumps on the website portal
But they also have disadvantages, the main of which is the reverse side of the main plus - the capital costs for their installation are very significant. Until recently, another disadvantage of heat pumps was the relatively low coolant temperature - no more than 60 C. But recent developments have made it possible to eliminate this disadvantage. True, the price of such models is higher than the standard ones.
A heat pump is a good alternative to the traditional heating of a private house. The device, which has been used for 30 years in Western countries, is still a novelty in Russia. Two factors prevent its widespread use: high cost and lack of knowledge about heat pumps, their advantages and principles of operation. An indicator of the practicality of a geothermal heating system is its popularity in the West. Thus, about 95% of houses are heated with heat pumps in Sweden and Norway. We invite you to learn more about the device and the principles of operation of this thermal equipment, which, of course, is the future.
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump is a device that absorbs low-potential thermal energy from the environment (water, earth, air) and transfers it to heat supply systems with a higher temperature.
The nature around us is saturated with energy. Even frost has warmth. Energy cannot be extracted from the environment only at a temperature of -273 °C. Therefore, even in the most severe winter, a country house can be heated by energy obtained from nature.
Depending on the source of energy (water, earth, air), modification of heat pumps. However, the most practical and tried and tested is the ground source heat pump. It is ideal for Russian conditions.
Geothermal heating works in one of three directions:
The use of geothermal heating, like any heat supply system, will not only heat the house, but also provide hot water, heat a parking lot or a greenhouse, heat water in a swimming pool
Benefits of using a heat pump

How a heat pump works
 The operation of a heat pump can be compared to that of a conventional refrigerator. Only instead of cold, the device produces heat. The substance that transmits energy is freon A gas or liquid with a low boiling point. When evaporating, it absorbs heat, and when condensing, it gives it away.
The operation of a heat pump can be compared to that of a conventional refrigerator. Only instead of cold, the device produces heat. The substance that transmits energy is freon A gas or liquid with a low boiling point. When evaporating, it absorbs heat, and when condensing, it gives it away.
The heat pump is the main element of the system. Its dimensions do not exceed the dimensions of the average washing machine which makes it easier to install the device. The pump itself is included in two circuits: internal and external.
Inner contour consists of a house heating system (pipes and radiators). Outer loop located in water or underground. It includes a collector-heat exchanger and pipes connecting the collector to the pump.
Heat pumps are equipped with various additional devices. It can be:
- communication device to control the system through a personal computer or mobile phone;
- cooling block for local or central cooling system;
- additional pump unit may be required for underfloor heating;
- circulation pump necessary for the circulation of hot water;
The pumping process consists of several stages:
- Anti-freeze mixture fed into the collector. Thermal energy is absorbed and transported to the pump.
- In the evaporator, energy is transferred to freon, where it heats up up to 8 °C, boils and turns into steam.
- As the pressure in the compressor increases, the temperature rises. It can reach 70°C.
- The internal heating system receives thermal energy through capacitor. Freon instantly cools and turns into a liquid state, while giving off the remaining heat. Then it goes back to the collector. Thus the cycle ends.
- Further work is repeated according to the same principle.
The heat pump operates most efficiently when there are underfloor heating in the house. Heat is distributed over the entire floor area evenly. There are no overheating zones. The heat carrier in the system rarely heats up more than 35 °C, and heating by floor heating is considered the most comfortable at 33 °C. This is 2 °C less than when heating with radiators. Hence arises saving up to 18% per year from the entire heating budget. In addition, it is believed that heating at floor level is the most comfortable for a person to live.
The heating system can be monovalent and bivalent. Monovalent systems have one heating source. It fully meets the year-round need for warmth. Bivalent, respectively, have two sources.
Heating the house in winter
In areas with more severe climatic conditions, it is important to use bivalent heating system. Due to the second heat source, the temperature range is extended. The operation of one heat pump is sufficient only up to a temperature level of -20 °C. With a larger decrease, an electric heater, fireplace, liquid fuel or gas boiler are connected. In this case, the power of the heat pump is limited from the maximum winter demand to 70 - 80%. The missing 20 - 30% gives an additional source of heat. This reduces the overall efficiency of the system. However, the decrease is insignificant.
With a complete transition to heating the building with a geothermal system (in the case when it is not planned to install an additional boiler or electrical appliance), the heat pump is used in conjunction with an indoor module containing a small built-in electric heater. It will support the instrument when the ambient temperature is below -20 °C.
When is the use of a heat pump justified?
The issue of heating a country house involves consideration of several options:
- Gas. In the absence of a gas pipeline near the house, this becomes impossible. In some regions, gas can only be bought in bottles.
- Coal or firewood. With them, heating turns into a laborious and inefficient process.
- Oil boiler requires high fuel costs and special premises. Special storage is also necessary for the fuel itself, which is inconvenient in a small house.
- Heating with electricity is very expensive.
 In this case, help comes geothermal heating system. It is used even where gas is available. Installing a heat pump is more expensive than installing gas heating equipment. However, in the future, gas will have to be paid constantly, unlike energy taken from the environment.
In this case, help comes geothermal heating system. It is used even where gas is available. Installing a heat pump is more expensive than installing gas heating equipment. However, in the future, gas will have to be paid constantly, unlike energy taken from the environment.
The payback of a heat pump is difficult to express in an average numerical value. It all depends on its initial cost. The essence of the installation of such heating is reduced to perspective. Although the amount consumed electricity - 3-5 times less than other heating systems, it is still necessary to calculate in monetary terms all energy costs for the year and compare them with the cost of the system, its installation and operation.
It is possible to achieve the maximum efficiency of the use of a heat pump if two important conditions:
- Heated building must be insulated, and the heat loss index should not exceed 100 W/m2. There is a direct relationship between how the house is insulated and how profitable the installation of a heat pump will be.
- Connecting the heat pump to low temperature heating sources(convectors, warm floors), the temperature regime of which ranges between 30 - 40 °C.
So, the heat pump will be a good alternative to traditional heating methods. The device guarantees economy and complete safety. The owner, after installing a geothermal heating system, will not have to depend on various external factors, such as interruptions in gas supply or calling a service provider. Energy taken from the environment does not require payment and is not exhausted.
Geothermal pumps will account for three-quarters of all heating equipment in 2020, according to the World Energy Committee.
The practice of using heat pumps: video
Reading 7 min.
The term heat pump means a set of units designed to accumulate heat energy from various sources in the environment and transfer this energy to consumers.
For example, such sources can be sewage risers, waste from various large industries, heat generated during operation from various power plants, etc. As a result, various media and bodies with a temperature of more than one degree can act as a source.
The task of a heat pump is to convert the natural energy of water, earth or air into thermal energy for the needs of the consumer. Since these types of energy are constantly self-regenerating, we can consider them an unlimited source.
Heat pump for home heating working principle
The principle of operation of heat pumps is based on the ability of bodies and media to give their thermal energy to other similar bodies and media. According to this feature, various types of heat pumps are distinguished, in which an energy supplier and its recipient are necessarily present.
In the name of the pump, the source of thermal energy is indicated in the first place, and the type of carrier to which the energy is transferred is indicated in the second place.

In the design of each heat pump for heating a house, there are 4 main elements:
- A compressor designed to increase the pressure and temperature of the steam resulting from the boiling of freon.
- An evaporator, which is a tank in which freon passes from a liquid state to a gaseous state.
- In the condenser, the refrigerant transfers heat energy to the internal circuit.
- The throttle valve regulates the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator.
The type of heat pump air air means that heat energy will be taken from the external environment (atmosphere) and transferred to the carrier, also air.
 Heat pump air air: principle of operation
Heat pump air air: principle of operation The principle of operation of this system is based on the following physical phenomenon: the medium in the liquid state, evaporating, lowers the temperature of the surface, from where it is dissipated.
For clarity, let's briefly consider the operation of the refrigerator freezer. Freon, circulating through the tubes of the refrigerator, takes heat from the refrigerator and heats up itself. As a result, the heat collected by it is transferred to the external environment (that is, to the room in which the refrigerator is located). Then the refrigerant, compressing in the compressor, cools down again and the circulation continues. An air source heat pump works on the same principle - it takes heat from the outdoor air and heats the house.
The design of the unit consists of the following parts:
- The external pump unit consists of a compressor, an evaporator with a fan and an expansion valve.
- Thermally insulated copper tubes are used to circulate freon
- A condenser with a fan on it. It serves to dissipate already heated air over the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises.

During the operation of an air source heat pump, when heating a house, the following processes occur in a certain order:
- The fan draws outside air into the unit and passes through the external evaporator. Freon, which makes a cycle in the system, collects all the heat energy from the outdoor air. As a result, it passes from a liquid state to a gaseous state.
- Subsequently, gaseous freon is compressed in the condenser and passes into the indoor unit.
- Then the gas passes into a liquid state, while giving off the accumulated heat to the air of the room. This process takes place in a condenser located in the room.
- The excess pressure leaves through the expansion valve, and freon in a liquid state goes to a new circle.
Freon will constantly take thermal energy from the street air, since its temperature will always be lower. The exception is when it is very cold outside. Under such conditions, the efficiency of the heat pump will decrease.
To increase the power of the unit, maximize the surfaces of the condenser and evaporator.
 Like any complex device, an air source heat pump has its pros and cons. Among the advantages it is worth highlighting:
Like any complex device, an air source heat pump has its pros and cons. Among the advantages it is worth highlighting:
1. Depending on the need, the unit can raise or lower the heating temperature of the house.
2. This type of pump does not pollute the environment with harmful products of fuel combustion.
3. The device is easy to install.
4. The air pump is absolutely safe in terms of fire.
5. The heat transfer coefficient of the pump is very high compared to energy costs (4 to 5 kW of heat is generated per 1 kW of electricity consumed)
6. Differ in reasonable price.
7. The device is convenient to use.
8. The system is controlled automatically.
Of the minuses of the air system, it is worth mentioning:
1. Slight noise generated by the operation of the device.
2. The efficiency of the device depends on the ambient temperature.
3. At low outdoor temperatures, electricity consumption increases. (below -10 degrees)
4. The system is entirely dependent on the availability of electricity. The problem can be solved by installing an autonomous generator.
5. Air pump cannot heat water.
In general, air-to-air devices are ideal for heating wooden houses, in which, due to the nature of the material, natural heat losses are reduced.
Before choosing an air pump, you should find out the following key points:
- Insulation index of rooms.
- Square of all rooms
- Number of people living in a private house
- climate conditions
In most cases, 10 sq. m. of the room should account for about 0.7 kW of device power.
Heat pumps for home heating water water.
When arranging a heating system in a private house, water-water class systems are well suited. In addition, they will be able to provide housing with hot water. Various reservoirs, groundwater, etc. are suitable as sources of natural heat.

The operation of the water-water pump is based on the law that a change in the state of aggregation (from liquid to gas and vice versa) of a substance, under the influence of various factors, entails the release or absorption of heat energy.
This type of pumps can be used for heating a house even at low ambient temperatures, since positive temperatures still remain in the deep layers of the earth.

The principle of operation of a water-to-water heat pump is as follows:
- A special pump drives water through the copper pipes of the system from an external source into the installation.
- In the device, water from the environment acts on the refrigerant (freon), the boiling point of which is from +2 to +3 degrees. Part of the heat energy of the water is transferred to freon.
- The compressor sucks in the gaseous refrigerant and compresses it. As a result of this process, the temperature of the refrigerant increases even more.
- Then the freon is sent to the condenser, where it heats the water to the required temperature (40-80 degrees). The heated water enters the pipeline of the heating system. Here the freon returns to a liquid state and the cycle begins anew.
It should be noted that water-water devices are used to heat a house with an area of 50-150 sq.m.
 Heat pump water water: principle of operation
Heat pump water water: principle of operation When choosing a device of this class, you should pay attention to certain conditions:
- As a source of energy, preference should be given to open reservoirs (it is easier to install pipes), at a distance of no more than 100 m. In addition, the depth of the reservoir for more northern regions should be at least 3 meters (water usually does not freeze at such a depth). Pipes leading to water must be insulated.
- The hardness of the water greatly affects the operation of the pump. Not every model is able to function at high rates of rigidity. As a result, before purchasing the device, a water sample is taken and, based on the results, a pump is selected.
- According to the type of operation, the units are divided into monovalent and bivalent. The former will perfectly cope with the role of the main source of heat (due to their high power). The latter can act as an additional source of heating.
- With the power of the pump, its efficiency increases, but at the same time, the consumption of electricity also increases.
- Additional features of the device. For example: soundproof housing, domestic water heating function, automatic control, etc.
- To calculate the required power of the device, you need to multiply the total area of \u200b\u200bthe premises by 0.07 kW (energy indicator per 1 sq.m.). This formula is valid for standard rooms, with a height of no more than 2.7 m.
Combustion of classical fuels (gas, wood, peat) is one of the ancient ways of generating heat. However, the depletion of traditional energy sources prompted people to look for more complex, but no less effective alternatives. One of them was the invention of a heat pump, whose work is based on the school laws of physics.
Heat pump operation
The principle of operation of heat pumps, which is very complicated at first glance, is based on several simple laws of thermodynamics and the properties of liquids and gases:
- When a gas becomes liquid (condensation), heat is released
- When a liquid changes to a gas (evaporation), heat is absorbed
Most liquids can boil at fairly high temperatures, close to 100 degrees. But there are substances with fairly low boiling points. In freon, it is about 3-4 degrees. Turning into a gas, it is easily compressed and the temperature inside the container begins to rise.
Theoretically, freon can be compressed to obtain any desired temperature, but in practice it is limited to 80-90 degrees, which is necessary for the full operation of a classical heating system.
Everyone encounters a heat pump more than once a day when they pass by a refrigerator. However, in it it works in the opposite direction, taking the heat of the products and dissipating it into the atmosphere.
Video about work technology
Heat pump diagram
The efficiency of most heat pumps is based on the heat of the ground, in which the temperature practically does not fluctuate throughout the year (within 7-10 degrees). Heat moves between three circuits:
- Heating circuit
- Heat pump
- Brine (aka earthen) contour
The classical principle of operation of heat pumps in a heating system consists of the following elements:

- Heat exchanger that gives the internal circuit the heat taken from the ground
- compressing device
- The second heat exchange device that transfers the energy received in the internal circuit to the heating system
- The mechanism that lowers the pressure in the system (throttle)
- Brine circuit
- earth probe
- Heating circuit
The pipe, which acts as the primary circuit, is placed in a well or buried directly in the ground. A non-freezing liquid coolant moves along it, the temperature of which rises to a similar characteristic of the earth (about +8 degrees) and enters the second circuit.

The secondary circuit takes heat from the liquid. Freon circulating inside begins to boil and transform into gas, which is sent to the compressor. The piston compresses it to 24-28 atm, due to which the temperature rises to + 70-80 degrees.

At this working stage, energy is concentrated into one small clot. As a result, the temperature rises.

The heated gas enters the third circuit, which is represented by hot water supply systems or even home heating. When transferring heat, losses of up to 10-15 degrees are possible, but they are not significant.

When freon cools down, there is a decrease in pressure, and it again turns into a liquid state. At a temperature of 2-3 degrees, it returns to the second circuit. The cycle repeats over and over.
Main types
The principle of operation of heat pumps is arranged so that they can be easily operated without interruption in a wide temperature range - from -30 to +40 degrees. The most popular are the following two types of models:
- absorption type
- Compression type
Absorption type models have a rather complex structure. They transfer the received thermal energy directly with the help of a source. Their operation significantly reduces the material costs of consumed electricity and fuel. Compression type models for heat transfer consume energy (mechanical and electrical).
Depending on the heat source used, pumps are divided into the following types:
- Processing secondary heat- the most expensive models that have gained popularity for heating objects in the industry, in which the secondary heat generated by other sources is spent nowhere
- Air- taking heat from the surrounding air
- Geothermal– choose heat from water or earth
By type of input / output, all models can be classified as follows - soil, water, air and their various combinations.
Geothermal heat pumps
Popular are geothermal models of pumps, which are divided into two types: closed or open type.
The simple arrangement of open systems makes it possible to heat the water passing inside, which subsequently enters the ground again. Ideally, it works in the presence of an unlimited volume of pure heat transfer fluid, which, after consumption, does not harm the environment.
Closed systems of geothermal heat pumps are divided into the following types:
- Aquatic - located in a reservoir at an unfrozen depth
- With vertical arrangement - the collector is placed in a well to a depth of 200 m and is applicable in areas with uneven terrain
- With a horizontal arrangement - the collector is placed in the ground to a depth of 0.5-1 m, it is very important to provide a large circuit in a limited area
Air-to-water pump
One of the most versatile options is the air-to-water model. During the warm periods of the year, it is very effective, but in winter the performance can drop significantly.

The advantage of the system is simple installation. Suitable equipment can be mounted in any convenient place, for example, on the roof. The heat that is removed from the room in the form of gas or smoke can be reused.
Water-to-water type
The water-to-water heat pump is one of the most efficient. But its use may be limited by the presence of a reservoir nearby or insufficient depth at which there is no significant drop in temperature in winter.
Low potential energy can be selected from the following sources:
- ground water
- Open type reservoirs
- Waste industrial water

The simplest principle of operation of heat pumps is for models that take heat from a reservoir. If the decision is made to use groundwater, a well may need to be drilled.
Soil-water type
Heat from the ground can be obtained throughout the year, since at depths of 1 m or more, the temperature practically does not change. As a heat carrier, "brine" is used - a non-freezing liquid that circulates.

One of the disadvantages of the "soil-water" system is the need for a large area to achieve the desired efficiency. They try to level it by laying pipes with rings.
The collector can be placed in a vertical position, but a well up to 150 m deep is required. Umbrellas are mounted at the bottom, which take away the heat of the soil.
Pros and cons of heating systems with a heat pump
Heat pumps are widely used in heating systems for private residential areas or industrial areas. They are gradually replacing more classical energy sources due to their reliability and efficiency.
Some of the many benefits of using a heat pump include:
- Saving money on maintenance of systems and coolant
- Pumps operate completely autonomously
- No harmful combustion products and other toxic substances are released into the environment
- Fire safety of the mounted equipment
- The ability to easily reverse the operation of the system
Despite the many advantages, it is necessary to take into account the negative aspects of operating a heat pump:
- Large initial investment in the arrangement of the heating system - from 3 to 10 thousand dollars
- In cold periods, when the temperature drops below -15 degrees, it is necessary to think about alternative heating options.
- Heating based on the operation of a heat pump is most effective only in systems with a low-temperature heat carrier
Another schematic video:
Summing up
Having learned and mastered the principle of operation of a heat pump, you can think and decide on the appropriateness of its installation and use. The initial costs, which may seem very large, will soon pay off and begin to bring a kind of profit in the form of savings on classic fuel.